Did you know that smoking is not only harmful to your internal organs but also has a significant impact on the largest organ of your body – the skin? Research has revealed shocking statistics about the detrimental effects of smoking on the skin, linking it to accelerated aging and a range of skin-related issues.
Smoking is associated with poor wound healing, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, oral cancer, acne, psoriasis, and even hair loss. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that tobacco smoke extract impairs collagen production, leading to abnormal elastosis material production and increased signs of premature aging. Moreover, reactive oxygen species play a role in tobacco smoke-induced skin aging.
These findings show the tremendous impact that smoking has on the skin, making it crucial for smokers to understand and address this issue. Join me as we delve deeper into the effects of smoking on the skin and discover how quitting smoking can have a positive impact on skin health and appearance.
Key Takeaways
- Smoking accelerates skin aging and is associated with a range of skin issues such as acne, psoriasis, and hair loss.
- Tobacco smoke extract impairs collagen production and increases signs of premature aging.
- Reactive oxygen species contribute to tobacco smoke-induced skin aging.
- Quitting smoking can lead to improvements in skin health and appearance.
- Understanding the negative effects of smoking on the skin can serve as motivation to quit.
Smoking and Skin Appearance
Smoking has a significant impact on the appearance of the skin, causing premature wrinkling and giving individuals a gray and aged appearance. This habit also contributes to increased skin sagging, particularly in the cheeks, resulting in a gaunt and hollow look. Studies have found that middle-aged smokers often exhibit as many wrinkles as non-smokers who are 60 years or older. In fact, smoking 30 cigarettes a day can accelerate skin aging by an additional 14 years by the age of 70.
When it comes to premature aging, smoking takes its toll on the skin. The effects of smoking on the skin’s appearance are more apparent when comparing smokers and non-smokers of the same age. The damaging substances in cigarettes, such as nicotine and carbon monoxide, restrict blood flow to the skin, depriving it of oxygen and essential nutrients.
The result? Skin cells become damaged, collagen and elastin fibers break down, and the skin loses its firmness and elasticity. This leads to the formation of wrinkles, the development of sagging skin, and a hollow look in the cheeks. Smokers often have deeper wrinkles around their mouths and eyes, making them look older than their actual age. In fact, studies have shown that middle-aged smokers’ skin can look as weathered as non-smokers who are 60 years old or older.
“Smoking not only affects the skin’s health but also dramatically ages its appearance. The chemicals in cigarette smoke accelerate the breakdown of collagen and elastin, increasing the likelihood of premature wrinkles and sagging. Over time, smoking can transform a young, vibrant face into a gaunt, aged visage.”
— Dr. Anna Johnson, Dermatologist
Furthermore, smoking also impairs the skin’s ability to heal itself. Wounds take longer to heal in smokers, and they are more prone to infections and scarring. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes hinder the production of collagen, a protein necessary for wound healing and maintaining skin elasticity.
The effects of smoking on the skin’s appearance are not limited to the face. The skin on other parts of the body, such as the hands and arms, can also exhibit signs of premature aging due to smoking. The harmful effects of smoking on the skin are reversible, but it requires quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
The Devastating Effects of Smoking on the Skin
Smoking deteriorates the skin’s appearance in multiple ways:
- Premature wrinkling: Smoking accelerates collagen and elastin breakdown, leading to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Aged appearance: The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can create a gray and dull complexion, making individuals look older than they actually are.
- Skin sagging: Smoking weakens collagen and elastin fibers, causing the skin to lose its firmness and elasticity, resulting in sagging skin.
- Gaunt look: The lack of blood flow to the skin, combined with collagen depletion, can result in a gaunt and hollow appearance, especially in the cheeks.
Understanding the detrimental effects smoking has on the skin’s appearance should serve as a strong motivator for smokers to quit this harmful habit and embark on a journey towards healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
Image: Smoking can have a significant impact on the appearance of the skin, causing premature aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a hollow look in the cheeks.
Collagen Depletion and Skin Elasticity

One of the main mechanisms through which smoking affects the skin is the depletion of collagen, a protein responsible for skin elasticity. Smoking increases the production of an enzyme that breaks down collagen, leading to reduced elasticity and increased signs of aging such as sagging and wrinkling.
