Did you know that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is responsible for up to 90% of skin aging? That’s right – the sun’s rays can cause significant damage to your skin, leading to premature aging and increasing the risk of skin cancer. Protecting your skin from the sun is not just about preventing sunburn; it’s a vital part of maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin as you age.
Key Takeaways:
- UV radiation from the sun is responsible for up to 90% of skin aging.
- Preventing sun damage is crucial to maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin.
- Sun damage can lead to dryness, discoloration, and wrinkles, as well as an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Protect your skin from the sun by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing.
- Make sun protection a habit year-round, as UV rays can still damage your skin on cloudy and cool days.
What is Photoaging and How Does it Differ from Chronological Skin Aging?
Photoaging is the result of prolonged exposure to UV radiation, either from the sun or artificial light sources. It causes DNA changes in the skin cells and increases the risk of skin cancer. Unlike chronological skin aging, which is a natural process determined by age and genetics, photoaging is largely preventable. By taking proactive measures to protect your skin from harmful UV rays, you can reduce the signs of photoaging and maintain a more youthful appearance.
While chronological aging cannot be prevented, photoaging can be minimized through sun protection measures. This includes wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses, and avoiding excessive sun exposure. These preventative actions not only reduce the risk of skin cancer but also help prevent the visible signs of photoaging such as wrinkles, sunspots, and uneven skin tone.
By understanding the difference between photoaging and chronological skin aging, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin from unnecessary damage. Incorporating sun protection into your daily skincare routine is essential for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin.
| Photoaging | Chronological Skin Aging |
|---|---|
| Caused by prolonged exposure to UV radiation | Natural process determined by age and genetics |
| Increases the risk of skin cancer | Does not increase the risk of skin cancer |
| Visible signs include wrinkles, sunspots, and uneven skin tone | Visible signs include sagging skin, loss of elasticity, and dryness |
| Preventable through sun protection measures | Cannot be prevented |
Who is at Risk for Sun-Damaged Skin?

Everyone is susceptible to sun-damaged skin, but certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing skin damage and skin cancer. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin and reduce the potential harm caused by prolonged sun exposure.
Risk Factors for Sun-Damaged Skin:
- Light skin tone: People with fair skin have less natural protection against harmful UV radiation, putting them at higher risk of sun damage.
- History of skin cancer or family history: Individuals with a personal or family history of skin cancer are more prone to developing sun-damaged skin.
- Many moles and freckles: Having numerous moles and freckles can indicate an increased susceptibility to sun damage.
- Easily burning: Individuals who burn easily when exposed to the sun are more likely to develop sun-damaged skin.
- Outdoor and tanning salon exposure: Spending significant time outdoors, especially without proper sun protection, or using tanning salons regularly increases the risk of skin damage.
- Certain health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or genetic disorders, can make the skin more sensitive to sun exposure and increase the risk of sun damage.
- Specific medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics, antifungal drugs, or certain cancer treatments, can increase sensitivity to sunlight and raise the risk of skin damage.
It’s important for individuals with these risk factors to take extra precautions when it comes to sun protection. By being aware of these risk factors and implementing appropriate preventive measures, such as wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and adopting a sun-safe lifestyle, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing sun-damaged skin and related conditions.
Image:
Can Sun Damage be Reversed?
Unfortunately, once UV radiation causes DNA damage in skin cells, it cannot be reversed. However, there are several treatments available that can help improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin.
Treatments for sun-damaged skin focus on reducing the visible signs of damage, such as spots, discolorations, wrinkles, and overall skin tone. These treatments can stimulate the production of new skin cells and collagen, resulting in a smoother and more youthful-looking complexion.
Some common treatments for sun-damaged skin include:
- Laser therapy: This treatment uses laser technology to target and remove damaged skin cells, promoting the growth of new, healthier skin.
- Chemical peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin to exfoliate and remove damaged outer layers, revealing fresh, rejuvenated skin.
- Microdermabrasion: This non-invasive procedure gently exfoliates the skin, removing dead skin cells, and promoting cell turnover.
- Topical creams and serums: Certain products containing ingredients like retinoids, antioxidants, and hyaluronic acid can help improve the texture, tone, and elasticity of sun-damaged skin.
