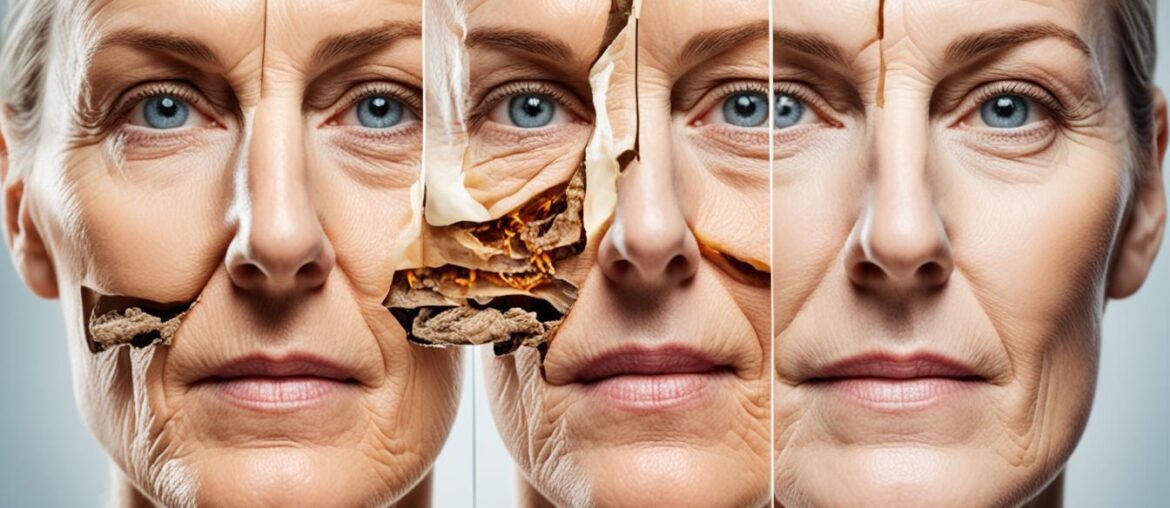
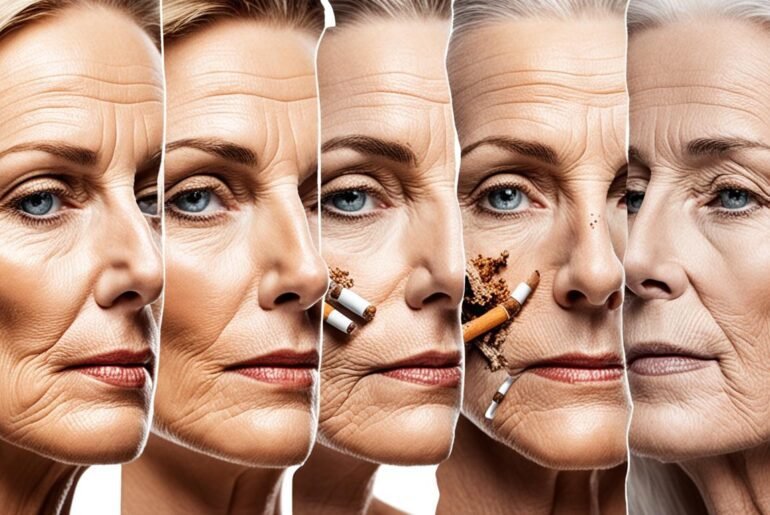
Did you know that smoking can accelerate the aging process and contribute to skin sagging? It’s true. Smoking has a significant impact on the skin, negatively affecting its elasticity and leading to the breakdown of collagen, a crucial protein for maintaining firmness and youthfulness. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow and nutrients to the skin, resulting in premature aging and the development of wrinkles.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking accelerates the aging process and contributes to skin sagging.
- It negatively affects skin elasticity and leads to collagen breakdown.
- Smoking damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow and nutrients to the skin.
- Premature aging and wrinkles are common effects of smoking.
- Quitting smoking can greatly improve skin health and slow down the aging process.
The Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging
Smoking has detrimental effects on the aging process of the skin, accelerating the development of wrinkles and sagging skin. The damaging effects of smoking on collagen, a vital protein responsible for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity, contribute to these visible signs of aging.
