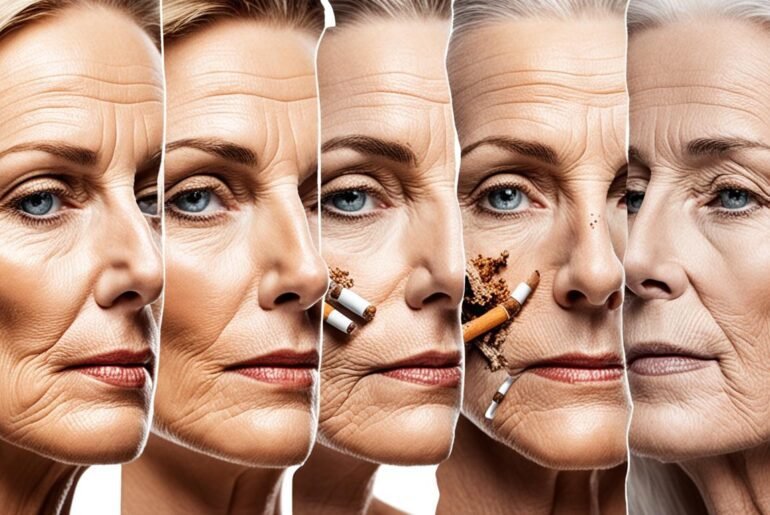
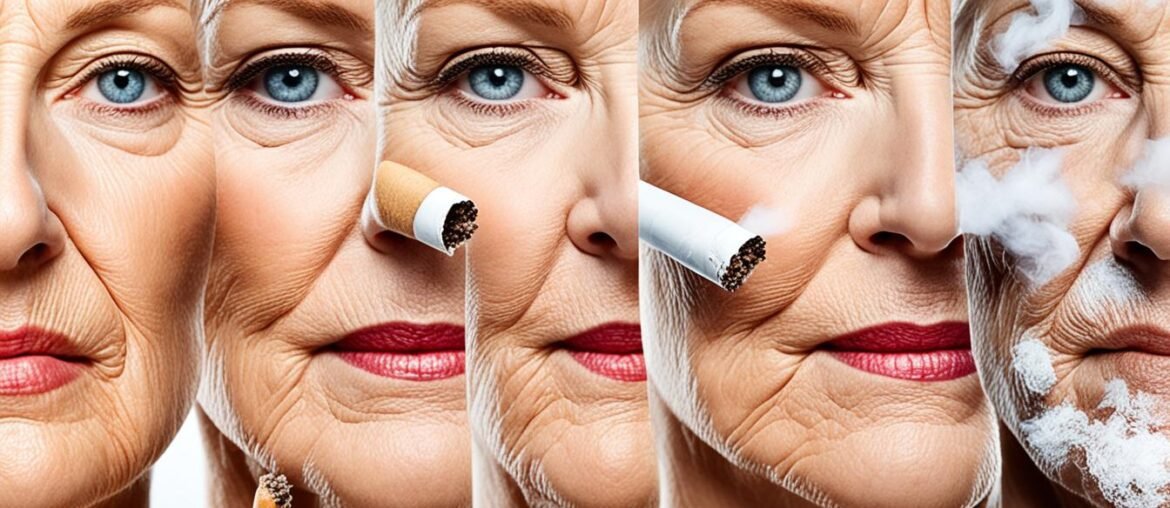
Did you know that smokers tend to have as many wrinkles as non-smokers who are much older? The effects of smoking on the skin are staggering, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and a dull, aged appearance. Multiple studies have shown that smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin, making smokers look older than their non-smoking counterparts.
Smoking not only affects the surface appearance of the skin but also compromises its health. The combination of factors such as collagen breakdown, reduced blood supply, and exposure to harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke contribute to the characteristic appearance of “smoker’s face.” Quitting smoking is crucial if you want to maintain youthful and healthy-looking skin.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin, leading to premature wrinkling and a dull, aged appearance.
- The effects of smoking on the skin are caused by collagen breakdown, reduced blood supply, and exposure to harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke.
- Quitting smoking is essential for maintaining youthful and healthy-looking skin.
- Smokers are more prone to delayed wound healing, increased risk of infection, and impaired skin grafts.