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional to determine which treatment options are most suitable for your specific needs and skin condition. They can provide personalized recommendations and guidance to help you achieve the best results.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Laser therapy | Uses laser technology to remove damaged skin cells and stimulate new skin growth. |
| Chemical peels | Applies a chemical solution to exfoliate and remove damaged outer layers of the skin. |
| Microdermabrasion | Non-invasive procedure that gently exfoliates the skin to promote cell turnover. |
| Topical creams and serums | Products containing ingredients like retinoids, antioxidants, and hyaluronic acid to improve the texture and tone of the skin. |
It’s important to remember that while these treatments can improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin, prevention is always better than cure. Practicing proper sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen and seeking shade, is essential to minimize the risk of future damage.
By combining professional treatments with a consistent sun protection routine, you can effectively repair and protect your skin from sun damage, helping it look and feel its best.
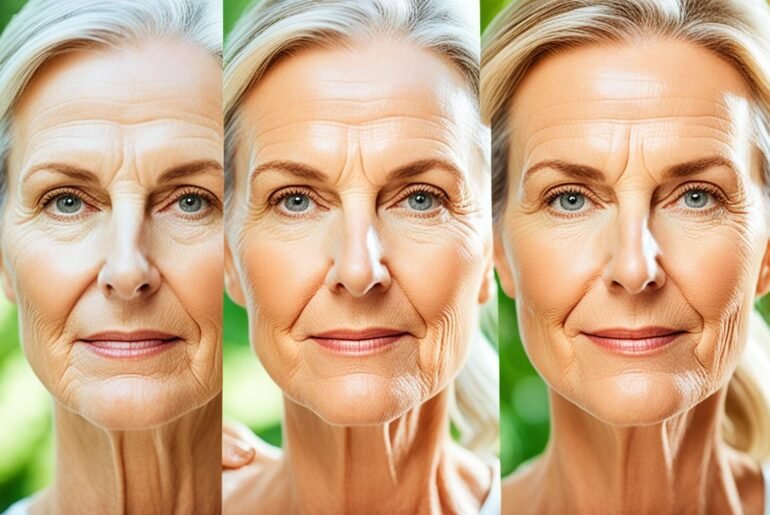
Visible Signs of Photoaging
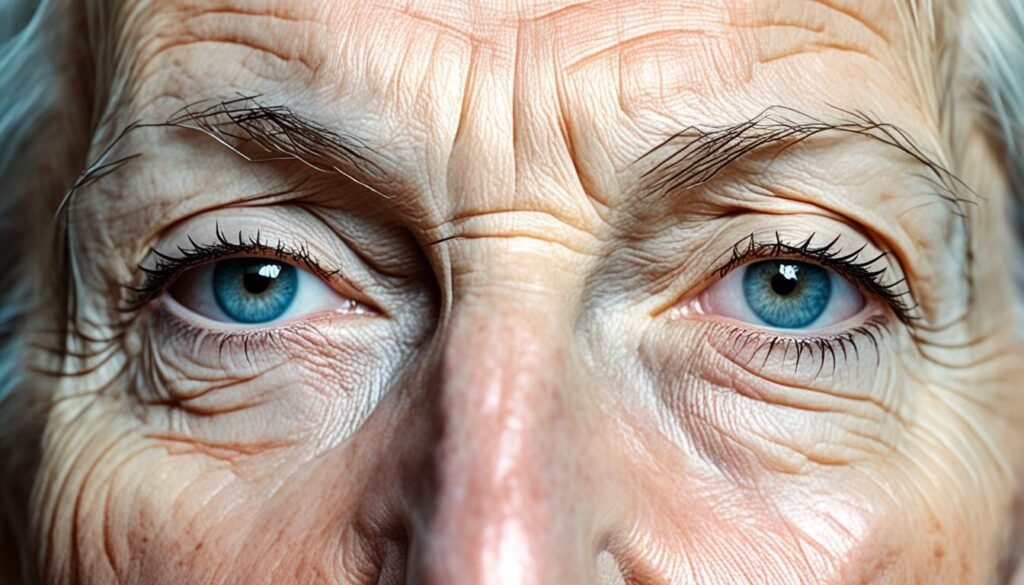
When it comes to photoaging, the visible signs of sun damage are hard to miss. These signs commonly appear on the face, neck, hands, arms, legs, and upper chest. Understanding and recognizing these signs can help you take proactive steps to protect and care for your skin.
