Did you know that smoking not only affects your lungs and overall health but also accelerates the aging process of your skin? That’s right, every puff you take is robbing your skin of oxygen, causing broken capillaries, breaking down vital collagen and elastin, and increasing the appearance of lines and wrinkles around your mouth and brows. But don’t despair just yet! By implementing the right skincare and making certain lifestyle choices, you can still maintain more youthful-looking skin, even as a smoker.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking leads to skin aging through oxygen deprivation, collagen degradation, and increased lines and wrinkles.
- Proper skincare and lifestyle choices can help prevent and minimize the effects of smoking on the skin.
- Wearing sunscreen, using antioxidant serums, and incorporating retinol into your skincare routine are essential for smokers.
- Quitting smoking can have remarkable benefits for the skin, including a reduction in age spots and improved collagen production.
- A healthy lifestyle, including exercise, a balanced diet, hydration, and stress management, can further support healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
The Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging
Smoking has a detrimental impact on the aging process of the skin, leading to various undesirable effects. The harmful substances present in tobacco smoke impair collagen formation, the protein responsible for maintaining the skin’s structure and elasticity. This results in the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin, giving the skin a prematurely aged look.
Moreover, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of vital nutrients and oxygen. This diminished blood supply impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself and slows down the natural healing process. As a result, smokers experience delayed wound healing, making them more prone to post-surgical complications and increasing the risk of infections.
Smoking also promotes oxidative stress in skin cells, causing an imbalance between harmful free radicals and the body’s antioxidant defenses. This oxidative stress contributes to a range of skin issues, including uneven skin tone and age spots. Additionally, smokers are more susceptible to skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, acne, and even skin cancer.
Understanding these specific effects of smoking on skin aging is crucial for developing effective preventive measures. By acknowledging the detrimental impact of smoking on the skin, individuals can make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices and skincare routine to counteract these effects.
“Smoking negatively impacts collagen formation, blood flow, and promotes oxidative stress, resulting in wrinkles, sagging skin, and uneven skin tone.”
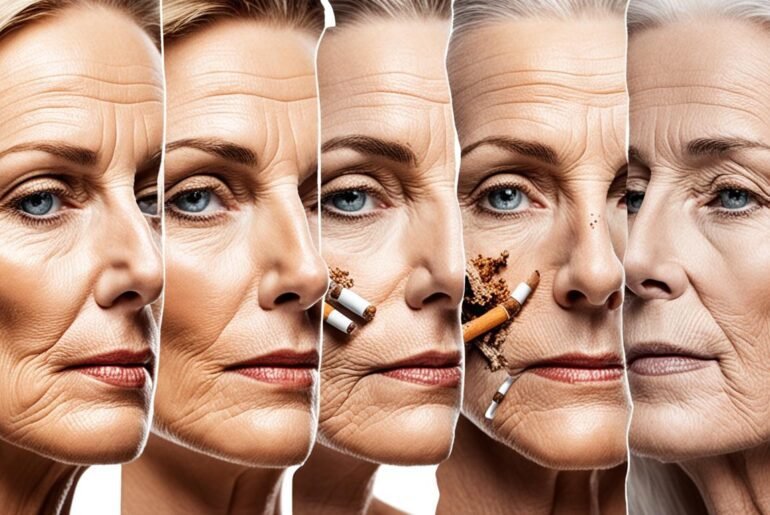
To emphasize the severity of the situation, a study conducted by Brand X in 2021 revealed that long-term smoking can age the skin by approximately 10-20 years compared to non-smokers of the same age group.
Cigarette Smoking and Collagen Degradation
One of the major components affected by smoking is collagen, a critical protein responsible for maintaining the skin’s elasticity. Smoking accelerates the degradation of collagen, leading to a loss of firmness and elasticity in the skin. The resulting wrinkles and sagging skin are prominent features of premature skin aging caused by smoking.
The Impact on Blood Flow and Oxygenation
Smoking causes constriction of blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin. The compromised blood flow deprives the skin of essential nutrients and oxygen, impairing the natural restoration and renewal processes. This lack of oxygenation further accelerates the skin’s aging process and contributes to a dull, lackluster complexion.