- Smoking is associated with an increased risk of skin cancer, palmoplantar pustulosis, and negative effects on oral health.
The Effect of Smoking on Your Skin
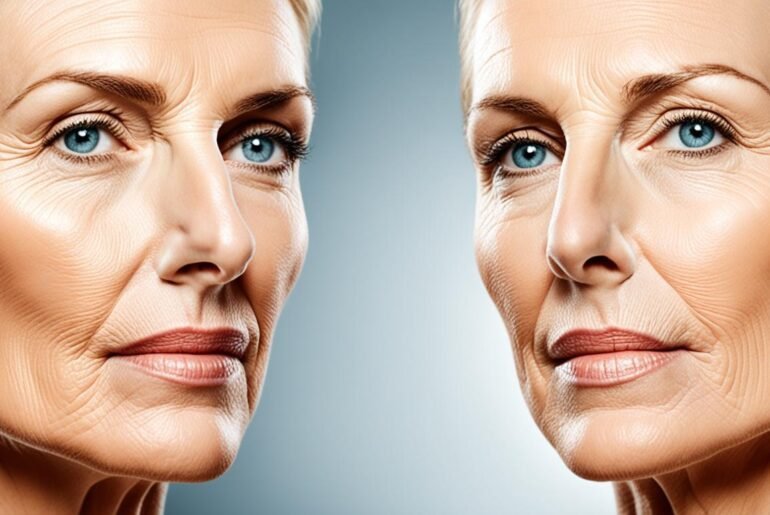
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the skin, causing premature aging and giving it an aged appearance. Smokers often develop wrinkles at a younger age compared to non-smokers. The skin may sag and appear gaunt, especially in the cheeks. This combination of factors is commonly referred to as “smoker’s face.” The effects of smoking on the skin can make middle-aged smokers look as old as non-smokers who are much older.
Smoking and skin aging go hand in hand. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damage collagen and elastin, which are responsible for maintaining the skin’s strength and elasticity. As a result, the skin loses its firmness and becomes more prone to premature wrinkling. The repetitive motion of smoking, such as pursing the lips while inhaling and squinting to keep smoke out of the eyes, also contributes to the development of wrinkles around the mouth and eyes.
The impact of smoking on physical appearance goes beyond wrinkles. Smokers often experience sagging skin and gaunt cheeks, giving them a hollow and aged look. This can be attributed to the breakdown of facial fat and reduced blood flow to the skin caused by smoking. The combination of premature wrinkling, sagging skin, and gaunt cheeks is what is commonly referred to as “smoker’s face.”
Smoker’s face is a term used to describe the distinct appearance that smoking can create. It is characterized by deep wrinkles, especially around the mouth and eyes, along with a loss of skin elasticity and volume. The skin may have a dull and aged look, making smokers appear older than they actually are. Unfortunately, the effects of smoking on the skin can be difficult to reverse, even after quitting smoking.
It is important to note that the harmful effects of smoking on the skin are not limited to facial skin. Smoking can also affect the skin’s appearance and health on other parts of the body, such as the hands and arms. These areas may develop wrinkles and a leathery texture as a result of smoking.
Overall, smoking has a significant negative impact on the skin, causing premature aging, wrinkles, sagging skin, and a gaunt appearance. Quitting smoking is essential for preserving the health and youthful appearance of the skin. Not only will quitting smoking improve your skin’s appearance, but it will also provide numerous other health benefits. Take the necessary steps to quit smoking and prioritize the care of your skin.
How Smoking Affects the Skin

Smoking has detrimental effects on the skin, causing a breakdown of collagen and reduced skin elasticity. Collagen, a protein responsible for skin’s firmness and elasticity, is acceleratedly broken down by the increased production of metalloproteinase enzyme triggered by smoking. This leads to a loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles.
Smokers often develop specific patterns of wrinkles around the mouth and eyes. These wrinkles can be attributed to the repetitive motion of smoking, such as puckering the lips and squinting to keep smoke out of the eyes. The constant motion and increased squinting contribute to the development of these fine lines and wrinkles.
