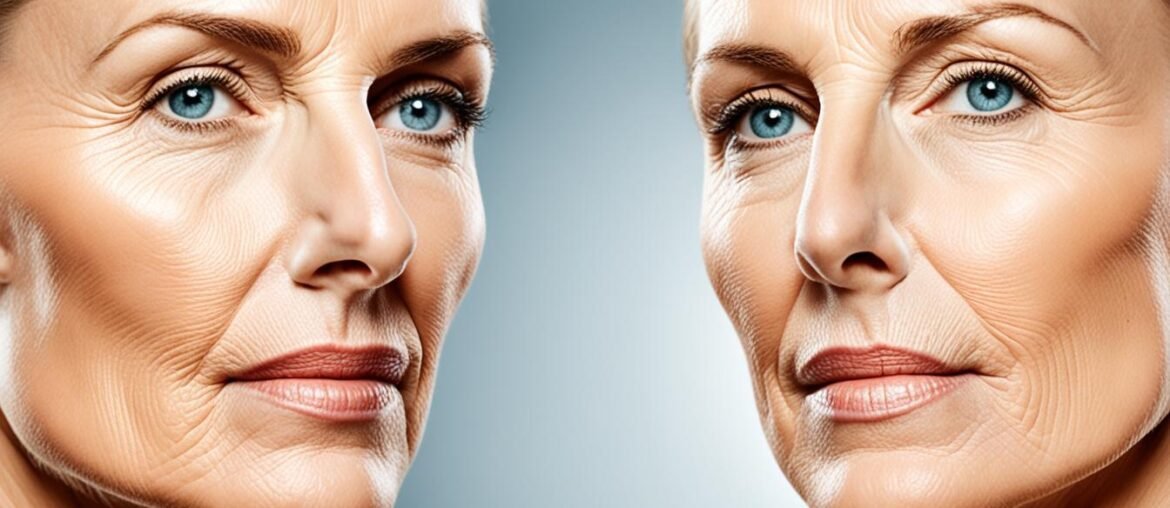
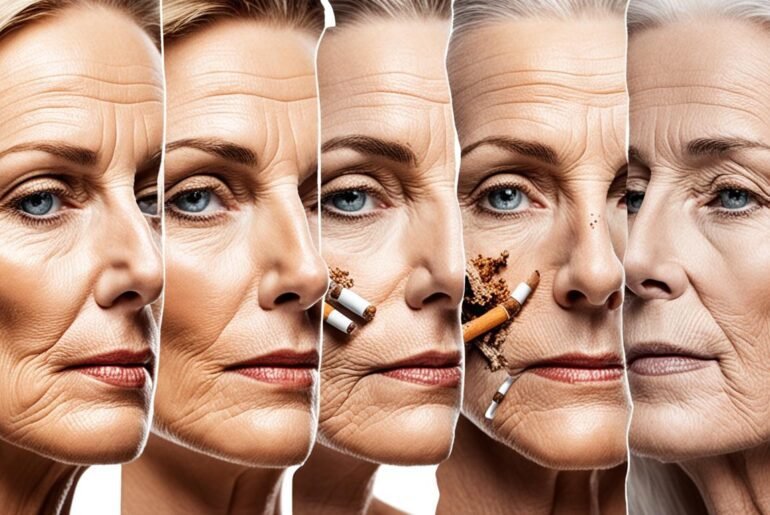
Did you know that smoking can cause premature skin aging and damage? It’s true! Numerous studies have shown that smoking is an independent risk factor for facial wrinkling and aging. The effects of smoking on the skin go beyond surface-level concerns. Smoking impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself, promotes the breakdown of collagen, constricts blood vessels, and deprives the skin of essential oxygen and nutrients. All of these factors contribute to accelerated skin aging in smokers.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking is linked to premature skin aging and damage.
- Smoking impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself.
- Collagen breakdown and reduced blood flow contribute to accelerated skin aging in smokers.
- Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining healthy skin.
- Preventing further skin damage is possible by quitting smoking.
The Effects of Smoking on Skin Elasticity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3DmVo3HO9I
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the elasticity of the skin, compromising its ability to bounce back and maintain a youthful appearance. Here’s how smoking impacts skin elasticity and contributes to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin:
The Breakdown of Collagen:
Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. However, smoking disrupts collagen production and leads to its breakdown. This is primarily due to the increased production of metalloproteinase (MMPs), enzymes that degrade collagen fibers.
As collagen breaks down, the skin loses its firmness and elasticity, making it more prone to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging.
