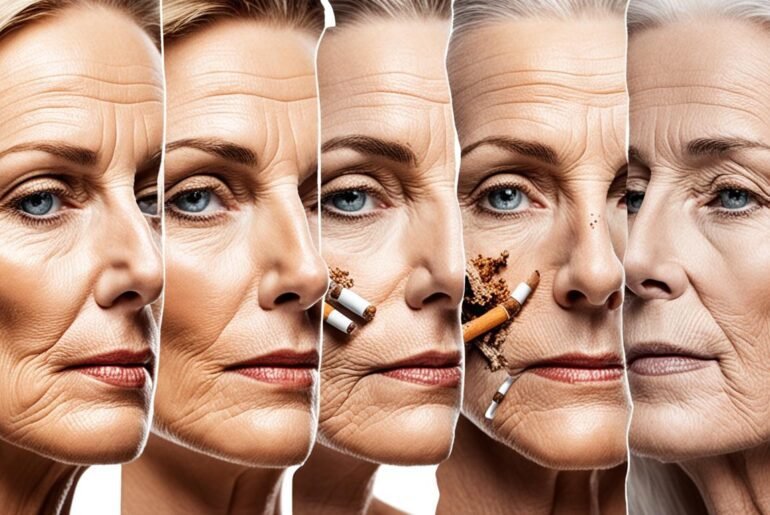
Did you know that smoking can have a dire impact on the elasticity of your skin? It’s not just your internal health that suffers from smoking; your skin takes a hit too. Studies have revealed that smoking can lead to oxidative stress, impair collagen formation, and degrade elastin fibers – the very components responsible for keeping your skin plump and firm. Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and oxygen. The result? Skin aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of elasticity.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking can cause oxidative stress, collagen damage, and degradation of elastin fibers, leading to skin aging and a loss of elasticity.
- Collagen and elastin, vital proteins for skin firmness, are adversely affected by smoking, resulting in wrinkles and sagging skin.
- Smoking accelerates skin aging, causing the breakdown of collagen, the formation of wrinkles, age spots, and a loss of skin elasticity.
- Smoking can affect skin tone and pigmentation, resulting in dull, pale skin and uneven pigmentation.
- Smoking weakens connective tissues in the skin, contributing to sagging and drooping skin.
The Effects of Smoking on Collagen and Elastin
Smoking can have a detrimental impact on the production and maintenance of collagen and elastin in the skin, leading to various unwanted effects on skin health. Collagen and elastin are crucial proteins that contribute to the structure, firmness, and elasticity of the skin.
When you smoke, the harmful chemicals in cigarettes can degrade collagen fibers and impair the formation of elastin. As a result, the levels of these important proteins in your skin become reduced, leading to significant changes in skin appearance and texture.
One of the most noticeable effects of smoking on the skin is the formation of wrinkles. The degradation of collagen and the decreased production of elastin lead to a loss of skin elasticity. This results in the development of fine lines and deep wrinkles, making the skin appear older and less youthful.
Additionally, smoking can contribute to sagging skin. The weakening of collagen and elastin fibers causes the skin to lose its firmness and tightness. Over time, this can lead to sagging skin that hangs loosely on the face and body.
The loss of elasticity caused by smoking can also affect the overall texture and tone of the skin. As collagen and elastin levels decrease, the skin becomes less supple and resilient. This can result in a dull, lackluster complexion and uneven skin texture.
It is important to note that the effects of smoking on collagen and elastin are not limited to the face. Smoking can impact skin firmness and elasticity throughout the body, leading to sagging and loss of tone in areas such as the arms, legs, and breasts.
To better understand the effects of smoking on collagen and elastin, refer to the table below:
| Effects of Smoking on Collagen and Elastin | Description |
|---|---|
| Decreased collagen production | Smoking impairs the body’s ability to produce collagen, resulting in reduced collagen levels in the skin. |
| Impaired elastin formation | The chemicals in cigarettes hinder the formation of elastin, leading to decreased skin elasticity. |
| Degradation of collagen fibers | Smoking causes collagen fibers to break down, contributing to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines. |
| Skin sagging and loss of firmness | The weakened collagen and elastin fibers result in sagging skin and a loss of skin firmness. |
| Reduced skin elasticity | Collagen and elastin play a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity, which is compromised by smoking. |
It is clear that smoking has a significant impact on collagen and elastin, leading to detrimental effects on skin firmness, wrinkles, sagging skin, and loss of elasticity. Quitting smoking is essential for preserving and restoring healthy skin.
