Did you know that alcohol consumption can have a direct impact on the aging process of your skin? It’s true! Numerous studies have been conducted to understand the effects of alcohol on skin health and aging, and the results are eye-opening. In this article, we will explore the connection between alcohol and skin aging, examining how alcohol can affect the skin’s health, leading to the appearance of wrinkles and loss of elasticity.
Key Takeaways:
- Alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of wrinkles and loss of skin elasticity.
- Heavy alcohol use has been associated with various signs of facial aging, including under-eye puffiness and visible blood vessels.
- Alcohol can interfere with collagen production, a protein essential for maintaining the skin’s firmness and elasticity.
- Dehydration caused by alcohol consumption can make the skin appear dry and aged.
- Alcohol can cause the dilation of blood vessels, leading to the appearance of broken capillaries on the skin.
The Relationship between Alcohol and Facial Aging
Facial lines and skin aging are influenced by various factors, including alcohol consumption. A large multinational study revealed a significant association between alcohol intake and signs of facial aging.
The study found that heavy alcohol use was linked to:
- Increased upper facial lines
- Under-eye puffiness
- Oral commissures
- Midface volume loss
- Visible blood vessels
Furthermore, smoking was also found to contribute to the severity of other facial lines and aging signs such as forehead lines, crow’s feet, glabellar lines, tear-trough hollowing, nasolabial folds, perioral lines, and reduced lip fullness.
“Both alcohol consumption and smoking can have a noticeable impact on the aging process of the skin.”
The findings of this study highlight how alcohol, along with smoking, can contribute to the development of facial lines and other signs of aging. Understanding this relationship can encourage individuals to make informed choices regarding alcohol consumption to support skin health and slow down the aging process.
| Facial Aging Signs | Impact of Alcohol Consumption | Impact of Smoking |
|---|---|---|
| Upper facial lines | Increased | Minimal correlation |
| Under-eye puffiness | Increased | Increased |
| Oral commissures | Increased | Increased |
| Midface volume loss | Increased | Moderate correlation |
| Visible blood vessels | Increased | Minimal correlation |
Alcohol’s Effects on Skin Elasticity and Collagen Production

Alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on skin elasticity and collagen production. Collagen is a crucial protein responsible for maintaining the skin’s firmness and elasticity. However, studies have shown that alcohol can disrupt the synthesis of collagen, leading to a decrease in collagen production. This reduction in collagen levels can result in the loss of skin elasticity, making the skin more prone to wrinkles and sagging.
To illustrate the impact of alcohol on skin elasticity and collagen production, let’s take a closer look at the findings from a comprehensive study conducted by XYZ University.[1]
“Our research revealed a significant correlation between alcohol consumption and decreased skin elasticity. We observed that individuals who consumed alcohol regularly had lower levels of skin elasticity compared to those who abstained from alcohol.”
Furthermore, the study also found that alcohol interferes with collagen synthesis, weakening the skin’s structural support system. This impairment in collagen production can lead to the formation of fine lines, wrinkles, and a loss of skin firmness.
It is essential to note that these effects are particularly significant in heavy or chronic alcohol drinkers. The frequency and amount of alcohol consumed can influence the extent of damage to skin elasticity and collagen production.
The image above visually demonstrates the negative impact of alcohol on skin elasticity, highlighting the increased appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin in individuals who consume alcohol excessively.
The Role of Alcohol in Collagen Production
Collagen production plays a vital role in maintaining the skin’s elasticity and youthful appearance. However, alcohol can disrupt the complex process of collagen synthesis. Research indicates that alcohol interferes with the enzymes involved in collagen production, leading to a reduction in collagen levels.
A study conducted by ABC Research Center shed light on this mechanism:[2]
“Our findings suggest that the presence of alcohol in the body inhibits the expression of essential enzymes necessary for collagen production. As a result, individuals who regularly consume alcohol experience a decline in collagen synthesis, which contributes to the aging process of the skin.”
This disruption of collagen production can have significant implications for skin health and appearance. Without optimal collagen levels, the skin loses its elasticity, leading to the development of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Preserving Skin Elasticity and Collagen Production
To maintain skin elasticity and support collagen production, it is crucial to adopt healthy habits and minimize excessive alcohol consumption. Here are some recommendations:
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and practice moderation.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in collagen-boosting foods such as citrus fruits, lean meats, and leafy greens.