Epidemiological studies have shown that smoking leads to an imbalance between collagen biosynthesis and degradation in the dermal connective tissue, resulting in accelerated skin aging. The effects of tobacco smoke on collagen can be observed through characteristic skin wrinkling patterns, such as lines around the mouth and crow’s feet around the eyes.
Smoking not only depletes collagen but also disrupts the delicate balance between collagen production and breakdown. This imbalance leads to a significant loss of elasticity in the skin, making it prone to sagging and wrinkles.
Impact of Smoking on Skin Elasticity
Research has shown that smoking significantly impairs skin elasticity, making it more susceptible to the effects of gravity and environmental factors. Reduced skin elasticity caused by smoking can result in deep wrinkles, loose and sagging skin, and a lack of firmness and resilience.
In addition to collagen depletion, smoking also affects the production of elastin, another vital protein that helps maintain skin elasticity. Elastin fibers provide the skin with its ability to snap back into place and retain its shape. Smoking disrupts the synthesis and maintenance of elastin, leading to the breakdown of these fibers and further compromising skin elasticity.
Tobacco Smoke and Collagen Breakdown
“The damaging effects of tobacco smoke on collagen are well-documented in scientific studies. Smoking not only accelerates collagen breakdown but also impairs its production, resulting in thinner and weaker skin.”
In a study published in the journal Dermato-Endocrinology, researchers found that tobacco smoke contains various chemicals that directly contribute to collagen degradation. These chemicals increase the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes responsible for breaking down collagen in the skin. This process further damages the collagen matrix and compromises the skin’s structural integrity.
| Effects of Smoking on Skin Elasticity | Impact |
|---|---|
| Collagen depletion | Increased sagging and wrinkling |
| Elastin degradation | Loss of skin elasticity and resilience |
| Matrix metalloproteinase activation | Collagen breakdown and impaired synthesis |
To sum up, smoking plays a significant role in collagen depletion and the subsequent loss of skin elasticity. The damaging effects of tobacco smoke on collagen lead to increased sagging, wrinkling, and other visible signs of premature aging. Quitting smoking is essential not only for overall health but also for preserving the youthfulness and elasticity of the skin.
Vascular effects and Dryness
Smoking has significant vascular effects on the skin, which can contribute to various skin issues. One of the key effects of smoking is vasoconstriction, a process in which the blood vessels narrow. This vasoconstriction reduces blood supply and oxygen delivery to the skin, leading to a range of negative consequences.
The reduced blood supply to the skin caused by smoking results in diminished nutrients reaching the skin cells. As a result, the skin becomes dry and lacks the healthy glow associated with good circulation. Dryness is a common symptom among smokers, and it can lead to a dull and washed-out appearance.
“Smoker’s face,” characterized by premature wrinkling, lack of vibrancy, and an aged appearance, can be attributed to the vascular effects of smoking.
Furthermore, smoking can cause direct burns to the facial skin due to the heat generated by the cigarette. These burns can result in facial scarring, redness, and irritation. The combination of vasoconstriction, reduced blood supply, skin dryness, and facial burns contributes to the development of what is commonly referred to as “smoker’s face.”
The image below depicts the impact of smoking on skin vascular effects:
Delayed Wound Healing and Psoriasis
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the healing process of wounds, both from injuries and surgical procedures.
When smokers sustain wounds, they face an increased risk of complications such as infections, poor adhesion of skin grafts or flaps, and the formation of blood clots. These adverse effects can be attributed to the reduced supply of blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the skin caused by smoking. Additionally, smoking decreases the production of collagen, a vital protein responsible for wound healing and skin health.
Studies have indicated that smokers are two to three times more likely to suffer from psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Psoriasis can significantly impact individuals’ appearance and overall well-being, causing discomfort and self-consciousness.
To ensure optimal healing and reduce the risk of complications, it is essential for smokers to quit smoking before undergoing surgical procedures or when recovering from injuries. By eliminating the factors that impede wound healing, smokers can significantly improve their chances of a successful recovery.