Here are some of the noticeable signs of photoaging:
- Coarse, dry skin: Prolonged exposure to the sun can lead to dryness and rough texture, making the skin feel coarse and dehydrated.
- Freckling and skin discoloration: Sunspots, freckles, and uneven skin tone are common indicators of sun damage. These dark spots and patches can be a result of excess melanin production caused by UV radiation.
- Leathery texture: Over time, the skin’s texture can become thick and leathery due to the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers, leading to a loss of elasticity.
- Deep wrinkles: One of the most noticeable signs of photoaging is the development of deep wrinkles and fine lines on areas exposed to the sun.
These visible signs of sun damage can be distressing, but the good news is that they can be minimized and managed through proper sun protection measures and skincare practices.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to protecting your skin from the harmful effects of sun damage.
Strategies for Preventing Sun Damage
Protecting your skin from the harmful effects of the sun is crucial for maintaining its health and preventing premature aging. By incorporating effective anti-aging skincare tips and sun protection strategies into your daily routine, you can safeguard your skin from sun damage and maintain its youthful appearance. Here are some key strategies to prevent sun damage:
- Wear Sunscreen with a High SPF: Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30 to shield your skin from both UVA and UVB rays. Remember to apply it generously to all exposed areas of your body, including your face, neck, hands, and arms. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Seek Shade During Peak Sun Hours: The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If possible, limit your sun exposure during these hours and seek shade under umbrellas, trees, or awnings.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Shield your skin from the sun by wearing long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses. Clothing with a tight weave and darker colors provides better sun protection.
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during summer months and in regions with high UV index levels. Take breaks indoors or under shade to reduce your overall sun exposure.
Quotes:
“Practicing effective sun protection strategies is the best way to prevent sun damage and maintain the health of your skin.” – Dr. Rachel Johnson, Dermatologist
Remember, protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays is an essential part of any anti-aging skincare routine. By following these sun protection strategies, you can safeguard your skin from sun damage, reduce the risk of skin cancer, and maintain a youthful and radiant complexion.
Treatment Options for Sun-Damaged Skin

As the signs of sun damage and aging skin become more advanced, it may be necessary to explore more invasive treatment options to rejuvenate the skin. There are several effective treatments available that can help minimize the appearance of wrinkles, scars, and other signs of sun damage.
1. Botulinum Toxin Injections: Botulinum toxin injections, commonly known as Botox, can temporarily smooth out fine lines and wrinkles by relaxing the underlying muscles. This treatment is particularly effective for reducing the appearance of crow’s feet and frown lines.
2. Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes the outer layer to peel off. This helps improve the texture and tone of the skin, reducing the appearance of wrinkles, age spots, and uneven pigmentation.
3. Dermal Filler Injections: Dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid-based fillers, can be injected into the skin to restore volume and smooth out deep wrinkles and lines. They can also be used to plump up the lips and enhance facial contours.
4. Dermabrasion: Dermabrasion involves removing the top layer of skin using a specialized device, revealing fresh, new skin. This treatment is effective for reducing the appearance of scars, fine lines, and age spots, and can improve overall skin texture.
5. Laser Skin Resurfacing: Laser skin resurfacing uses laser technology to remove damaged skin cells and stimulate collagen production. This treatment can effectively reduce wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, and improve skin texture and tone.
6. Intense Pulsed Light Therapy: Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy utilizes flashes of intense light to target and break down pigmented and damaged skin cells. This treatment can help reduce the appearance of sun spots, freckles, and redness caused by sun damage.
7. Tretinoin Treatment: Tretinoin, a topical medication derived from vitamin A, can be used to improve the texture and appearance of sun-damaged skin. It promotes collagen production, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and helps even out skin tone.
Incorporating these treatment options into a comprehensive skin care plan can help rejuvenate sun-damaged skin and restore a more youthful appearance. It is important to consult with a qualified dermatologist or aesthetician to determine the most suitable treatment options based on individual skin concerns and goals.