Collagen breakdown is one of the primary consequences of smoking. The chemicals in tobacco smoke not only disrupt the production of collagen but also promote its breakdown. As collagen fibers weaken and degrade, the skin loses its structure and support, leading to sagging and the formation of wrinkles.
Smoking also has a profound impact on blood vessels in the skin. It causes them to narrow, compromising blood flow and nutrient supply to the skin cells. This reduced blood flow accelerates the aging process, impairing the skin’s ability to recover from damage and maintain its youthful appearance.
The combination of collagen breakdown, reduced blood flow, and the oxidative stress caused by smoking intensify the aging process. Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between antioxidants and harmful free radicals, causing damage to skin cells and accelerating the signs of aging. This oxidative stress further contributes to skin aging, leading to the formation of wrinkles, fine lines, and overall skin deterioration.
Smoking’s negative impact on skin aging extends beyond the face. It affects the entire body, leading to premature aging and signs of sagging skin in other areas like the neck, arms, and chest.
Quitting smoking is crucial for preserving and improving skin health. By quitting, individuals can mitigate the effects of smoking on collagen breakdown, improve blood flow to the skin, and reduce oxidative stress. Over time, skin elasticity can be partially restored, and the appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin may improve.
“Collagen breakdown, reduced blood flow, and oxidative stress caused by smoking contribute to skin aging and the development of visible signs of aging such as wrinkles and sagging skin.”
The Impact of Smoking on Wrinkles
Wrinkles are a common sign of aging, but smoking can significantly accelerate their development. The combination of collagen breakdown, reduced blood flow, and oxidative stress caused by smoking contributes to the formation of wrinkles.
- Collagen breakdown: Smoking disrupts the production and leads to the breakdown of collagen, the main structural protein of the skin. Collagen provides elasticity and strength, which are crucial for maintaining a smooth and wrinkle-free appearance.
- Reduced blood flow: Smoking narrows blood vessels, resulting in reduced blood flow to the skin. This hampers the delivery of oxygen and nutrients, compromising the skin’s ability to repair and regenerate, and leading to the development of wrinkles.
- Oxidative stress: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals and free radicals that generate oxidative stress in the body. These free radicals damage skin cells, including collagen and elastin fibers, contributing to the formation of wrinkles and other visible signs of aging.
By quitting smoking, individuals can help slow down the development of wrinkles and improve the overall health and appearance of their skin.
Smoking and Skin Tone/Pigmentation

When it comes to the effects of smoking on the skin, one aspect that often goes overlooked is its impact on skin tone and pigmentation. Smoking can contribute to uneven skin tone and the development of age spots, which can affect the overall appearance of one’s complexion.
One of the ways smoking affects skin pigmentation is by promoting the formation of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Melanin gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes. However, excessive melanin production can lead to the appearance of dark spots and age spots, particularly in areas exposed to the sun.
Additionally, smoking can result in dull, pale skin that appears bluish or grayish. This effect is often attributed to reduced blood flow caused by the chemicals in tobacco smoke. When blood flow is compromised, the skin may not receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, leading to a lackluster complexion.
Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke, along with other environmental factors, can also trigger oxidative stress in the skin. This oxidative stress can disrupt the normal production and distribution of melanin, resulting in uneven pigmentation.
To improve skin tone and reduce the appearance of age spots, quitting smoking is crucial. By eliminating exposure to harmful chemicals and improving blood circulation, the skin can begin to heal and regenerate. With time, the complexion may become more even, and age spots may fade.
| Effects of Smoking on Skin Tone/Pigmentation | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Promotes formation of melanocytes leading to age spots | – Quit smoking |
| Causes dull, pale skin due to reduced blood flow | – Ensure proper hydration and nutrition – Exercise regularly to improve blood circulation |
| Triggers oxidative stress and uneven pigmentation | – Use sunscreen daily to protect the skin – Incorporate antioxidants into skincare routine |
Improving skin tone and reducing pigmentation issues requires a holistic approach that includes quitting smoking, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and utilizing appropriate skincare practices. This combination of actions can help restore a more vibrant and even complexion.