Smoking Cessation and Improved Skin
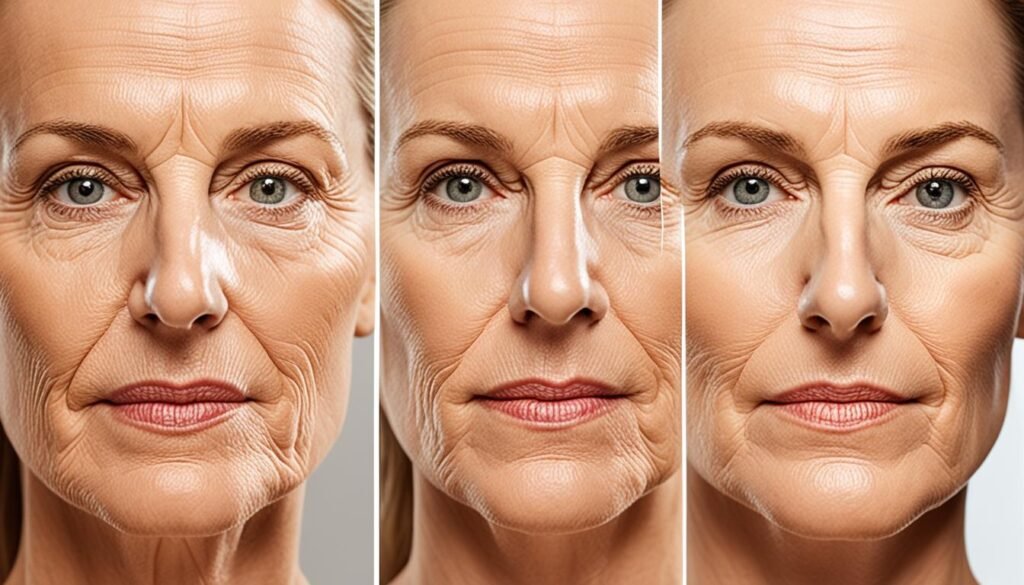
The benefits of quitting smoking extend far beyond improving one’s overall health. The positive effects of smoking cessation on skin color and appearance are remarkable. Research has demonstrated that smokers who quit experience significant improvements in their skin’s color and texture.
Quitting smoking promotes healthier and more vibrant skin, effectively reducing the signs of aging caused by smoking. By quitting, individuals give their skin the chance to recover and rejuvenate, resulting in a fresher and more youthful appearance.
Furthermore, studies have shown that quitting smoking can decrease the risk of developing skin cancer and other dermatological conditions associated with smoking. By eliminating this harmful habit, individuals protect their skin from further damage and improve their long-term skin health.
Risks Reduced by Smoking Cessation:
- Reduced risk of premature skin aging
- Lower likelihood of skin cancer
- Avoidance of skin damage and discoloration caused by smoking
Overall, the decision to quit smoking has numerous benefits for both overall health and skin appearance. By prioritizing smoking cessation, individuals can achieve remarkable improvements in skin color, texture, and overall youthfulness.
| Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Skin | Positive Effects of Smoking Cessation on Skin Appearance |
|---|---|
| Improved skin color | Reduced signs of aging |
| Enhanced skin texture | Fresher and more vibrant appearance |
| Decreased risk of skin cancer | Improved long-term skin health |
Methods to Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is a challenging but highly beneficial endeavor for both maintaining a youthful appearance and safeguarding overall health. Fortunately, there are numerous methods and treatments available to aid in smoking cessation. These options can provide the necessary support and tools to overcome nicotine addiction and achieve long-term success.
Medication:
Two commonly prescribed medications for smoking cessation are Zyban and Chantix. Zyban, also known as bupropion, is an antidepressant that can help reduce nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Chantix, or varenicline, works by blocking nicotine receptors in the brain, reducing the pleasurable effects of smoking. These medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Nicotine Replacement Products:
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) provides a safer alternative to cigarettes by supplying controlled doses of nicotine without the harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke. Popular NRT options include nicotine patches, gums, inhalers, e-cigarettes (vapes), and smokeless tobacco. These products help satisfy nicotine cravings while gradually reducing dependence. It is essential to follow the recommended usage guidelines for each NRT product.
“Quitting smoking is easy. I’ve done it a thousand times.” – Mark Twain
Behavioral Support:
Combining behavioral support with medication or NRT can significantly increase the chances of successful smoking cessation. Behavioral support can take the form of individual counseling, group therapy, or support groups. These approaches provide valuable guidance, encouragement, and strategies to cope with triggers and cravings. Counseling sessions may also address underlying psychological factors associated with smoking.