Importance of Sun Protection for People of Color

While people of color are less likely to get sunburned due to higher melanin production, it is important to understand that they can still experience sun damage and an increased risk of skin cancer. This misconception can lead to a lack of awareness about the importance of sun protection for darker skin tones. To ensure the health and well-being of people of color, it is crucial to recognize the need for sun protection measures tailored to their specific needs.
Research has shown that individuals with darker skin tones are at a lower risk of developing skin cancer compared to those with lighter skin tones. However, this does not mean that they are immune to sun damage. Sunburn may not always be visible on darker skin, but the harmful effects of UV radiation can still penetrate the skin and cause long-term damage.
It is essential for people of color to implement sun protection strategies to minimize the risk of sun damage. This includes wearing sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Sunscreen should be applied generously and reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if sweating or swimming. Additionally, seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts, and using sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays are important preventive measures.
While there is a need for further research to understand the specific skin cancer risks faced by people of color, it is evident that a proactive approach to sun protection is vital. By prioritizing sun protection, individuals with darker skin tones can minimize the risk of sun damage and maintain the health and well-being of their skin.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to sun damage in darker skin. By embracing sun protection as a daily routine, people of color can reduce their susceptibility to skin cancer and ensure the longevity of their skin’s health and beauty.
| Skin Cancer Risks | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Skin Tones | Darker Skin Tones | ||
| Visible signs of sun damage | More prominent | Less prominent | |
| Visible sunburn | Common | Rare | |
| Skin cancer risk | Higher | Lower | |
Sun Protection Tips for Everyone

When it comes to preventing sun damage and protecting your skin from harmful UV radiation, everyone should prioritize sun protection. By incorporating these simple yet effective tips into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of sunburn, skin damage, and long-term effects such as premature aging and skin cancer.
1. Wear Sunscreen with a Minimum SPF of 15
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 to all exposed areas of your skin. Make sure to reapply it every two hours, especially if you are sweating or swimming.
2. Seek Shade During Peak Sun Hours
Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun’s rays are strongest. Seek shade under an umbrella, tree, or use a sunshade to minimize exposure to harmful UV radiation.
3. Wear Protective Clothing
Protect your skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat. This will provide an additional layer of defense against the sun’s rays and minimize direct exposure to your skin.
4. Use Sunglasses That Block UVA and UVB Rays
Invest in sunglasses that offer 100% UVA and UVB protection. This will not only shield your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays but also protect the delicate skin around your eyes from sun damage.
5. Be Aware of the UV Index
Check the UV index in your area before heading outdoors. The UV index is a measure of the strength of the sun’s UV radiation and can help you determine the level of sun protection you need. The higher the index, the more precautions you should take.
6. Limit Sun Exposure During Peak Hours
Try to minimize your time in direct sunlight during peak hours. If possible, schedule outdoor activities for early morning or late afternoon when the sun’s rays are less intense.
By following these sun protection tips, you can safeguard your skin from sun damage, reduce the risk of skin cancer, and maintain healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| You don’t need sunscreen on cloudy days. | UV rays can penetrate through clouds, so it’s important to wear sunscreen even on overcast days. |
| All sunscreen is the same. | Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays for optimal sun protection. |
| Tanning beds are a safe alternative to sun exposure. | Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation and can increase the risk of skin cancer. |
| Sunscreen is only necessary at the beach. | UV rays are present even during everyday activities, so it’s important to wear sunscreen daily. |
| Darker skin tones don’t need sunscreen. | While darker skin has some natural sun protection, it is still susceptible to sun damage and skin cancer. |
The Importance of Year-Round Sun Protection

Sun protection should be a priority not only during the summer months but also throughout the year. Many people mistakenly believe that sun damage only occurs on hot and sunny days. However, UV rays can still reach your skin on cloudy and cool days. Furthermore, these harmful rays can reflect off surfaces like water, sand, and snow, increasing the risk of sun damage even in the winter.
It is essential to make sun protection a habit regardless of the season or weather conditions. By consistently practicing year-round sun protection, you can safeguard your skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation. Whether it’s sunny or overcast, hot or cold, wearing protective clothing, seeking shade, and applying sunscreen are crucial steps in preventing sun damage.