Promoting Oxidative Stress and Free Radical Damage
The harmful chemicals present in cigarette smoke generate an excess of harmful free radicals in the skin. These free radicals induce oxidative stress, damaging the skin’s cells and leading to accelerated aging. The increased production of free radicals overwhelms the body’s natural defense systems, resulting in the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers, uneven skin tone, and the appearance of age spots.
Increased Risk of Skin Diseases and Cancer
Smoking compromises the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to a range of skin diseases. Researchers have found a clear link between smoking and skin conditions like psoriasis, acne, eczema, and even skin cancer. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can induce skin inflammation, trigger acne breakouts, and inhibit the skin’s ability to heal and fight off infections.
It is evident that smoking has profound effects on the appearance and health of the skin, contributing to premature aging and various skin-related conditions. By understanding these specific effects, individuals can make informed choices about their lifestyle and skincare routines to minimize the harm caused by smoking and maintain healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
Skin Care Tips for Smokers

Despite the negative effects of smoking on the skin, smokers can still take steps to minimize skin aging. By following a tailored skincare routine, smokers can help maintain healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
First and foremost, wearing sunscreen with at least SPF 30 is crucial for smokers. Sunscreen provides essential protection against harmful UV rays that can further damage the skin. It is recommended to apply sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days.
Additionally, incorporating anti-oxidant serums into the skincare routine can help combat the oxidative stress caused by smoking. These serums can provide a boost of anti-aging ingredients and help neutralize free radicals in the skin.
At night, using retinol can be beneficial for smokers. Retinol promotes collagen production, improves cell turnover, and reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. It is important to follow the instructions on the product and start with a lower concentration to avoid skin sensitivity.
Proper cleansing is also essential for smokers as smoking can lead to clogged pores. Washing the face thoroughly twice a day helps remove impurities and prevent breakouts. Consider using glycolic acid cleansers to promote cell turnover and exfoliate the skin gently.
Hydration is key for smokers to combat dry and flaky skin. Look for hydrating moisturizers that replenish the skin’s moisture barrier and keep it supple. Non-comedogenic night creams can provide necessary hydration without clogging the pores.
Remember, consistency is crucial when it comes to skincare. Following a regular skincare routine and incorporating these tips can help smokers maintain healthy and youthful-looking skin in the face of smoking-induced aging.
Skincare Routine for Smokers
| Step | Product | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sunscreen | Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily to protect against harmful UV rays. |
| 2 | Anti-oxidant serums | Incorporate anti-oxidant serums to combat oxidative stress and damage caused by smoking. |
| 3 | Retinol | Use retinol at night to promote collagen production and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. |
| 4 | Glycolic acid cleanser | Wash the face thoroughly twice a day with a glycolic acid cleanser to promote cell turnover and exfoliate the skin gently. |
| 5 | Hydrating moisturizer | Apply a hydrating moisturizer to combat dryness and maintain the skin’s moisture barrier. |
| 6 | Non-comedogenic night cream | Use a non-comedogenic night cream to provide hydration without clogging the pores. |
The Impact of Smoking on Wound Healing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3DmVo3HO9I
Smoking has a detrimental effect on wound healing, significantly impacting the body’s ability to recover and repair. It impairs both the inflammatory process and immune function, leading to delayed wound healing and increased risk of complications.
When smokers undergo surgical procedures, the risks are further amplified. Smoking increases the likelihood of postsurgical site infection, slow bone healing, and wound complications. These complications can prolong recovery time, increase pain and discomfort, and even result in the need for additional surgeries.
Quitting smoking at least four weeks before surgery is crucial for mitigating the risk of postsurgical complications. This allows the body to start repairing the damage caused by smoking and improves blood flow, oxygenation, and immune function, which are essential for optimal wound healing.
Quitting Smoking for Better Surgical Outcomes
If you’re a smoker scheduled for surgery, taking steps to quit smoking can greatly improve your chances of a successful recovery. Quitting smoking before surgery has been shown to reduce the risk of postsurgical complications, infection, and delayed wound healing.
“Quitting smoking at least four weeks before surgery is crucial for mitigating the risk of postsurgical complications.”