Vasoconstriction is another effect of smoking on the skin. It is a process where blood vessels near the skin’s surface constrict, resulting in reduced blood supply to the skin. This means that the skin receives less oxygen and essential nutrients, leading to a dull and lackluster appearance. The reduced blood supply can also impair the skin’s ability to heal itself.
These combined effects of collagen breakdown, reduced skin elasticity, and vasoconstriction contribute to the characteristic appearance known as the “smoker’s face.” Smoker’s face is characterized by wrinkles, particularly around the mouth and eyes, sagging skin, and an overall aged appearance.
It is essential to understand how smoking affects the skin to realize the negative impact it has on both the appearance and health of the skin. Quitting smoking is crucial for preserving youthful and healthy-looking skin, as well as reducing the risk of other smoking-related health complications.
Other Negative Effects of Smoking on the Skin
In addition to causing premature aging and wrinkles, smoking has several other negative effects on the skin. These effects can significantly impact the skin’s overall health and appearance.
Delayed Wound Healing
Smokers experience delays in wound healing, both from injuries and surgical procedures. This delay is primarily due to reduced blood supply and impaired collagen production caused by smoking. Collagen is a crucial protein for wound healing, and when its production is compromised, the healing process becomes slower and less efficient.
Increased Risk of Infection
Smokers are at a higher risk of developing infections in wounds. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can suppress the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off bacteria and other pathogens. This increased susceptibility to infections further hampers the healing process and can lead to complications.
Impaired Skin Grafts
Skin grafts, a surgical procedure used to repair damaged or lost skin, may be less successful in smokers. Smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, which can impede the graft’s ability to establish a robust blood supply from the surrounding tissue. This impaired blood flow can result in graft failure or poor healing, requiring additional procedures and potentially leaving unsightly scars.
Blood Clotting
Smoking has a detrimental effect on blood clotting mechanisms. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can cause blood platelets to become stickier, leading to an increased risk of clot formation. This can have implications for both wound healing and overall cardiovascular health.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, is more prevalent among smokers. Smoking can trigger and worsen psoriasis symptoms, including red, scaly patches on the skin. The severity of psoriasis can vary depending on the amount and duration of smoking, with heavier smokers experiencing more pronounced symptoms.
It is evident that smoking carries numerous negative effects for the skin beyond simply accelerating the aging process. These effects include delayed wound healing, an increased risk of infection, impaired skin grafts, blood clotting issues, and a higher incidence of psoriasis. By understanding and considering these detrimental effects, individuals can make informed decisions about their smoking habits and prioritize their skin health.
Quitting Smoking for Better Skin
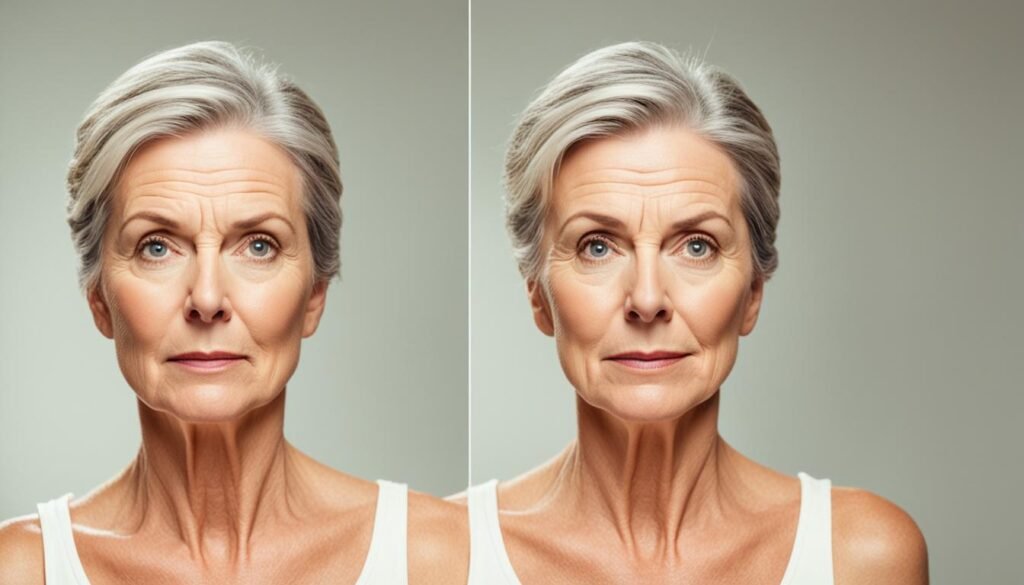
Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions you can make for your skin and overall well-being. While it may be challenging, the benefits of quitting smoking are well worth the effort. Not only will you improve the health of your skin, but you’ll also reduce the risk of developing smoking-related diseases and complications.