Remember that sun damage accumulates over time, and the effects of prolonged sun exposure are not limited to the summer season. In fact, studies have shown that sunburns during childhood significantly increase the risk of developing skin cancer later in life. By incorporating year-round sun protection into your daily routine, you can minimize the risk of sun damage and maintain the health and integrity of your skin.
| Year-Round Sun Protection Tips |
|---|
| 1. Wear sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of at least 30 every day, even when it’s cloudy. |
| 2. Apply sunscreen generously and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating. |
| 3. Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses. |
| 4. Seek shade during the peak hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. when the sun’s rays are strongest. |
| 5. Be aware of the UV index in your area and take extra precautions when it’s high. |
| 6. Keep newborns and infants out of direct sunlight and protect them with hats and lightweight clothing. |
| 7. Avoid artificial UV tanning booths and sunlamps, as they can also contribute to skin damage. |
Remember, sun protection is a year-round commitment. By taking proactive steps to protect your skin from the sun, you can enjoy the outdoors and maintain healthy and radiant skin for years to come.
Conclusion
Protecting your skin from sun damage is crucial for maintaining a youthful appearance and reducing the risk of skin cancer. By understanding the risks of photoaging, practicing sun protection strategies, and seeking appropriate treatments for sun-damaged skin, you can maintain the health and radiance of your skin as you age.
Remember to prioritize sun protection all year round and make it a part of your daily skincare routine. Incorporating sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing, can significantly reduce the harmful effects of UV radiation. It is also important to be aware of the visible signs of photoaging, such as dryness, discoloration, and wrinkles, and take proactive steps to minimize them.
By adopting a comprehensive approach to sun protection, you can safeguard your skin’s health and maintain its youthful glow. Take care of your skin today to enjoy beautiful and radiant skin in the years to come.
FAQ
What is photoaging and how does it differ from chronological skin aging?
Photoaging is the premature aging of the skin caused by exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. It can lead to skin cancer and has visible effects such as dryness, discoloration, and wrinkles. It differs from chronological skin aging, which is a natural process determined by age and genetics. While chronological aging cannot be prevented, photoaging can be reduced through sun protection measures.
Who is at risk for sun-damaged skin?
Everyone is susceptible to sun-damaged skin, but certain factors increase the risk. These include having a light skin tone, a history of skin cancer or family history of skin cancer, having many moles, freckles, and burning easily, and spending a lot of time outdoors or at tanning salons. People with certain health conditions and those taking specific medications are also at an increased risk.
Can sun damage be reversed?
Once UV radiation causes DNA damage in skin cells, it cannot be reversed. However, the appearance of sun-damaged skin can be improved through various treatments. These treatments can remove spots and discolorations, reduce wrinkles, stimulate new skin and collagen production, and improve the overall tone and quality of the skin.
What are the visible signs of photoaging?
Photoaging most commonly affects the face, neck, hands, arms, legs, and upper chest. It can cause coarse, dry skin, freckling and skin discoloration, leathery texture, and deep wrinkles. These visible signs of sun damage can be minimized through proper sun protection.
What strategies can I use to prevent sun damage?
Preventing sun damage involves practicing sun protection strategies such as wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing, including hats and sunglasses, and avoiding excessive sun exposure. It is important to incorporate these strategies into your daily skincare routine and lifestyle habits to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
What treatment options are available for sun-damaged skin?
Advanced signs of sun damage and aging skin may require more invasive treatment procedures such as botulinum toxin injections, chemical peels, dermal filler injections, dermabrasion, laser skin resurfacing, intense pulsed light therapy, and tretinoin treatment. These treatments can help minimize the appearance of wrinkles, scars, and other signs of sun damage.
Is sun protection important for people of color?
While people of color are less likely to get sunburned due to higher melanin production, they can still experience sun damage and an increased risk of skin cancer. People of color should also practice sun protection measures, including wearing sunscreen and seeking shade. Further research is needed to understand skin cancer risks and effectiveness of treatments in darker-skinned individuals.
What are some sun protection tips for everyone?
Everyone should prioritize sun protection to prevent sun damage. This includes wearing sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 15, seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats, and using sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the UV index and limit sun exposure during peak hours.
Is sun protection necessary year-round?
Sun protection should be practiced throughout the year, not just during the summer months. UV rays can reach the skin on cloudy and cool days as well, and they can reflect off surfaces like water, sand, and snow. It is essential to make sun protection a habit regardless of the season or weather conditions.