Constricting Effect on Blood Vessels:
Smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin. This decreased blood flow deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, further damaging its elasticity.
The constricting effect of smoking on blood vessels also inhibits the skin’s ability to repair itself, making it more difficult for new collagen to form and support the skin’s structure.
Decreased Skin Elasticity:
The combination of collagen breakdown and reduced blood flow results in decreased skin elasticity. Without sufficient collagen and proper blood supply, the skin loses its ability to snap back after stretching.
This loss of elasticity contributes to the development of wrinkles, creases, and the characteristic sagging seen in long-term smokers.
“Smoking damages the skin’s natural elasticity by breaking down collagen and constricting blood vessels, leading to premature aging and sagging.”
Factors contributing to the effects of smoking on skin elasticity
| Factors | Impact on Skin Elasticity |
|---|---|
| Increased production of metalloproteinase (MMPs) | Breakdown of collagen fibers, reducing skin elasticity |
| Constricted blood vessels | Decreased blood flow, depriving skin of oxygen and nutrients |
| Impaired skin repair | Difficulty in forming new collagen to support skin structure |
| Loss of collagen | Reduced ability of skin to bounce back after stretching |
By damaging collagen and impairing blood flow, smoking significantly diminishes skin elasticity, contributing to the development of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Smoking and Wrinkles
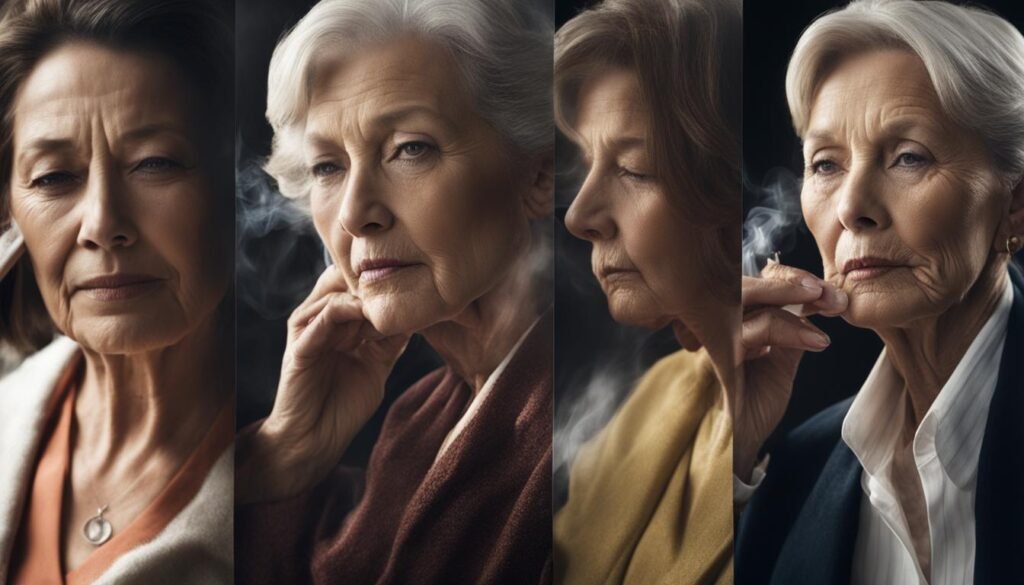

Smoking is strongly associated with the development of wrinkles. The repetitive motion of sucking on a cigarette and the increased squinting caused by the irritation of tobacco smoke can lead to the formation of wrinkles around the mouth, known as smoker’s lines, and the eyes, known as crow’s feet.
Additionally, smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin, leading to the premature development of wrinkles in smokers compared to non-smokers. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke damage the skin’s collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining its elasticity and firmness. As a result, the skin becomes less supple and more prone to wrinkling.
Furthermore, smoking reduces the blood flow to the skin, depriving it of oxygen and vital nutrients. This impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself and regenerate new cells, further contributing to the formation of wrinkles and other signs of aging.
Smoking not only causes wrinkling but also speeds up the skin’s aging process. The combination of repetitive facial movements and the harmful effects of tobacco smoke can lead to noticeable wrinkles and a prematurely aged appearance.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve your skin’s health and appearance. By quitting, you can reduce further damage to your skin and allow it to start repairing itself. Within a few months, you may notice a reduction in the number and depth of wrinkles, as well as an improvement in skin elasticity.
| Effects of Smoking on Wrinkles | Non-Smokers | Smokers |
|---|---|---|
| Premature development of wrinkles | Less susceptible | More susceptible |
| Formation of smoker’s lines | Rare | Common |
| Presence of crow’s feet | Rare | Common |
| Improvement after quitting smoking | Not applicable | Possible |
As shown in the table, smoking increases the likelihood of premature wrinkling and the formation of smoker’s lines and crow’s feet. However, quitting smoking can help reverse some of these effects and improve the overall appearance of your skin.