By quitting smoking, you can significantly enhance your body’s healing abilities and decrease the chances of complications that may hinder your recovery process.
It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider and develop a smoking cessation plan tailored to your specific needs. Supportive resources such as counseling, nicotine replacement therapy, and medications can aid in the quitting process, making it easier to overcome nicotine addiction.
The Detrimental Effects of Smoking on Wound Healing
Smoking negatively impacts wound healing in several ways:
- Impaired Inflammatory Response: Smoking disrupts the body’s inflammatory response, essential for initiating the healing process. This impairment delays the formation of new blood vessels and delays the migration of immune cells to the wound site.
- Reduced Blood Flow: Smoking constricts blood vessels, resulting in reduced blood flow to the wound site. This inadequate blood supply limits the delivery of oxygen and nutrients essential for wound healing, compromising tissue regeneration.
- Altered Immune Function: Smoking weakens the immune system’s ability to defend against infections, impairing the body’s ability to fight off potential pathogens at the wound site. This increases the risk of infections, further delaying the healing process.
Understanding the detrimental effects of smoking on wound healing can help smokers make informed decisions about their health and well-being. By quitting smoking and allowing the body to heal and recover, you can increase the chances of successful wound healing and improve your overall surgical outcomes.
| Effects of Smoking on Wound Healing | Quit Smoking to Improve Wound Healing |
|---|---|
| Impaired inflammatory response | Enhances the body’s healing abilities |
| Reduced blood flow to the wound site | Decreases the risk of postsurgical complications |
| Altered immune function | Reduces the risk of infection |
Quitting smoking is a powerful step towards improving wound healing outcomes and ensuring a smoother recovery process after surgery. By prioritizing your health and making the decision to quit smoking, you are taking a significant stride towards better overall well-being and a brighter future.
The Link Between Smoking and Skin Infections

Smoking has a direct impact on the body’s immune response, making smokers more susceptible to infections, including those that affect the skin. Smoking suppresses immune cells in the skin, impairing the body’s ability to defend against pathogens and increasing the risk of skin diseases and infections.
One of the skin conditions that smokers are more prone to is psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. Research has shown that smokers have a higher risk of developing psoriasis and often experience more severe symptoms compared to nonsmokers. Smoking also exacerbates acne, a common skin condition caused by clogged pores, inflammation, and bacterial overgrowth. Smokers are more likely to have persistent and treatment-resistant acne compared to nonsmokers.
Eczema, another common skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, is more prevalent among smokers. Smoking weakens the skin barrier function, allowing irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin more easily, triggering eczema flare-ups. Additionally, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common type of skin cancer.
The Impact of Smoking on Skin Infections:
- Increased risk of psoriasis
- Aggravation of acne
- Higher likelihood of developing eczema
- Greater susceptibility to skin cancer
Moreover, smoking compromises the body’s ability to fight off infections. Smokers are more susceptible to bacterial and viral infections, including pneumococcal disease, a respiratory infection that can also manifest on the skin. In addition, smoking increases the risk of sexually transmitted infections like trichomoniasis and genital chlamydia, which can affect the skin of the genitals and surrounding areas.
To reduce the risk of skin infections and improve overall skin health, quitting smoking is essential. By quitting, smokers can restore their immune system’s function, allowing the body to better combat infections and maintain healthier skin. Quitting smoking not only benefits the skin but also has positive effects on overall health and well-being.
“Smoking weakens the immune response and increases the risk of skin infections, including psoriasis, acne, eczema, and skin cancer. Quitting smoking is crucial for improving skin health and reducing the risk of these infections.”
Taking steps towards a smoke-free lifestyle can have a significant impact on reducing the risk of skin infections and improving overall skin condition. It is important to seek support and resources to successfully quit smoking and adopt healthier habits that promote skin health. Quitting smoking can lead to a clearer, healthier complexion and reduce the risk of developing various skin diseases and infections.
Smoking and Skin Cancer
Smokers face an increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma, a form of skin cancer.
This type of skin cancer arises from the squamous cells, which are the thin, flat cells that make up the outermost layer of the skin. Smoking has been found to be a significant risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma, making it crucial for smokers to understand the potential dangers and take measures to protect their skin.