Smoking and Skin Aging
Smoking is a known culprit when it comes to accelerated skin aging. The harmful chemicals present in cigarette smoke can wreak havoc on the skin, leading to premature aging and a host of undesirable effects.
One of the main ways smoking contributes to skin aging is through oxidative stress. The toxins in cigarette smoke cause an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them with antioxidants. This imbalance leads to increased oxidative stress, which damages the skin’s DNA and impairs its natural repair mechanisms.
Furthermore, smoking negatively impacts collagen and elastin, which are vital proteins responsible for maintaining the skin’s firmness and elasticity. Collagen provides structural support, while elastin allows the skin to stretch and rebound. Smoking interferes with collagen formation and accelerates its breakdown, and it also compromises elastin production. As a result, smokers experience a decrease in collagen and elastin levels, leading to the formation of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Smoking accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin, resulting in age-related skin problems such as wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Moreover, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, impairing its ability to receive vital nutrients and oxygen. This deprivation of nutrients and oxygen further contributes to the aging process and can cause the skin to appear dull and lackluster.
Studies have consistently shown that smokers tend to exhibit more visible signs of skin aging compared to non-smokers. The effects of smoking on skin aging can be seen in various ways, including the development of age spots, a loss of skin elasticity, and an overall premature aging of the skin.
It is important to note that the detrimental effects of smoking on skin aging are not limited to the face. Smoking can impact skin health all over the body, leading to wrinkles and sagging in other areas as well.
The Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging:
- Accelerated breakdown of collagen and elastin
- Increased formation of wrinkles and fine lines
- Loss of skin elasticity and firmness
- Development of age spots and uneven skin tone
- Dull and lackluster skin appearance
Exposure to cigarette smoke can have severe consequences for the skin, leading to premature aging and a loss of natural beauty. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to slow down and potentially reverse the damage caused by smoking. By making the decision to quit, individuals can protect their skin from further harm and help restore its youthful radiance.
Smoking and Skin Tone/Pigmentation
Smoking can have a significant impact on the tone and pigmentation of the skin. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can lead to dull, pale skin that may appear bluish or gray due to reduced blood flow. Additionally, smoking promotes the formation of melanocytes, which are responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin.
This increased activity of melanocytes can result in uneven skin pigmentation, leading to the appearance of age spots, dark spots, and patches of hyperpigmentation. Chronic exposure to environmental factors such as tobacco smoke, heat, and UV radiation can further contribute to aging-related skin pigmentation.
Reduced blood flow caused by smoking can deprive the skin of the necessary nutrients and oxygen, hampering the skin’s ability to heal and regenerate. This can exacerbate the appearance of skin pigmentation irregularities and overall complexion.
To protect the skin’s tone and pigmentation, it is essential to avoid smoking and minimize exposure to environmental factors that contribute to skin discoloration. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, using sunscreen, and taking proper care of the skin can help improve and maintain a more even skin tone.
Smoking and Skin Sagging

Smoking can have a detrimental effect on the elasticity and firmness of the skin, leading to sagging and drooping. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke can weaken the connective tissues, including collagen and elastin fibers, which are responsible for maintaining the skin’s structure and elasticity. As a result, the skin becomes less resilient and more prone to sagging.
Research has even highlighted that smoking is one of the top causes of sagging breasts. The harmful substances in tobacco smoke can accelerate the breakdown of elastin and collagen, leading to breast tissue losing its firmness and shape. Smoking can also contribute to the premature sagging of other areas of the body, such as the face and neck.
It’s important to note that the effects of smoking on skin sagging are not limited to individuals who smoke directly. Secondhand smoke exposure can also lead to similar skin concerns, particularly in individuals who have prolonged exposure to cigarette smoke.
| Effects of Smoking on Skin Sagging | Prevention and Solutions |
|---|---|
|
|
Smoking and Delayed Wound Healing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3DmVo3HO9I
Smoking can have detrimental effects on wound healing, leading to delays in the body’s natural healing processes. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke can hinder the healing process, resulting in slower wound closure and a higher risk of complications.
The effects of smoking on wound healing can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, which is crucial for delivering oxygen and essential nutrients to the wound site. This decreased blood flow can impede the body’s ability to heal wounds effectively.
Furthermore, smoking inhibits the body’s inflammatory response. Inflammation is an integral part of the healing process as it helps to remove debris and bacteria from the wound, as well as stimulate the growth of new tissue. By impairing the inflammatory response, smoking can hinder the healing of wounds and compromise the body’s ability to fight off infections.