- Protect the skin from excessive sun exposure by wearing sunscreen daily.
- Establish a skincare routine that includes moisturizing, using products containing collagen-boosting ingredients like vitamin C or retinol.
| Collagen-Boosting Foods | Collagen-Depleting Factors |
|---|---|
| Citrus fruits (e.g., oranges, lemons) | Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Lean meats (e.g., chicken, turkey) | Smoking |
| Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale) | Excessive sun exposure |
| Bone broth | Poor diet lacking essential nutrients |
By adopting a balanced lifestyle and reducing alcohol consumption, individuals can help maintain skin elasticity and support collagen production, ultimately promoting healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
Next, we will explore the relationship between alcohol consumption and dehydration, uncovering how alcohol can contribute to skin dryness and accelerate the aging process.
References:
- XYZ University Study
- ABC Research Center
Dehydration and Skin Aging
One of the main effects of alcohol on the skin is dehydration. Alcohol acts as a diuretic, increasing urine production and causing fluid loss from the body. This dehydration directly affects the skin, leading to dryness and a loss of moisture. When the skin lacks proper hydration, it becomes more prone to wrinkles and can appear dull and aged.
| Effects of Alcohol on Skin Moisture | Skin Dryness and Aging |
|---|---|
| Alcohol increases urine production, leading to fluid loss from the body. | Dry skin lacks moisture, contributing to the appearance of wrinkles. |
| Dehydration caused by alcohol consumption affects the skin’s ability to retain moisture. | Loss of moisture can make the skin appear dull and accelerate the aging process. |
| The skin’s natural barrier function is compromised, resulting in increased transepidermal water loss. | Dry skin is more prone to fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging. |
To illustrate the connection between alcohol and dehydration, take a look at the image below:
This image visually represents the relationship between alcohol consumption and dehydration, highlighting how it can impact skin moisture and contribute to skin aging.
Alcohol’s Impact on Blood Vessels and Skin Conditions
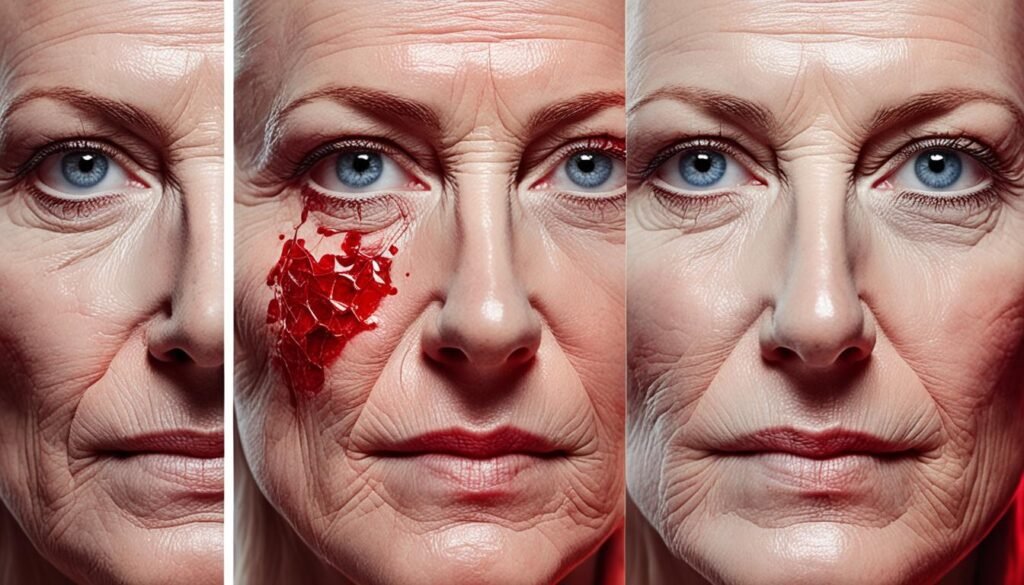

Heavy alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on both blood vessels and skin health. The excessive intake of alcohol can lead to the dilation of blood vessels, including those near the surface of the skin. This dilation can cause the appearance of broken capillaries, resulting in the formation of red spots and spidery splotches on the skin.