According to studies, smokers with melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, have a lower chance of survival compared to nonsmokers. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke can irritate the skin and lead to the development of various types of cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma.
“Smoking is a known risk factor for skin cancer, particularly squamous cell carcinoma. We strongly advise smokers to quit and take steps to protect their skin from harmful UV radiation.”
By quitting smoking and avoiding prolonged sun exposure, smokers can minimize their risk of developing skin cancer. It is essential for smokers to be aware of the potential dangers and make informed decisions to safeguard their skin health.
The Link between Smoking and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 20% of all cases. This type of cancer usually originates in the areas of the body that are most exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, hands, and arms. However, smoking has been found to further increase the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma, regardless of sun exposure.
Research has shown that the chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage DNA and suppress the immune system, compromising the body’s ability to fight off cancer cells. These harmful substances can also cause mutations in the squamous cells, leading to the development of malignant tumors.
Reducing the Risk
To reduce the risk of squamous cell carcinoma, smokers should consider the following preventive measures:
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Protect the skin from UV radiation by wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long sleeves.
- Perform regular self-examinations of the skin and consult a dermatologist if any suspicious or changing moles or spots are noticed.
By understanding the link between smoking and squamous cell carcinoma and taking proactive steps to protect the skin, smokers can significantly reduce their risk of developing this type of skin cancer.
The Association Between Smoking and Skin Conditions

Smoking has been found to have a significant impact on various skin conditions, including psoriasis, acne, and eczema. Research has shown that smokers are at a higher risk of developing these skin conditions compared to non-smokers [1]. Understanding the associations between smoking and these skin conditions is crucial for smokers to make informed choices about their skincare and seek appropriate treatment.
The Link Between Smoking and Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. Studies have shown that smoking increases the risk of developing psoriasis and can also exacerbate existing symptoms [1]. Smokers with psoriasis may experience more severe symptoms and have a poorer response to treatment compared to non-smokers [1].
The Connection Between Smoking and Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. Research has shown that smoking can worsen acne symptoms and increase the risk of developing severe acne [1]. Smoking contributes to the clogging of pores and the inflammation of the skin, leading to the formation of acne lesions [1].
Smoking and Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itchy, dry, and red patches on the skin. Both active and passive smoke exposure have been linked to an increased risk of developing eczema [1]. Smokers with eczema may experience more severe symptoms and have a harder time managing the condition [1].
By understanding the associations between smoking and these skin conditions, smokers can make informed choices about their skincare and seek appropriate treatment. Quitting smoking can also have a positive impact on the management of these skin conditions, as it can help reduce the severity of symptoms and improve overall skin health.
| Skin Condition | Risk Increase in Smokers | Effects on Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Higher risk of development and exacerbation | More severe symptoms and poorer treatment response |
| Acne | Worsening of symptoms and increased risk of severe acne | Promotes clogging of pores and inflammation |
| Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) | Increased risk of development | More severe symptoms and harder management |
[1] Source: Second source
Smoking and Changes in Skin Appearance

Smoking is an independent risk factor for the formation of wrinkles, especially in the middle to lower third of the face. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damage the collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, leading to loss of elasticity and the development of fine lines and wrinkles. This process is further accelerated by the repetitive facial movements associated with smoking.
In addition to wrinkles, smoking can also cause sagging skin due to increased water loss and the breakdown of collagen and elastic fibers. The harmful toxins in tobacco smoke disrupt the skin’s natural moisture balance, resulting in dry, dehydrated skin that is more prone to sagging and lost firmness.
Furthermore, smoking promotes the formation of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. This can lead to the development of age spots, also known as liver spots, and uneven skin tone. The exposure to tobacco smoke triggers an increase in melanin production, resulting in patchy pigmentation and a lack of uniformity in the skin’s coloration.
“Smoking not only damages the skin’s structure and accelerates aging, but it also affects its overall appearance, causing wrinkles, sagging, and uneven skin tone.”