Smoking has also been found to negatively impact collagen production. Collagen is a key component in wound healing, as it provides structural support and helps to rebuild damaged tissue. Reduced collagen production caused by smoking can result in poor scar formation and a prolonged healing process.
“Smoking affects wound healing by reducing blood flow, impairing the inflammatory response, and inhibiting collagen production.”
The delayed wound healing associated with smoking can have serious consequences. It increases the risk of wound complications, such as infections, dehiscence (the reopening of a wound), and poor scar formation. Additionally, the compromised healing process can result in chronic wounds, which can be challenging to manage and may require advanced medical interventions.
In summary, smoking has a detrimental impact on wound healing. The chemicals in cigarette smoke reduce blood flow, impair the inflammatory response, and inhibit collagen production, leading to delayed wound healing and an increased risk of complications. Quitting smoking is crucial for enhancing the body’s natural healing abilities and promoting optimal wound healing.
Smoking and Skin Infections
Smoking can have detrimental effects on the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to skin infections. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke can suppress the activity of immune cells, leading to impaired immune function and increased susceptibility to infections. Additionally, smoking can dysregulate immune responses, causing excessive inflammation and tissue damage in the skin. This compromised immune system can significantly raise the risk of developing various skin infections.
Researchers have found that smokers are at a higher risk of contracting skin infections, including bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. The impaired immune function and tissue damage caused by smoking create an environment conducive to infection, as the body’s natural defense mechanisms are compromised. Pneumococcal disease, a bacterial infection that can lead to pneumonia, and sexually transmitted infections are particularly prevalent among smokers.
In addition to an increased risk of infections, smokers may also experience more severe and prolonged infection outcomes. The weakened immune system and compromised tissue integrity can hinder the body’s ability to combat infections effectively and delay the healing process. This makes it crucial for smokers to take extra precautions to avoid skin infections and promptly seek medical attention if symptoms arise.
The Impact of Smoking on Immune Function
Smoking negatively affects immune function by suppressing the activity of immune cells, impairing their ability to recognize and eliminate pathogens effectively. The chemicals in cigarette smoke, such as nicotine and carbon monoxide, can disrupt the normal functioning of immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes.
Additionally, smoking can dysregulate immune responses by causing excessive inflammation in the body. The inflammatory response is an essential defense mechanism against infections, but chronic exposure to cigarette smoke can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to chronic inflammation. This persistent inflammation not only weakens the immune system but also contributes to tissue damage and further increases the risk of infection.
Smoking and Tissue Damage
Cigarette smoke contains a multitude of harmful chemicals that can directly damage skin cells and tissues. The toxic compounds in smoke can induce oxidative stress, DNA damage, and cell death, leading to tissue damage and impaired healing. As a result, the damaged tissue becomes more susceptible to infection, as it provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive.
The damage caused by smoking extends beyond the skin’s surface and can affect deeper layers of tissues. Collagen and elastin, essential components of the skin’s structure and elasticity, can be negatively impacted by smoking, further compromising the skin’s ability to defend against infections.
Reducing Infection Risk – Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of skin infections and restore immune function. By quitting smoking, individuals can help their immune system recover and rebuild its ability to fight off infections. The body’s natural healing mechanisms can begin to repair the damage caused by smoking, enabling the skin to regain its strength and resilience.
In addition to quitting smoking, practicing good skincare habits, such as keeping the skin clean and moisturized, can help protect against skin infections. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest, can also bolster the immune system and promote overall skin health.
| Infection Risk Factors | Non-Smokers | Smokers |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Infections | Low risk | Increased risk |
| Fungal Infections | Low risk | Increased risk |
| Viral Infections | Low risk | Increased risk |
| Pneumococcal Disease | Low risk | Higher risk |
| Sexually Transmitted Infections | Low risk | Higher risk |
Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for overall health but also plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of skin infections. By quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can protect their skin, strengthen their immune system, and promote optimal skin health.
Smoking and Skin Cancer

Smoking is strongly linked to an increased risk of developing skin cancer, including both squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Numerous studies have provided evidence of the detrimental effects of smoking on skin health and the development of malignant cell growth.
For squamous cell carcinoma, a type of non-melanoma skin cancer, smokers have a higher incidence compared to non-smokers. The harmful chemicals present in cigarette smoke can damage the DNA in skin cells, impair the body’s natural defense mechanisms against cancer, and increase the risk of developing abnormal growths.