Smoking and Skin Discoloration
Smoking can have significant effects on the appearance of the skin, leading to skin discoloration. The decrease in blood flow caused by constricted blood vessels can result in a pale or grayish complexion. Additionally, the drying effect of tobacco smoke can contribute to a dull appearance of the skin. In some cases, smoking can even lead to oral melanin pigmentation, causing darker patches on the gums and oral mucosa.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Discoloration:
- Reduced blood flow due to constricted blood vessels
- Pale or grayish complexion
- Dull skin appearance
- Oral melanin pigmentation
It is important to note that smoking-related skin discoloration can impact not only the face but also other parts of the body exposed to tobacco smoke. The chemicals and toxins present in cigarette smoke can have a detrimental effect on the skin’s overall appearance.
Smoking not only affects internal health but also manifests in outward signs such as skin discoloration. By quitting smoking, individuals can not only improve their overall health but also enhance the appearance and vibrancy of their skin.
It is advisable to seek professional help and support when quitting smoking to ensure a successful and lasting outcome. Quitting smoking can have numerous benefits for the skin, including improving blood flow, reducing skin discoloration, and restoring a healthier, more youthful complexion.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Discoloration
| Effects | Description |
|---|---|
| Pale or grayish complexion | Reduced blood flow due to constricted blood vessels can lead to a pale or grayish appearance of the skin. |
| Dull skin appearance | The drying effect of tobacco smoke can contribute to a lackluster and dull complexion. |
| Oral melanin pigmentation | Smoking can cause darker patches on the gums and oral mucosa. |
By addressing the underlying cause of skin discoloration and adopting a smoke-free lifestyle, individuals can improve the health and appearance of their skin.
Smoking and Wound Healing
Smoking has detrimental effects on the process of wound healing. The habit of smoking delays the natural healing timeline, making it take longer for wounds to close and heal properly. This delay can result in increased pain, discomfort, and the potential for complications.
One of the key reasons smoking impedes wound healing is its negative impact on blood circulation. Smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin and the wound site. This decrease in blood flow restricts the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients necessary for efficient wound healing.
Additionally, smoking compromises the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to infections. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke impair the body’s ability to fight off infection and can lead to further complications during the healing process.
Furthermore, smoking affects the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. Angiogenesis plays a crucial role in wound healing as it supplies the wound with fresh blood, promoting the growth of healthy tissues. However, smoking inhibits angiogenesis, hindering the creation of these vital blood vessels, and slowing down the healing process.
The Effects of Smoking on Wound Healing:
- Delays healing process
- Increases risk of infections
- Impairs formation of new blood vessels
- Reduces blood flow to the wound site
- Restricts delivery of oxygen and nutrients
“Smoking prolongs the healing time of wounds, making it essential for individuals undergoing surgical procedures or recovering from injuries to quit smoking for optimal healing and recovery.” – Dr. Emily Johnson, Dermatology Specialist
If you’re a smoker and have an upcoming surgery or are dealing with a wound, it’s crucial to quit smoking to support the healing process. By abstaining from smoking, you can improve blood circulation, enhance oxygen supply, and lower the risk of complications.
Remember, your body has incredible healing abilities, and quitting smoking can significantly enhance the healing process, resulting in better outcomes and reduced chances of prolonged recovery.
Smoking and Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Emerging research suggests that smoking can have a detrimental impact on the development and severity of psoriasis.
A number of studies have found a strong association between smoking and an increased risk of developing psoriasis. In fact, smokers are reported to have a higher risk compared to non-smokers. Additionally, heavy and long-term smoking is particularly linked to a higher risk of developing psoriasis.
The effects of smoking go beyond increasing the risk of psoriasis. Smokers with psoriasis also tend to experience more severe symptoms compared to non-smokers. This includes larger affected areas, more frequent flare-ups, and increased resistance to treatment.
The exact mechanisms through which smoking influences psoriasis are not fully understood. However, it is believed that the harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, such as nicotine and tar, can trigger an exaggerated immune response in susceptible individuals. This inflammation can contribute to the development and worsening of psoriasis symptoms.