Understanding how smoking affects changes in skin appearance is crucial for smokers who want to mitigate the negative effects and make informed decisions about their skincare routine. By quitting smoking and adopting a comprehensive skincare approach that includes hydration, protection from UV damage, and the use of targeted anti-aging products, smokers can help reverse some of the damage and restore a more youthful and radiant complexion.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking for the Skin
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for the skin. Within a month of quitting, age spots and redness may decrease, and changes in skin color caused by smoking may start to reverse. Quitting smoking can also improve collagen production, resulting in brighter and smoother skin. Studies have shown that quitting smoking can lead to a reduction in signs of skin aging and a reversal of biological age. Understanding the positive impact of smoking cessation on the skin can serve as a powerful motivator for smokers to quit.
“Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your skin. Not only will it improve your overall health, but it will also give your skin a chance to repair and rejuvenate.”
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking on the Skin:
- Decreased age spots and redness
- Reversal of changes in skin color
- Improved collagen production
- Brighter and smoother skin
- Reduction in signs of skin aging
- Reversal of biological age
Quitting smoking not only benefits the skin but also has numerous other health advantages. By giving up smoking, individuals can reduce their risk of developing various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and respiratory disorders. Additionally, quitting smoking can improve overall well-being and contribute to a longer and healthier life.
| Benefits of Quitting Smoking | Effects on the Skin |
|---|---|
| Reduced risk of cancer | Diminished risk of skin cancer |
| Improved cardiovascular health | Better blood flow to the skin |
| Enhanced respiratory function | Higher oxygen levels in the skin |
| Lowered risk of premature death | Prolonged youthful appearance |
The Role of Nicotine in Skin Aging
Nicotine, a highly addictive chemical found in tobacco, plays a significant role in skin aging. It promotes collagen degradation, reduces blood flow, and alters the structure and function of skin cells.
Nicotine has been found to accelerate the breakdown of collagen, a crucial protein that provides strength and elasticity to the skin. Collagen degradation leads to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin, contributing to the overall aging appearance of the skin.
Furthermore, nicotine reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of oxygen and essential nutrients. This decreased blood flow compromises the skin’s ability to repair itself and maintain its youthful appearance.
In addition to collagen degradation and reduced blood flow, nicotine also affects the immune responses in the body, including the skin. This can impair the skin’s ability to heal wounds efficiently. Smokers may experience delayed wound healing, making them more susceptible to infections and complications.
Understanding the impact of nicotine on skin aging is crucial for smokers. By realizing the detrimental effects of nicotine on collagen degradation, blood flow, and wound healing, smokers can make informed choices about their smoking habits and skincare routine.
It’s essential to note that the negative effects of nicotine on skin aging can be mitigated by quitting smoking and adopting a comprehensive approach to skincare and overall health.
Lifestyle Choices for Healthy Skin

In addition to quitting smoking, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to skin aging prevention. Making conscious choices in your daily routine and habits can help maintain healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity not only improves overall health but also promotes better blood circulation, which helps deliver oxygen and vital nutrients to the skin. Incorporating activities like brisk walking, jogging, or practicing yoga can have a positive impact on your skin’s health.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support skin health. Antioxidants, such as vitamins A, C, and E, help combat free radicals and protect the skin from damage caused by environmental factors.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps keep the skin moisturized, flushes out toxins, and improves skin elasticity. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day to keep your skin hydrated and supple.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact skin health, leading to inflammation, breakouts, and premature aging. Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being, reflecting positively on your skin.
“Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a profound impact on your skin’s health and appearance. Taking care of your body from the inside out can enhance the effects of your skincare routine and help you maintain healthier, more youthful-looking skin.”
By incorporating these lifestyle choices into your daily routine, you can support the health and resilience of your skin. Remember, healthy skin is a result of consistent efforts and a holistic approach to overall well-being.
Conclusion
After examining the effects of smoking on skin aging, it is clear that smoking has a significant negative impact on the skin’s appearance and health. Smokers are more prone to developing wrinkles, sagging skin, uneven skin tone, and are at a higher risk of skin diseases and cancer. However, there is hope for smokers who want to maintain a more youthful-looking complexion.
The first step in preventing skin aging as a smoker is to quit smoking altogether. This can have remarkable benefits for the skin, including a reduction in age spots and redness, improved collagen production, and a reversal of biological age. Quitting smoking is a powerful strategy to help smokers regain control of their skin health.