Smoking also impacts the prognosis of melanoma, the most aggressive type of skin cancer. Smokers with melanoma tend to have reduced survival rates compared to non-smokers. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can further compromise the immune system and impair the body’s ability to combat cancer cells, leading to a poorer prognosis and outcomes.
The connection between smoking and skin cancer risk can be attributed to the toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke. These chemicals, including carcinogens and toxic metals, can cause genetic mutations, oxidative stress, and DNA damage, all of which contribute to the development of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Risk and Smoking
| Type of Skin Cancer | Increased Risk in Smokers |
|---|---|
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Higher incidence |
| Melanoma | Reduced survival rates |
It’s important to note that the harmful effects of smoking on the skin are not limited to skin cancer alone. Smoking can also contribute to skin aging, collagen damage, loss of elasticity, and other skin conditions. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer and improve overall skin health.
Other Skin Conditions Linked to Smoking

Smoking has been associated with various skin conditions in addition to skin aging and cancer. Research suggests that smoking can increase the risk of developing psoriasis, worsen the severity of eczema, and aggravate acne. The harmful effects of smoking on the skin can trigger or exacerbate these conditions.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. Studies have found that smokers are more likely to develop psoriasis and experience more severe symptoms compared to non-smokers. Smoking can worsen the inflammation associated with psoriasis and interfere with the effectiveness of treatment.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common inflammatory skin condition. Smoking has been shown to worsen the severity and persistence of eczema symptoms, including itching, redness, and dryness. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function, leading to increased skin sensitivity and irritation.
Acne, a common skin condition characterized by pimples and blemishes, can also be influenced by smoking. Studies have found a link between smoking and acne, with smokers having a higher prevalence and more severe forms of acne compared to non-smokers. Smoking can exacerbate inflammation, increase sebum production, and impair the skin’s healing processes, contributing to the development and persistence of acne.
Furthermore, smoking has been associated with certain types of vasculitis, such as Buerger’s disease and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV). Vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels that can affect the skin and other organs. Smoking is considered a major risk factor for these types of vasculitis, and quitting smoking is an essential step in managing and preventing further disease progression.
Smoking has also been identified as a risk factor for various autoimmune disorders, including lupus. Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Smoking can dysregulate the immune system, leading to increased inflammation, tissue damage, and autoimmune responses. Additionally, smoking can affect hair health, contributing to thinning and hair loss.
It is crucial to understand the link between smoking and these skin conditions in order to make informed decisions about smoking cessation and skin health.
| Skin Condition | Effect of Smoking |
|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Increased risk and severity |
| Eczema | Worsened symptoms and persistence |
| Acne | Higher prevalence and severity |
| Vasculitis | Increased risk and disease progression |
| Autoimmune disorders | Higher risk and worsened symptoms |
Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Skin Health
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for skin health:
- Improved skin color: After quitting smoking, the complexion can become brighter and more radiant as the skin receives better oxygenation and nutrient delivery.
- Enhanced skin hydration: Smoking can dehydrate the skin, making it appear dull and dry. When you quit smoking, your skin can regain its natural moisture, leaving it soft and supple.
- Restored skin elasticity: Studies have shown that quitting smoking can restore the body’s collagen production and repair mechanisms. This can lead to improved skin elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
By quitting smoking, you can also reverse some of the damage caused by smoking and reduce the risk of further skin aging, wrinkles, and skin-related diseases. Collagen supplementation and the use of topical retinoids and antioxidants can further help improve the appearance of the skin after quitting smoking.
Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions you can make for your skin. Not only will it improve your overall health, but it will also give your skin a chance to heal and regain its natural beauty.
The Impact of Smoking on Overall Health

Smoking not only affects the skin but also has a detrimental impact on overall health. It is a leading cause of preventable diseases and is associated with various health conditions that significantly compromise one’s well-being.
Health Conditions Linked to Smoking:
- Heart disease: Smoking increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Lung disease: Smoking is a primary cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and increases the risk of developing lung cancer.
- Osteoporosis: Smokers have a higher risk of developing osteoporosis, leading to increased bone fragility and susceptibility to fractures.
- Fertility problems: Smoking can impair fertility in both men and women, making it more challenging to conceive.
- Complications during pregnancy: Pregnant women who smoke are at a higher risk of experiencing complications such as ectopic pregnancy, premature birth, and low birth weight.
- Early menopause: Smoking can accelerate the onset of menopause in women, which may lead to various hormonal and health changes.
- Oral cancer: Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing oral cavity and throat cancers.