It is essential for individuals with psoriasis to be aware of the potential impact of smoking on their condition. Quitting smoking can not only improve overall health but also help manage and reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized advice and support in quitting smoking.
Key Points:
- Smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis.
- Heavy and long-term smoking further elevate the risk of psoriasis.
- Smokers with psoriasis tend to experience more severe symptoms.
- The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke may trigger inflammation contributing to psoriasis development and worsening.
- Quitting smoking is crucial for managing and reducing the severity of psoriasis symptoms.
Smoking and Palmoplantar Pustulosis

Smoking has been identified as a significant risk factor for palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP), a distressing skin condition characterized by severe inflammation of the hands and feet. Cigarette smoke is believed to be a contributing factor to the development and progression of this condition.
Research has shown that the majority of patients diagnosed with palmoplantar pustulosis are smokers. Furthermore, heavy smoking has been associated with an increased risk of developing PPP. The precise mechanisms by which smoking influences the occurrence and severity of palmoplantar pustulosis are still being investigated, but it is clear that smoking plays a significant role.
Palmoplantar pustulosis can cause painful blisters, redness, and scaling on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The symptoms can be debilitating and greatly impact an individual’s quality of life. Consequently, individuals experiencing these symptoms should consult a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Smoking and Inflammation
One possible explanation for the association between smoking and palmoplantar pustulosis is the pro-inflammatory effects of cigarette smoke on the skin. Smoking has been shown to promote inflammation throughout the body, including in the skin. This chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and exacerbation of various skin conditions, including PPP.
Smoking Cessation and Palmoplantar Pustulosis
While the exact relationship between smoking and palmoplantar pustulosis is still being studied, there is evidence to suggest that smoking cessation may have a positive impact on the condition. Quitting smoking can lead to improvements in skin health and overall well-being.
If you or someone you know is struggling with palmoplantar pustulosis or any other skin condition, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice. Dermatologists can provide accurate diagnosis, offer appropriate treatment options, and help individuals develop strategies, including smoking cessation, to manage and improve their skin health.
Smoking and Weight Gain

Quitting smoking can have an impact on body weight. Research suggests that successful quitters may experience an average weight gain of 4 to 5 kilograms over the span of a year. Various factors, such as age, socioeconomic status, and smoking intensity, can influence the amount of weight gained after quitting smoking. However, it is important to note that the health benefits associated with quitting smoking far outweigh the potential weight gain.
It is common for individuals to be concerned about weight gain when attempting to quit smoking. However, the risks associated with smoking, such as cardiovascular disease, respiratory issues, and cancer, far outweigh the temporary weight gain that may occur. It is essential to prioritize overall health and well-being over concerns about weight.
Quitting smoking leads to numerous positive effects on the body, including improved lung function, reduced risk of diseases, and increased life expectancy. While weight gain may occur due to various factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help manage weight and maintain overall health.
Below is a table summarizing the effects of smoking on body weight:
| Effects of Smoking on Body Weight | |
|---|---|
| Increased risk of weight gain after quitting smoking | |
| Factors such as age, socioeconomic status, and smoking intensity can influence weight gain | |
| Health benefits of quitting smoking outweigh potential weight gain |
Smoking and Body Shape

Smoking can have a significant impact on body shape by altering fat distribution. Research has shown that smokers tend to have a higher waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) compared to non-smokers.
This means that smokers have more fat stored around the waist and upper torso, which can have negative effects on their health. The abnormal fat distribution associated with smoking is linked to an increased risk of various diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
Studies have also indicated a correlation between smoking and an increase in visceral fat, which is the fat that surrounds the abdominal organs. This type of fat is particularly dangerous as it has been linked to insulin resistance and metabolic disorders.
It is important to note that the relationship between smoking and body shape is complex and multifaceted. Other factors such as diet, exercise, and genetics also play a role in determining body shape. However, smoking can exacerbate the negative effects of an unhealthy lifestyle on body composition.
Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for overall health but can also have a positive impact on body shape. By quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases associated with abnormal fat distribution.
The Effects of Smoking on Body Shape
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) | Smokers tend to have a higher WHR, indicating more fat stored around the waist and upper torso. |
| Visceral fat accumulation | Smoking is associated with an increase in visceral fat, which is linked to insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. |
| Risk of chronic diseases | Abnormal fat distribution caused by smoking increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. |
| Interaction with lifestyle factors | Smoking can exacerbate the negative effects of an unhealthy lifestyle on body shape and composition. |
Quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help individuals improve their body shape and reduce their risk of chronic diseases.