Alternative Therapies:
Some individuals find success in quitting smoking through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, hypnosis, or mindfulness techniques. While the effectiveness of these approaches in smoking cessation varies, they offer additional options for those seeking unconventional methods of support.
Personal Willpower and Commitment:
Regardless of the method chosen, quitting smoking requires personal willpower and commitment. It is important to acknowledge that smoking cessation aids are not a guaranteed solution on their own. However, with the right mindset and determination, they can provide invaluable assistance in overcoming nicotine addiction.
By quitting smoking, individuals can experience numerous benefits, including improved skin health, reduced risk of chronic illnesses, and enhanced overall well-being. The journey to a smoke-free life begins with a commitment to quit and the utilization of available resources and support.
Importance of Avoiding Smoking
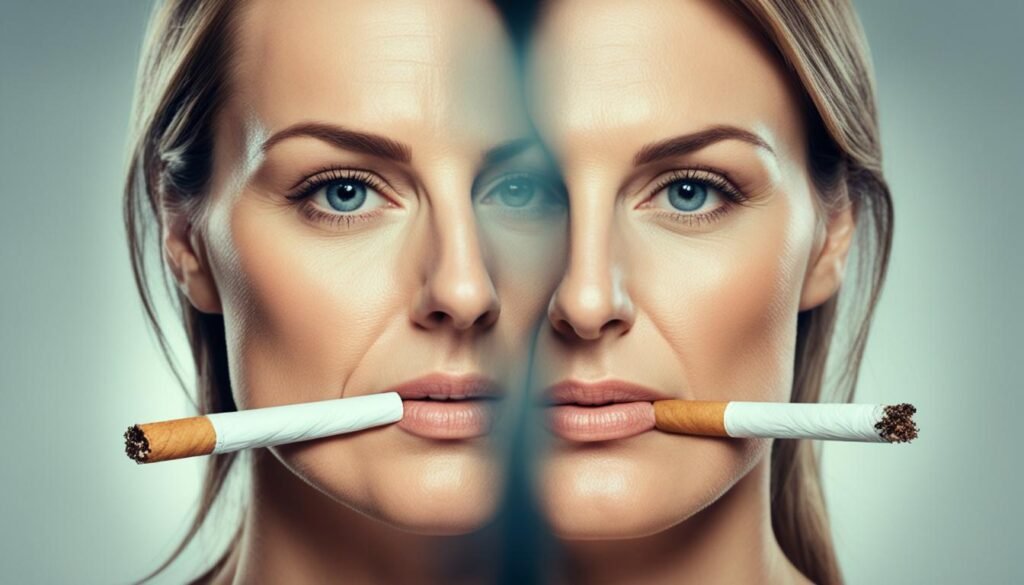

While the effects of smoking on the skin may not be as life-threatening as lung cancer or heart disease, they are certainly undesirable. Quitting smoking is crucial for avoiding premature skin aging and maintaining a healthy and attractive appearance.
Smoking is known to have negative effects on the skin, contributing to wrinkles, sagging, and a dull complexion. The toxins in cigarette smoke can damage collagen and elastin, leading to decreased skin elasticity and firmness. Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and oxygen, resulting in dryness and a lackluster appearance.
Avoiding smoking has numerous benefits for preserving skin health. It improves wound healing, as smoking hampers the body’s ability to repair damaged skin and can lead to complications after surgeries. In addition, smokers are at higher risk of developing psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can affect the appearance and overall well-being.
By prioritizing the avoidance of smoking, individuals can preserve their skin health and enhance their overall well-being.
Reasons to Quit Smoking:
- Preserve youthful and vibrant skin
- Enhance wound healing and recovery after surgeries
- Reduce the risk of psoriasis and other dermatological conditions
- Improve overall health and well-being
“The decision to quit smoking is an investment in your skin’s health and appearance. By quitting, you can reverse some of the negative effects of smoking and maintain a healthier, more youthful complexion.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson
It’s important to remember that quitting smoking is not a simple task, but there are various resources and support available to help you on your journey. From nicotine replacement therapies to counseling programs, explore the options that best suit your needs and seek professional guidance if necessary.
| Negative Effects of Smoking on Skin | Reasons to Quit Smoking | Preserving Skin Health |
|---|---|---|
| Premature skin aging | Preserve youthful and vibrant skin | Enhance wound healing |
| Wrinkles and sagging | Reduce the risk of psoriasis | Improve overall health and well-being |
| Dull complexion | ||
| Dry and dehydrated skin |
Remember, your skin deserves to be healthy and radiant. Quit smoking today and prioritize the preservation of your skin’s natural beauty.