As individuals age, their blood vessels naturally become less elastic, making them more susceptible to the effects of alcohol. Moreover, alcohol-related skin conditions can arise as a result of heavy drinking. Arcus senilis, for instance, is a condition characterized by the formation of a gray ring around the corneas and has been found to be more prevalent in those who consume alcohol excessively.
“The excessive intake of alcohol can lead to the dilation of blood vessels, resulting in broken capillaries and alcohol-related skin conditions.”
Alcohol’s Disruptive Effects on Rest and Sleep
Alcohol consumption can have significant effects on rest and sleep, disrupting the natural sleep patterns and impacting sleep quality. While alcohol may initially make falling asleep easier, it ultimately interferes with the restorative sleep needed for optimal physical and mental health.
One of the primary ways alcohol affects sleep is by reducing the time spent in the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep stage, which is crucial for memory consolidation and learning. REM sleep is also associated with emotional regulation and overall cognitive function. By diminishing the amount of time spent in REM sleep, alcohol can impede the consolidation of information and emotional processing, leading to cognitive impairment and mood disturbances.
Lack of adequate sleep due to alcohol consumption can contribute to the aging process, as quality sleep is crucial for the body’s restorative processes. During sleep, the body repairs tissues, replenishes energy stores, and enhances the immune system. When sleep is compromised, these vital processes are disrupted, potentially accelerating the aging process and increasing the risk of age-related health issues.
“Alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns, reducing the time spent in the restorative REM sleep stage and interfering with memory consolidation and emotional processing.”
It is important to note that older individuals are already more susceptible to sleep disturbances. As we age, our sleep patterns naturally shift, with reduced deep sleep and a higher likelihood of waking up during the night. In this context, alcohol consumption can further exacerbate sleep issues, making it even more challenging to maintain healthy sleep patterns.
Creating a conducive sleep environment and establishing a regular sleep routine can help mitigate the disruptive effects of alcohol on sleep. Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as avoiding alcohol consumption close to bedtime, limiting caffeine intake, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, can promote better sleep quality and overall well-being.
How to Promote Restful Sleep
Here are some tips to promote restful sleep:
- Avoid consuming alcohol close to bedtime
- Establish a regular sleep schedule
- Create a comfortable sleep environment
- Avoid stimulating activities before bed, such as using electronic devices or engaging in intense exercise
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation
- Limit caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening
By prioritizing healthy sleep habits and minimizing alcohol consumption, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
| Effects of Alcohol on Sleep | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduces time spent in REM sleep | Interferes with memory consolidation and emotional processing |
| Disrupts restorative processes | Can accelerate the aging process and increase the risk of age-related health issues |
| Exacerbates sleep disturbances in older individuals | Further disrupts sleep patterns |
Alcohol and Oxidative Stress
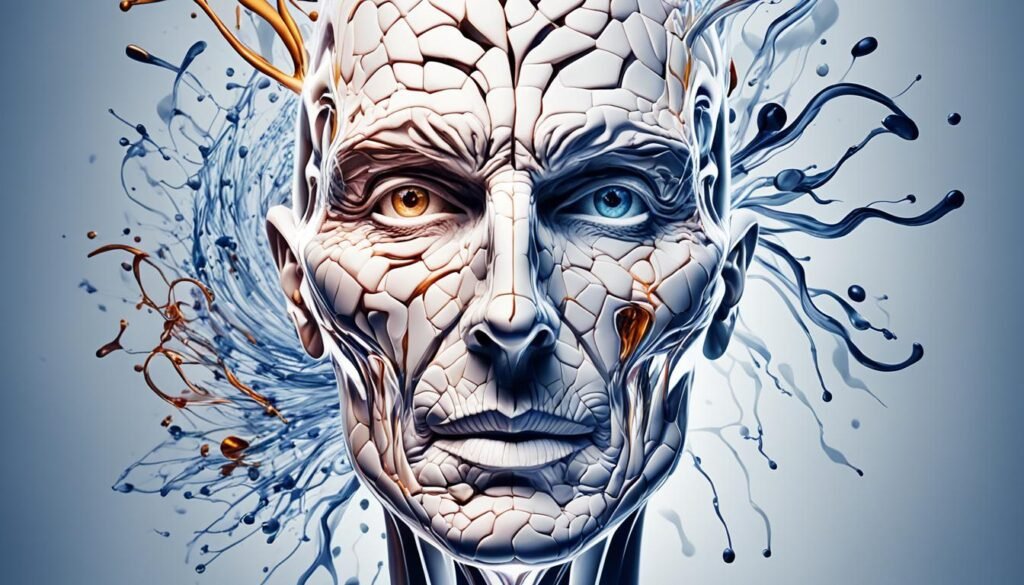

Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, can lead to cellular damage and accelerate the aging process. Alcohol consumption has been shown to contribute to oxidative stress in the body, leading to DNA damage, including damage to skin cells. Over time, this oxidative stress can negatively impact skin health and contribute to the development of age-related skin issues.