Smoking and Oral Health

Smoking can have detrimental effects on your oral health. Not only does it stain your teeth, but it also contributes to bad breath and an increased risk of gum inflammation, known as periodontitis. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke can impair the healing process, leading to delayed wound healing in the mouth. Furthermore, smoking increases the chances of implant failure, making it more difficult for smokers to receive successful dental implants.
Smokers are also more prone to developing certain oral conditions. Smoker’s melanosis, characterized by brown or black pigmentation on the gums, is more commonly found in smokers. Similarly, smokers have a higher risk of developing leukoplakia, a condition that causes white patches in the mouth.
To maintain good oral health, it is essential to quit smoking. By quitting, you can reduce the risk of oral diseases, improve the appearance of your teeth, and promote better overall oral hygiene. Consulting with a dental professional can provide further guidance on quitting smoking and maintaining optimal oral health.
Effects of Smoking on Teeth and Gums:
- Stained teeth
- Bad breath
- Increased risk of periodontitis (gum inflammation)
- Delayed wound healing
- Increased risk of implant failure
Conclusion
Smoking has significant negative effects on the skin, including premature aging, wrinkles, discoloration, impaired wound healing, and an increased risk of certain skin conditions. The combination of smoking-related toxins and the constriction of blood vessels near the skin’s surface deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, leading to accelerated aging. The production of enzymes like metalloproteinase (MMPs) breaks down collagen, resulting in sagging skin and reduced elasticity.
Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing further damage. While quitting smoking may be associated with weight gain, the overall health benefits far outweigh this potential downside. Quitting smoking improves skin health by allowing the skin to repair itself, promoting better blood flow and the delivery of vital nutrients and oxygen to the skin. By quitting smoking, individuals can regain a more youthful appearance and protect their skin from future damage.
Taking steps to quit smoking not only benefits the skin but also has broader health implications. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of various diseases, including cardiovascular conditions, respiratory disorders, and certain types of cancer. With the right support and resources, individuals can successfully quit smoking and improve their overall well-being. Consider reaching out to healthcare professionals or support groups to start the journey towards healthier skin and a smoke-free lifestyle.
FAQ
What are the effects of smoking on skin aging?
Smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin, leading to premature wrinkles, sagging skin, and a grayish, wasted appearance.
How does smoking affect skin elasticity?
Smoking reduces skin elasticity by breaking down collagen, a key component for maintaining skin elasticity. This can result in the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin.
Does smoking contribute to the development of wrinkles?
Yes, smoking increases the risk of developing wrinkles. The repetitive motion of smoking and the irritation of tobacco smoke can lead to the formation of wrinkles around the mouth and eyes.
Can smoking cause skin discoloration?
Smoking can cause skin discoloration by reducing blood flow, resulting in a pale or grayish appearance. The drying effect of tobacco smoke can also contribute to a dull complexion.
What are the effects of smoking on wound healing?
Smoking delays wound healing, increases the risk of infections, and impairs the formation of new blood vessels. The reduced blood supply to the skin caused by smoking hinders the delivery of oxygen and nutrients necessary for proper wound healing.
Is there a link between smoking and psoriasis?
Yes, smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing and exacerbating psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition. Smokers are at a higher risk of developing psoriasis, and the severity of symptoms is also increased in smokers compared to non-smokers.
How does smoking relate to palmoplantar pustulosis?
The majority of patients with palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP), an inflammatory skin condition, are smokers. Heavy smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing PPP, and cigarette smoke is believed to play a role in its development and progression.
Does smoking contribute to weight gain?
Yes, research indicates that successful quitters may gain an average of 4 to 5 kilograms over a year. However, the health benefits of quitting smoking far outweigh the potential weight gain.
How does smoking affect body shape?
Smokers tend to have a higher waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), meaning they have more fat stored around the waist and upper torso. This abnormal fat distribution is associated with an increased risk of diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
What are the effects of smoking on oral health?
Smoking has numerous detrimental effects on oral health, including stained teeth, bad breath, increased risk of periodontitis (gum inflammation), delayed wound healing, and an increased risk of implant failure. Smokers are also more likely to experience oral conditions such as smoker’s melanosis and leukoplakia.
How can quitting smoking benefit my skin?
Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing further damage. It can improve skin aging, elasticity, appearance, wound healing, and reduce the risk of certain skin conditions. The overall health benefits of quitting smoking far outweigh any potential downsides.