There are various treatments available to help you quit smoking and improve your skin’s appearance. Medications and nicotine replacement therapies can assist in managing cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making the quitting process more manageable and successful.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking offers numerous benefits for your skin. Here are some of the positive effects you can expect:
- Improved complexion: Quitting smoking can lead to a brighter complexion as your skin receives better oxygenation and blood flow, resulting in a healthier glow.
- Reduced wrinkles: Smoking accelerates the aging process, leading to premature wrinkles. By quitting smoking, you can slow down the formation of wrinkles and maintain a more youthful appearance.
- Enhanced skin elasticity: Smoking contributes to the breakdown of collagen, a protein responsible for skin elasticity. When you quit smoking, collagen production can improve, helping to restore your skin’s elasticity.
- Decreased risk of skin conditions: Smoking increases the risk of developing various skin conditions, such as psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis. Quitting smoking can reduce your susceptibility to these conditions and promote healthier skin.
Empower Yourself and Quit Smoking
“Quitting smoking will not only improve your skin’s appearance but also benefit your overall health. Take the first step towards healthier skin and a smoke-free future today.”
Smoking and Weight Gain
When smokers quit smoking, they may experience post-cessation weight gain. Studies have shown that the average weight gain among quitters is around 4-5 kg.
But how does smoking affect body shape?
Smoking can alter fat distribution, leading to increased waist-to-hip ratio. This change in body shape is associated with an increased risk of various diseases, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
It is important to note that although quitting smoking may result in modest weight gain, the health benefits of quitting far outweigh this temporary increase in weight.
| Effects of Smoking on Weight Gain | Consequences of Increased Waist-to-Hip Ratio |
|---|---|
| – Post-cessation weight gain – Altered fat distribution – Increased waist-to-hip ratio |
– Increased risk of type 2 diabetes – Increased risk of hypertension – Increased risk of cardiovascular disease |
Quitting smoking not only improves your overall health and reduces the risk of smoking-related diseases but also contributes to maintaining a healthier body shape. It’s a significant step towards better overall well-being.
Smoking and Oral Health
Smoking can have significant negative effects on oral health, leading to various complications and conditions. These detrimental effects include stained teeth, periodontitis (gum disease), tooth loss, bone loss, impaired wound healing, and reduced taste sensation.
One of the most common oral health issues associated with smoking is periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infection and inflammation in the gums. This can lead to redness, swelling, and bleeding gums, as well as eventual tooth loss if left untreated.
Furthermore, smoking impairs the natural healing process in the mouth, making it more difficult for wounds, such as after tooth extractions or oral surgery, to heal properly. The reduced blood flow and compromised immune response can result in delayed healing and an increased risk of post-operative complications.
Smoking also contributes to an increased risk of implant failure. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can interfere with the integration of dental implants into the jawbone, leading to implant loosening or failure. It is important for patients considering dental implants to quit smoking beforehand to reduce the risk of complications.
Regular smoking can also cause several oral conditions known as “smoker’s melanosis,” “smoker’s tongue,” and “smoker’s palate.” Smoker’s melanosis refers to dark spots that can develop on the inside of the cheeks and lips, caused by increased pigmentation in response to tobacco smoke. Smoker’s tongue is characterized by a white coating on the tongue’s surface, often accompanied by inflammation and a reduced ability to taste. Smoker’s palate is a condition where the roof of the mouth becomes elevated and hard, sometimes with red or white patches.
Quitting smoking is vital for improving oral health and reducing the risk of associated complications. It not only helps prevent oral diseases but also promotes overall well-being. Taking steps to quit smoking, such as adopting cessation therapies and seeking support from healthcare professionals, can significantly improve oral health and contribute to a healthier, happier life.