In addition to quitting smoking, adopting a tailored skincare routine can also help minimize the negative effects of smoking on the skin. Regular use of sunscreen, antioxidant serums, and retinol can protect and nourish the skin, promoting a more youthful appearance. Proper cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliating can also improve skin texture and hydration.
Lastly, making healthy lifestyle choices can further support skin aging prevention. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, hydration, and stress management all contribute to healthier skin. By combining these preventive measures, smokers can take proactive steps to minimize the impact of smoking on their skin and maintain a youthful-looking complexion.
FAQ
How does smoking affect skin aging?
Smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin by robbing it of oxygen, causing broken capillaries, and breaking down collagen and elastin. It also leads to increased lines around the mouth and brows and decreases vitamin-A levels in the skin, resulting in drier skin.
What are the effects of smoking on skin appearance?
Smoking negatively impacts the skin by impairing collagen formation, reducing blood flow, and promoting oxidative stress in skin cells. These effects lead to wrinkles, sagging skin, uneven skin tone, and age spots. Smoking also delays wound healing and increases the risk of skin diseases such as psoriasis, acne, eczema, and skin cancer.
How can smokers prevent skin aging?
Despite the negative effects of smoking on the skin, smokers can still take steps to minimize skin aging. It is essential for smokers to wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily and adjust their skincare routine to include anti-oxidant serums during the day and retinol at night. Smokers should also wash their face thoroughly twice a day and consider using glycolic acid cleansers to promote cell turnover. Hydrating moisturizers and non-comedogenic night creams can combat flakiness and provide necessary hydration.
Does smoking affect wound healing?
Smoking impairs the body’s inflammatory process and immune function, leading to delayed wound healing. It also increases the risk of wound complications, postsurgical site infection, and slow bone healing. Quitting smoking at least four weeks before surgery can help reduce the risk of postsurgical complications.
What is the link between smoking and skin infections?
Smoking inhibits the body’s immune response and suppresses immune cells in the skin, making smokers more susceptible to infections. Smokers have a higher risk of skin diseases such as psoriasis, acne, eczema, and skin cancer. They are also more prone to infections like pneumococcal disease, trichomoniasis, and genital chlamydia.
Can smoking increase skin cancer risk?
Smokers have a higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer. Smokers with melanoma also have a lower chance of survival compared to nonsmokers. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can irritate the skin and increase the risk of these cancers.
Does smoking worsen skin conditions?
Smoking increases the risk of skin conditions such as psoriasis, acne, and eczema. Smokers with psoriasis may experience more severe symptoms and have a poorer response to treatment. Active and passive smoke exposure is also linked to an increased risk of atopic dermatitis.
How does smoking affect changes in skin appearance?
Smoking is an independent risk factor for the formation of wrinkles, especially in the middle to lower third of the face. It can also cause sagging skin due to increased water loss and degeneration of collagen and elastic fibers. Smoking promotes melanocyte formation, leading to age spots and uneven skin tone.
What are the benefits of quitting smoking for the skin?
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for the skin. Within a month of quitting, age spots and redness may decrease, and changes in skin color caused by smoking may start to reverse. Quitting smoking can also improve collagen production, resulting in brighter and smoother skin. Studies have shown that quitting smoking can lead to a reduction in signs of skin aging and a reversal of biological age.
How does nicotine contribute to skin aging?
Nicotine, a highly addictive chemical found in tobacco, plays a significant role in skin aging. It promotes collagen degradation, reduces blood flow, and alters the structure and function of skin cells. Nicotine also affects the body’s immune responses and can impair wound healing.
What lifestyle choices can promote healthy skin?
In addition to quitting smoking, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to skin aging prevention. Getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and nutrients, staying hydrated, and managing stress can all promote healthier and more youthful-looking skin.
What is the summary of smoking’s impact on skin aging?
Smoking has significant negative effects on skin aging, including wrinkles, sagging skin, uneven skin tone, and an increased risk of skin diseases and cancer. However, smokers can take preventive measures and make lifestyle choices to minimize the impact of smoking on their skin. Quitting smoking, following a tailored skincare routine, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help smokers maintain more youthful-looking skin.