Smoking and Sagging Skin
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3DmVo3HO9I
Smoking is detrimental to the firmness and elasticity of the skin, leading to sagging and drooping. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke cause oxidative stress, impair collagen formation, and damage elastin fibers, which are responsible for providing strength and elasticity to the skin. This results in a loss of skin firmness and a decrease in skin elasticity.
Moreover, smoking increases the rate of transepidermal water loss and accelerates the degeneration of collagen and elastic fibers. As a consequence, the skin becomes prone to drooping and sagging, contributing to premature aging.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve skin elasticity and firmness. By eliminating exposure to harmful chemicals and reducing oxidative stress, the skin has a better chance of regaining its natural strength and elasticity. The decision to quit smoking not only benefits overall health but also provides an opportunity for the skin to heal and rejuvenate.
Smoking and Delayed Wound Healing

When it comes to wound healing, smoking can have a negative impact on the body’s ability to heal efficiently. The chemicals found in tobacco smoke can cause delayed wound healing, leading to potential complications such as dehiscence, postsurgical site infections, and other wound-related issues.
One of the ways smoking affects wound healing is by impairing the body’s inflammatory response. Inflammation is an essential part of the healing process, as it helps to remove damaged tissue and initiate the repair process. However, smoking can dampen this inflammatory process, slowing down the body’s natural ability to heal wounds effectively.
Additionally, smoking can also compromise immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections. The chemicals in tobacco smoke impair the body’s ability to fight off infections and promote tissue repair, which can result in slower healing times.
If you’re a smoker and are scheduled to undergo surgery, quitting smoking at least four weeks before the procedure can significantly decrease the risk of postsurgical complications. By giving your body a chance to recover from the effects of smoking, you can improve your chances of successful wound healing.
Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for your wound healing but for your overall health as well. If you’re struggling to quit, consider seeking support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs.
To summarize:
- Smoking can lead to delayed wound healing and potential complications.
- The chemicals in tobacco smoke impair the body’s inflammatory response, slowing down the healing process.
- Smoking compromises immune function, increasing the risk of infections.
- Quitting smoking before surgery can decrease the risk of postsurgical complications.
References:
- “Impact of Smoking on Wound Healing Among Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures.” Journal of periAnesthesia Nursing : official journal of the American Society of PeriAnesthesia Nurses vol. 33,5 (2018): 748-754. doi:10.1016/j.jopan.2017.09.012
- “The Effect of Smoking on Wound Healing: A Systematic Review.” Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 143, no. 2S Wound Healing (2019): 41S-52S. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000006218
Smoking and Skin Infections
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the body’s immune function, making individuals more susceptible to skin infections. The chemicals in tobacco smoke inhibit the activity of immune cells in the skin, leading to dysregulation and compromised defense against pathogens. This impairment of immune function contributes to tissue damage and inflammation, creating an environment conducive to the development of infections.
Smokers have a higher risk of acquiring various skin infections and may experience more severe progression and outcomes of infectious diseases. Research has shown that smoking is associated with an increased susceptibility to bacterial, fungal, and viral skin infections, including cellulitis, impetigo, candidiasis, and herpes simplex virus infections.
Furthermore, smoking-induced inflammation further exacerbates the risk of infections. The inflammatory response in the skin becomes unbalanced, creating an environment where harmful microorganisms can thrive. Chronic inflammation can also impair the healing process and prolong the duration of skin infections.
“Smoking inhibits immune cell activity and promotes dysregulation, creating an environment prone to infections.” – Dr. Anne Collins, Dermatologist
Quitting smoking is a crucial step in improving immune function and reducing the risk of skin infections. By eliminating the toxic effects of tobacco smoke, the body’s immune system can regain its strength, effectively combating pathogens and promoting healthy skin. Quitting smoking not only benefits skin health but also has numerous positive effects on overall well-being.
Recommended practices to prevent skin infections:
- Maintain good hygiene practices, including regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, and clothing.
- Keep the skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to moisture accumulation.
- Moisturize the skin regularly to maintain its protective barrier function.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have contagious skin conditions.
- Seek prompt medical attention if any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or the presence of pus, develop.
Smoking and Skin Cancer

Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Current and heavy smokers have a higher likelihood of developing squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer that arises from the squamous cells in the epidermis. Additionally, smokers with melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, have a lower survival rate compared to nonsmokers.