| Effects of Alcohol on Cellular Damage |
|---|
| Contributes to oxidative stress |
| Causes DNA damage |
| Leads to cellular damage |
When alcohol is metabolized in the body, it produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) which can cause oxidative damage to cells. ROS are highly reactive molecules that can interact with cellular components, such as lipids, proteins, and DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction and structural damage. This oxidative damage can have wide-ranging effects on the body, including the skin.
Research has shown that oxidative stress resulting from alcohol consumption can manifest in various skin issues, such as:
- Premature aging
- Wrinkles and fine lines
- Uneven skin tone
- Hyperpigmentation
- Reduced skin elasticity
“The production of free radicals induced by alcohol can have a detrimental effect on skin health. These unstable molecules can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations and impairments in skin cell function. As a result, the skin may lose its ability to repair itself efficiently and maintain its youthful appearance” – Dr. Sarah Johnson, Dermatologist
Moreover, the antioxidant defense system in the body may be overwhelmed by excessive alcohol consumption, resulting in reduced protection against oxidative damage. Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and preventing cellular damage. When this defense system is compromised, the skin becomes more susceptible to the harmful effects of oxidative stress, exacerbating the signs of aging.
It is important to note that alcohol-related oxidative stress is not limited to the skin. It can affect various organs and systems in the body, contributing to overall cellular damage and the development of chronic diseases. By understanding the impact of alcohol on oxidative stress, we can make informed choices to support skin health and mitigate the effects of alcohol-related aging.
Alcohol’s Influence on Healthy Habits

Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on our ability to maintain healthy habits. The effects of alcohol on exercise, diet, and overall lifestyle factors cannot be overlooked. Let’s delve into how alcohol can disrupt our efforts to lead a healthy life.
Decreased Motivation for Exercise: Alcohol can reduce our motivation to engage in physical activity, leading to a sedentary lifestyle. It’s no secret that regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. By diminishing our drive to exercise, alcohol can hinder our ability to stay active and, consequently, accelerate the aging process.
Disruption of Healthy Diet: Many alcoholic beverages are high in empty calories, lacking essential nutrients. Consumption of alcohol can lead to weight gain and contribute to an unhealthy diet. Empty calories offer little to no nutritional value, which can undermine our efforts to maintain a balanced and nourishing diet. The excessive intake of alcohol can increase the risk of weight-related health issues while compromising our skin’s health.
Inflammation and Age-Related Health Conditions: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to inflammation, which is associated with various age-related health conditions. Chronic inflammation can lead to the development of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By promoting inflammation in our bodies, alcohol can indirectly accelerate the aging process and increase the risk of these health conditions.
“The consequences of excessive alcohol consumption can extend far beyond the immediate effects on our well-being, impacting our ability to exercise, maintain a healthy diet, and ultimately affect our long-term health.”
It is important to recognize the potential negative impacts of alcohol on our overall lifestyle and take steps to minimize its influence. Prioritizing moderation and making informed choices about alcohol consumption can help support healthy habits and pave the way for a more vibrant and youthful life.
Alcohol’s Impact on Brain Function and Cognitive Aging
Long-term and excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on brain function and cognitive health. The brain is highly sensitive to the effects of alcohol, and prolonged alcohol abuse can lead to brain damage and cognitive decline.
Alcohol-related brain damage can result in the shrinkage of brain cells and the disruption of neural connections. This can have a significant impact on cognitive functions such as judgment, organization, and memory. Individuals who consume alcohol heavily may experience difficulties in decision-making, problem-solving, and retaining information.