Conclusion
Smoking is a harmful habit that greatly accelerates the aging process of the skin. The detrimental effects of smoking on skin appearance and overall health are undeniable. By depleting collagen, reducing elasticity, and affecting blood flow to the skin, smoking leads to premature aging, wrinkles, sagging, and a dull complexion.
However, there is hope for smokers who want to improve their skin and overall well-being. Quitting smoking offers numerous benefits, including the restoration of skin color, texture, and elasticity. By prioritizing skin health and quitting smoking, individuals can reverse some of the damage caused by tobacco and reduce the risk of developing serious dermatological conditions associated with smoking.
Preserving skin health is of utmost importance as healthy skin not only enhances physical appearance but also serves as a vital barrier against environmental toxins and infections. By quitting smoking, individuals can take a proactive step towards maintaining skin health, preventing premature aging, and safeguarding their overall well-being.
FAQ
How does smoking accelerate skin aging?
Smoking accelerates skin aging through various mechanisms, including collagen depletion, reduced elasticity, and vascular effects. Tobacco smoke extract impairs collagen production, increases the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), and leads to abnormal elastosis material production. Reactive oxygen species also play a role in tobacco smoke-induced premature skin aging.
What effects does smoking have on skin appearance?
Smoking has a significant impact on the appearance of the skin. It causes premature wrinkling, gives the skin a gray and aged appearance, and contributes to increased skin sagging, particularly in the cheeks. Middle-aged smokers often exhibit as many wrinkles as non-smokers who are 60 years or older. Smoking 30 cigarettes a day can accelerate skin aging by an additional 14 years by the age of 70.
How does smoking affect collagen and skin elasticity?
Smoking depletes collagen, a protein responsible for skin elasticity, by increasing the production of an enzyme that breaks down collagen. This leads to reduced elasticity and increased signs of aging such as sagging and wrinkling. Epidemiological studies have shown that smoking leads to an imbalance between collagen biosynthesis and degradation in the dermal connective tissue, resulting in accelerated skin aging.
What are the vascular effects of smoking on the skin?
Smoking causes vasoconstriction, leading to reduced blood supply and oxygen to the skin. This results in diminished nutrients reaching the skin, causing dryness and a washed-out appearance. Furthermore, the heat of the cigarette can cause direct burns to the face. These factors contribute to the development of “smoker’s face,” characterized by premature wrinkling, a lack of vibrancy, and an aged appearance.
How does smoking affect wound healing and psoriasis?
Smoking delays the healing of wounds, both from injuries and surgical procedures, due to reduced blood supply, oxygen, and nutrients to the skin. Smokers have an increased risk of infection, poor adhesion of skin grafts or flaps, and blood clots. Additionally, smokers are two to three times more likely to suffer from psoriasis, an inflammatory skin condition that can have a negative impact on appearance and overall well-being.
Does quitting smoking improve the appearance of the skin?
Yes, research has shown that smokers who quit experience improvements in skin color and texture. The skin becomes healthier and more vibrant, reducing the signs of aging caused by smoking. Quitting smoking can also decrease the risk of skin cancer and other dermatological conditions associated with smoking.
What methods are available to quit smoking?
Numerous methods and treatments are available to aid in smoking cessation, including medications like Zyban and Chantix, nicotine replacement products such as patches, gums, inhalers, e-cigarettes, and smokeless tobacco. Quitting smoking requires willpower and commitment from the individual.
Why is it important to avoid smoking?
Smoking has significant negative effects on the skin, causing premature aging, poor wound healing, and an increased risk of various dermatological conditions. Quitting smoking is essential for maintaining a youthful appearance, protecting overall health, and preserving skin health.
What are the benefits of quitting smoking?
Quitting smoking not only improves the appearance of the skin but also reduces the risk of developing serious dermatological conditions associated with smoking. It also improves wound healing, reduces the risk of psoriasis, and protects against various other smoking-related health issues.