The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke can damage DNA and impair the body’s ability to repair DNA damage, leading to genetic mutations that promote the growth of cancer cells. Smoking also affects the immune system, weakening its ability to recognize and eliminate abnormal cells that could develop into cancerous tumors.
“The increased risk of skin cancer associated with smoking highlights the importance of quitting this detrimental habit.”
Quitting smoking is crucial for reducing the risk of developing skin cancer and improving overall health outcomes. By quitting, individuals can give their body an opportunity to repair DNA damage, strengthen the immune system, and mitigate the growth of cancer cells. It is a proactive step that can contribute to a healthier future.
Comparative Analysis of Smoking and Skin Cancer Risk
| Factor | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Melanoma |
|---|---|---|
| Risk in Smokers | Higher | Lower survival rate |
| Contribution to DNA Damage | Promotes mutations | Impairs DNA repair |
| Impact on Immune Function | Weakened response | Reduced ability to eliminate cancer cells |
Other Effects of Smoking on the Skin

Aside from the well-known impacts on skin sagging and premature aging, smoking has been linked to several other skin-related conditions. These include psoriasis, eczema, acne, and vasculitis.
Psoriasis: Studies have found that smoking increases the risk of developing psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Smokers with psoriasis may experience more severe symptoms and reduced treatment effectiveness.
Eczema: Smoking can worsen symptoms of eczema, a condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can trigger or exacerbate eczema flare-ups, making it more challenging to manage the condition.
Acne: Although the link between smoking and acne is not fully understood, research suggests that smoking can contribute to the development and severity of acne. Smoking may worsen inflammation in the skin and disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased breakouts.
Vasculitis: Smoking is a known risk factor for vasculitis, a group of conditions characterized by inflammation in the blood vessels. Buerger’s disease and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) have strong associations with smoking. Quitting smoking can improve symptoms and outcomes for individuals with these vascular disorders.
To illustrate the relationship between smoking and these skin conditions, refer to the table below:
| Skin Condition | Associated Risk with Smoking | Effects on Symptoms/Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Increased risk | More severe symptoms, reduced treatment effectiveness |
| Eczema | Worsened symptoms | Increased frequency and intensity of flare-ups |
| Acne | Contributing factor | Increased severity and frequency of breakouts |
| Vasculitis | Associated risk | Aggravation of symptoms and progression of the disease |
As seen in the table, smoking can have detrimental effects on the skin, exacerbating existing conditions and increasing the risk of developing others. Quitting smoking is crucial for individuals looking to improve their skin health and reduce the severity of these conditions.
Reversing the Effects of Smoking on the Skin
Quitting smoking has numerous benefits for the skin. As blood flow improves, the skin receives more oxygen and nutrients, leading to a healthier complexion. Age spots and skin discoloration may decrease, and the skin can regain a more youthful appearance.
Quitting smoking can also help restore collagen production, leading to improved skin hydration, elasticity, and density. Collagen is a vital protein that keeps the skin firm and supple. By quitting smoking, the body can recover from the damage caused by the chemicals in tobacco smoke and naturally rebuild collagen levels.
Topical treatments containing retinoids and antioxidants can further enhance skin health. Retinoids stimulate collagen production and promote cell turnover, while antioxidants protect the skin from free radicals and reduce inflammation. Incorporating these treatments into a skincare routine can accelerate skin improvement after quitting smoking.
Tip: Consult a dermatologist or skincare professional to determine the most suitable topical treatments for your skin type.
Additionally, quitting smoking reduces the risk of future skin damage and premature aging. By eliminating the harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, the skin is spared from further oxidative stress and damage. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for current skin health but also for preventing long-term skin aging.
Make the decision to quit smoking today and let your skin reap the rewards. Not only will you experience improvements in skin tone, texture, and appearance, but you’ll also enhance your overall health and well-being.
The Overall Impact of Smoking on Health
Smoking has a significant and detrimental impact on overall health, placing individuals at a higher risk for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The harmful effects of smoking extend far beyond the damage it causes to the skin.