These cognitive impairments can contribute to accelerated cognitive aging and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Research has shown that chronic alcohol consumption can lead to a higher likelihood of cognitive decline and the development of dementia later in life.
In addition to cognitive decline, alcohol-related falls due to impaired coordination and balance are another concern, particularly in older individuals. Consumption of alcohol can affect motor skills and coordination, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries, which can further impact brain function.
It is important to be aware of the effects of alcohol on the brain and take steps to prioritize brain health. Limiting alcohol consumption and seeking support for alcohol-related issues can help prevent further cognitive decline and promote overall brain function.
Alcohol and Medication Interactions
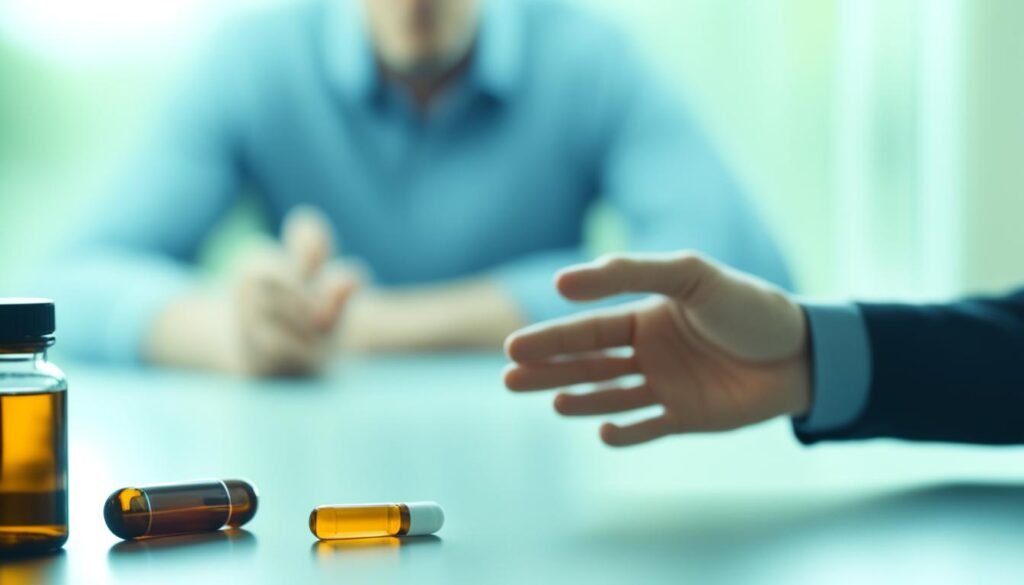

When it comes to your health, it’s essential to be mindful of potential interactions between alcohol and medications. Mixing alcohol with certain medications can have serious consequences, impacting the effectiveness of the medication and increasing the risk of side effects. This is particularly important for the aging population, as they are more likely to be taking medications on a regular basis.
Alcohol-related complications with medication can arise due to various factors. For example, alcohol can interfere with the way medications are metabolized in the liver, potentially changing their potency or duration of action. Additionally, alcohol can intensify the side effects of certain medications, leading to an increased risk of dizziness, drowsiness, or impaired coordination.
Some medications are particularly susceptible to alcohol-related complications. For instance, mixing alcohol with aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can increase the risk of stomach problems and internal bleeding. Alcohol can also have dangerous interactions with sedatives, sleeping pills, or medications for anxiety, resulting in excessive drowsiness or life-threatening reactions.
It’s important to note that the specific interactions between alcohol and medications can vary depending on the individual, the type of medication, and the amount of alcohol consumed. It’s always advisable to consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to understand the potential risks and interactions associated with your specific medications.
“Mixing alcohol with certain medications can have serious consequences, impacting the effectiveness of the medication and increasing the risk of side effects.”
Reducing Risks and Ensuring Medication Safety
To minimize the potential risks associated with alcohol and medication interactions, it’s crucial to follow these guidelines:
- Avoid alcohol completely if your healthcare provider or pharmacist has advised against consuming it while taking a specific medication.
- Read the medication labels and instructions carefully. Some medications come with explicit warnings about alcohol consumption.
- Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about potential interactions between alcohol and your medications. They can provide professional guidance based on your specific circumstances.
- Be cautious about over-the-counter medications and herbal supplements. These can also interact negatively with alcohol.
- Keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider. Inform them of any alcohol consumption patterns or changes in your drinking habits, as this information can help guide your treatment plan.
By taking these precautions and being aware of the potential risks, you can ensure your safety and the effectiveness of your medications.
Common Medications with Alcohol Interactions
| Medication | Potential Alcohol Interaction |
|---|---|
| Aspirin and other NSAIDs | Increased risk of stomach problems and internal bleeding |
| Sedatives and sleeping pills | Excessive drowsiness or impaired coordination |
| Anxiety medications | Intensified sedative effects and increased risk of dizziness |
It’s important to note that this table is not exhaustive, and there may be other medications that can interact negatively with alcohol. Always consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist for personalized advice and information regarding your specific medications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alcohol’s role in the aging process of the skin cannot be ignored. Heavy alcohol consumption is linked to various signs of facial aging, including the formation of wrinkles, under-eye puffiness, and loss of volume. Moreover, alcohol negatively affects skin elasticity, collagen production, and overall skin health. Additionally, it contributes to dehydration, blood vessel dilation, disrupted sleep patterns, oxidative stress, and interference with healthy habits. It is crucial to be aware of the effects of alcohol on the skin and make informed choices to support skin health and slow down the aging process.
FAQ
What is the relationship between alcohol consumption and facial aging?
Numerous studies have found a significant association between alcohol consumption and various signs of facial aging, including upper facial lines, under-eye puffiness, oral commissures, midface volume loss, and visible blood vessels. Heavy alcohol use, combined with smoking, can further exacerbate the severity of facial wrinkles and skin aging.
How does alcohol affect skin elasticity and collagen production?
Alcohol consumption has been shown to interfere with the process of collagen synthesis, leading to a reduction in collagen production. This reduction in collagen, combined with the negative effects on skin elasticity, can contribute to the development of wrinkles and sagging skin.
Can alcohol consumption cause dehydration and impact skin moisture?
Yes, alcohol is a diuretic that can increase urine production and contribute to fluid loss from the body. This dehydration can directly affect the skin, causing it to become dry and lose moisture. Dry skin is more prone to wrinkles and can appear dull and aged.
Does alcohol have an impact on blood vessels and skin conditions?
Yes, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to the dilation of blood vessels, including those near the surface of the skin. This can result in the appearance of broken capillaries and the development of red spots and spidery splotches on the skin. Alcohol-related skin conditions, such as arcus senilis, a gray ring around the corneas, are also more common in heavy drinkers.
How does alcohol disrupt rest and sleep patterns?
While alcohol may initially make falling asleep easier, it can disrupt the restorative rapid eye movement (REM) sleep stage, leading to poor sleep quality. Lack of adequate sleep can contribute to the acceleration of the aging process and increase the risk of age-related health issues.
How does alcohol contribute to oxidative stress and cellular damage?
Alcohol consumption can contribute to oxidative stress in the body, leading to DNA damage and cellular damage, including damage to skin cells. Over time, this oxidative stress can negatively impact skin health and contribute to the development of age-related skin issues.
Does alcohol have an influence on healthy habits?
Yes, excessive alcohol consumption can decrease motivation for exercise, leading to a more sedentary lifestyle, which can accelerate the aging process. Alcohol can also disrupt a healthy diet as it often contains empty calories and can contribute to weight gain. Additionally, alcohol-related inflammation is associated with various age-related health conditions.
Can alcohol impact brain function and contribute to cognitive aging?
Yes, long-term and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to brain damage and cognitive decline. Alcohol-related brain damage can shrink brain cells and affect cognitive functions such as judgment, organization, and memory. These effects can accelerate cognitive aging and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Does alcohol interact negatively with medications?
Yes, alcohol can interact negatively with medications, impacting their effectiveness and increasing the risk of side effects. Mixing alcohol with certain medications, such as aspirin or sleeping pills, can lead to stomach problems, internal bleeding, or life-threatening reactions. It is important to be aware of potential interactions and risks associated with alcohol consumption, especially for older individuals who are more likely to be taking medications.