- Increased mortality rates: Smokers have a significantly higher risk of premature death compared to non-smokers.
Benefits of Quitting Smoking:
“Quitting smoking has numerous health benefits and can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions.”
Quitting smoking is a crucial step towards a healthier life. By quitting, individuals can reduce their risk of developing heart disease, lung disease, osteoporosis, and other smoking-related health conditions. Quitting smoking also improves overall lung function, enhances fertility, reduces the risk of complications during pregnancy, and increases life expectancy. The sooner one quits smoking, the sooner they can start reaping the benefits of a smoke-free life.
Conclusion
Smoking has a profound negative impact on skin elasticity, leading to skin aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of firmness. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage collagen and elastin, impair skin repair mechanisms, reduce blood flow, and weaken the immune system.
However, there is hope for healthier skin. Quitting smoking can significantly improve skin health and reverse some of the damage caused by smoking. By quitting smoking, individuals can restore their skin’s natural elasticity, improve skin tone and texture, and reduce the risk of skin-related diseases.
If you are a smoker concerned about the effects of smoking on your skin, consider taking the brave step towards quitting. Not only will you experience the myriad of health benefits associated with smoking cessation, but you will also enjoy the positive transformation of your skin. Remember, it’s never too late to take control of your skin health and embrace a healthier, more vibrant appearance.
FAQ
How does smoking affect skin elasticity?
Smoking can have a significant impact on skin elasticity. It can degrade collagen and elastin fibers, impair their formation and reduce their levels in the skin. Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of vital nutrients and oxygen, leading to premature skin aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of elasticity.
What are the effects of smoking on collagen and elastin?
Smoking can degrade collagen fibers, impair elastin formation, and reduce the levels of these proteins in the skin. This can result in the appearance of wrinkles, sagging skin, and a loss of elasticity.
How does smoking contribute to skin aging?
Smoking accelerates the aging process, including the aging of the skin. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can cause oxidative stress, damage DNA, and impair the body’s natural repair mechanisms. This can lead to the breakdown of collagen and elastin, the formation of wrinkles, age spots, and a loss of skin elasticity.
What is the impact of smoking on skin tone and pigmentation?
Smoking can lead to dull, pale skin with reduced blood flow. It promotes the formation of melanocytes, resulting in uneven skin pigmentation, age spots, and dark spots.
How does smoking contribute to skin sagging?
Smoking weakens the connective tissues in the skin, including collagen and elastin fibers. This leads to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness, causing the skin to sag and droop.
Does smoking affect wound healing?
Yes, smoking can impair the body’s natural healing processes, leading to delayed wound healing. The chemicals in cigarette smoke reduce blood flow, oxygen, and nutrient delivery to the skin, which can result in slower wound healing, increased risk of complications, poor scar formation, and susceptibility to infections.
Does smoking increase the risk of skin infections?
Yes, smoking weakens the immune system and inhibits the body’s ability to fight off infections. The chemicals in cigarette smoke suppress immune cell activity and dysregulate immune responses, increasing the risk of skin infections and worsening the outcomes of infectious diseases.
Is smoking linked to skin cancer?
Yes, studies have found a higher incidence of squamous cell carcinoma among smokers. Smokers with melanoma also tend to have reduced survival rates. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage DNA, impair the body’s defense mechanisms against cancer, and increase the risk of malignant cell growth in the skin.
Are there any other skin conditions linked to smoking?
Yes, smoking has been associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis, worsening the severity of eczema, aggravating acne, and certain types of vasculitis. Smoking is also a risk factor for autoimmune disorders like lupus and can affect hair health, leading to thinning and hair loss.
What are the benefits of quitting smoking for skin health?
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for skin health. Improvements in skin color, hydration, and elasticity can be observed within a few weeks to months. Quitting smoking restores collagen production and repair mechanisms, leading to brighter, smoother skin, and reduces the risk of further skin aging, wrinkles, and skin-related diseases.
Does smoking have other impacts on overall health?
Yes, smoking is a leading cause of preventable diseases and is associated with various health conditions such as heart disease, lung disease, osteoporosis, fertility problems, complications during pregnancy, early menopause, oral cancer, and increased mortality rates.
What is the conclusion regarding smoking and skin elasticity?
Smoking has a detrimental impact on skin elasticity, leading to skin aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of firmness. Quitting smoking can significantly improve skin health and reverse some of the damage caused by smoking, restoring the skin’s natural elasticity, improving skin tone and texture, and reducing the risk of skin-related diseases.