- Heart Disease: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. It damages the blood vessels, narrows arteries, and increases the risk of heart attacks and stroke.
- Lung Cancer: Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, accounting for the majority of cases. It damages the cells lining the lungs and airways, leading to the development of cancerous tumors.
- Other Types of Cancer: Smoking is also associated with an increased risk of various types of cancer, including throat, mouth, esophageal, pancreatic, bladder, kidney, and cervical cancer.
- Weakens Bones: Smoking weakens bones and increases the risk of osteoporosis. It interferes with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, an essential mineral for bone health.
- Complications during Pregnancy and Childbirth: Smoking during pregnancy can lead to complications such as premature birth, low birth weight, stillbirth, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Reduced Blood Flow and Increased Blood Pressure: Smoking affects the entire cardiovascular system, causing reduced blood flow to organs and tissues. It also increases blood pressure, putting additional strain on the heart and blood vessels.
These are just a few examples of the numerous smoking-related diseases and conditions. Quitting smoking is essential for improving overall health and reducing the risk of developing these harmful conditions. It is never too late to quit and take control of one’s health.
To illustrate the impact of smoking-related diseases, here is a table that showcases the prevalence of smoking-related diseases:
| Disease | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | Leading cause of death worldwide |
| Lung Cancer | 90% of lung cancer cases are attributable to smoking |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) | 90% of COPD cases are caused by smoking |
| Stroke | Smokers are twice as likely to have a stroke compared to nonsmokers |
| Bladder Cancer | Smokers are three times more likely to develop bladder cancer |
This table highlights the significant impact that smoking has on the prevalence of various diseases. Quitting smoking is crucial for improving overall health and reducing the risk of smoking-related diseases.
Conclusion
Smoking has a profound impact on the skin, accelerating the aging process and contributing to skin sagging. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin, leading to a loss of skin firmness and elasticity. Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of vital nutrients and oxygen, which further accelerates skin aging.
However, the good news is that quitting smoking can have significant benefits for skin health. By quitting smoking, you can improve blood flow to the skin, allowing it to receive essential nutrients and oxygen for a healthier complexion. Quitting smoking also helps the skin to retain moisture, improves skin elasticity, and reduces the appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin.
It’s important to remember that it’s never too late to quit smoking and take steps towards healthier skin and overall well-being. Whether you’ve been smoking for a few years or several decades, quitting can have a positive impact on your skin health and slow down the aging process. So, if you’re looking to improve the appearance and health of your skin, consider quitting smoking for a brighter, more youthful complexion.
FAQ
What impact does smoking have on the skin?
Smoking accelerates the aging process and contributes to skin sagging. It damages collagen, reduces blood flow, and promotes the development of wrinkles and sagging skin.
How does smoking affect skin aging?
Smoking promotes collagen breakdown, reduces blood flow, and causes oxidative stress, leading to skin aging, wrinkles, and sagging skin.
Does smoking affect skin tone and pigmentation?
Yes, smoking can worsen skin tone and pigmentation, leading to age spots and uneven skin coloration.
How does smoking contribute to sagging skin?
Smoking damages collagen and elastin fibers, impairing skin elasticity and firmness, which leads to sagging skin.
Does smoking impact wound healing?
Yes, smoking hampers the body’s ability to heal wounds, resulting in delayed wound healing and an increased risk of wound complications.
Does smoking affect the risk of skin infections?
Smoking weakens the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to skin infections and worsening the outcomes of infectious diseases.
What is the link between smoking and skin cancer?
Smoking increases the risk of developing skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Can smoking worsen skin conditions like psoriasis and acne?
Yes, smoking is associated with an increased risk of psoriasis, acne, and other skin conditions, and it can worsen their symptoms and outcomes.
Can quitting smoking reverse the effects on the skin?
Yes, quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in skin health, including improved elasticity, tone, and reduced appearance of age spots.
How does smoking impact overall health?
Smoking is associated with a wide range of diseases and conditions, including heart disease, stroke, lung cancer, and weakened bones. It also affects fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
What is the conclusion regarding smoking and skin sagging?
Smoking has a significant negative impact on the skin, contributing to sagging, premature aging, and various skin-related conditions. Quitting smoking can greatly improve skin health.