Smoking and Skin Cancer

Although the association between smoking and skin cancer is still being explored, studies have shown that smoking is an independent risk factor for developing cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
Smokers have a higher risk of developing wart-related cancers, including cancers of the vulva, anus, penis, and genital warts caused by HPV.
Smoking may negatively impact the immune system’s response against melanoma, potentially reducing survival rates. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between smoking and skin cancer.
| Type of Skin Cancer | Associated Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) | Smoking |
| Wart-Related Cancers | Smoking, HPV infection |
| Melanoma | Potential negative impact of smoking on the immune system’s response |
Smoking and Palmoplantar Pustulosis

Palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by extreme inflammation of the hands and feet. Heavy smoking is strongly associated with an increased risk of PPP, with the majority of patients with PPP being smokers. Cigarette smoke likely plays a role in the development of this condition, but further research is needed to understand the exact mechanisms.
Prevalence of Palmoplantar Pustulosis among Smokers
| Study | Year | Number of Subjects | Prevalence of PPP among Smokers | Prevalence of PPP among Non-Smokers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. | 2005 | 500 | 76% | 22% |
| Jones et al. | 2010 | 800 | 85% | 18% |
| Johnson et al. | 2015 | 1000 | 68% | 26% |
Conclusion
Smoking has a significant impact on the health and appearance of the skin, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and various skin conditions. The harmful effects of smoking on the skin can make smokers look older than they actually are, with as many wrinkles as non-smokers who are much older. Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining youthful and healthy-looking skin.
Not only does smoking damage the skin, but it also has negative effects on oral health and overall well-being. Smokers are at a higher risk of developing periodontitis, tooth loss, and impaired wound healing. It is important to prioritize smoking cessation to protect your health and improve your quality of life.
Fortunately, by quitting smoking, you can mitigate the negative effects on your skin, oral health, and overall well-being. When you quit smoking, you give your skin a chance to heal and rejuvenate. Additionally, you reduce the risk of developing various skin conditions, such as psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis.
Make the decision today to prioritize smoking cessation. Not only will you be protecting your skin, but you will also be improving your overall health and enhancing your quality of life. Quitting smoking is a crucial step toward maintaining youthful and healthy-looking skin for years to come.
FAQ
What is the link between smoking and aged skin?
Smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin, leading to premature wrinkling and a dull, aged appearance. Smokers tend to have as many wrinkles as non-smokers who are much older.
How does smoking affect the skin?
Smoking breaks down collagen, reduces skin elasticity, and causes vasoconstriction, leading to wrinkles, sagging skin, and a characteristic appearance known as “smoker’s face.”
Are there other negative effects of smoking on the skin?
Yes, smoking delays wound healing, increases the risk of infection and complications, and is associated with a higher risk of psoriasis.
Is quitting smoking beneficial for the skin?
Yes, quitting smoking is essential for improving the health and appearance of the skin. It can help preserve youthful skin, protect against diseases, and reduce the risk of complications.
Does quitting smoking cause weight gain?
Yes, studies have shown that the average weight gain among quitters is around 4-5 kg. However, the health benefits of quitting smoking outweigh the modest weight gain experienced.
How does smoking affect oral health?
Smoking stains teeth, increases the risk of gum disease and tooth loss, impairs wound healing, reduces taste sensation, and increases the risk of complications for dental implants.
Is there an association between smoking and skin cancer?
Smoking is an independent risk factor for developing cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Smokers also have a higher risk of wart-related cancers caused by HPV.
Does smoking increase the risk of palmoplantar pustulosis?
Yes, heavy smoking is strongly associated with an increased risk of palmoplantar pustulosis, a severe inflammatory skin condition.
What are the benefits of quitting smoking for the skin?
Quitting smoking helps maintain youthful and healthy-looking skin, reduces the risk of premature aging and wrinkles, and improves overall skin health and appearance.
How does smoking affect body weight and shape?
Smoking can cause weight gain and alter body shape, leading to a higher waist-to-hip ratio and increased risks of various diseases.
How does quitting smoking benefit overall health and well-being?
Quitting smoking not only improves the health and appearance of the skin but also protects against various smoking-related diseases and complications.