Did you know that smoking can have long-lasting effects on the aging process of your skin? It’s not just a short-term impact, but a chronic issue that can affect your skin for years to come. The nicotine found in tobacco smoke can be absorbed by your skin, leading to premature aging, delayed wound healing, and increased risk of infections. Smoking can also contribute to the development of various skin diseases such as psoriasis, acne, eczema, and even skin cancer.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking can have long-lasting effects on the aging process of the skin.
- Nicotine found in tobacco smoke can lead to premature skin aging, delayed wound healing, and increased risk of infections.
- Smoking can contribute to the development of skin diseases such as psoriasis, acne, eczema, and skin cancer.
- Quitting smoking can help reverse some of the damage and improve skin health.
- It’s important to prioritize quitting smoking to protect your skin and reduce the risk of various diseases and health complications.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging
Smoking has detrimental effects on the aging process of the skin. It can hinder the production of collagen and elastin, which are crucial for maintaining the plumpness and firmness of the skin. The nicotine present in tobacco smoke promotes cell death in skin cells, damages blood vessels within the skin, and reduces blood flow. Consequently, smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles, uneven skin tone, sagging skin, and delayed wound healing. These effects can be noticeable as early as a person’s 20s or 30s.
The harmful impact of smoking on skin aging can be attributed to multiple factors. Firstly, smoking disrupts collagen synthesis and accelerates its breakdown, resulting in a decrease in collagen levels over time. Collagen is responsible for maintaining the skin’s structure and elasticity, so its reduction leads to sagging and wrinkling. Secondly, nicotine-induced vasoconstriction narrows blood vessels, impeding nutrient and oxygen supply to the skin. This compromises skin health and contributes to diminished collagen production. Additionally, smoking triggers the generation of free radicals, causing oxidative stress and accelerating skin aging processes.
Furthermore, studies have shown that the harmful effects of smoking on the skin are not solely limited to external signs of aging. Smoking can impact the skin’s internal structure, impairing its natural barrier function and making it more susceptible to external irritants and infections. This can lead to a higher risk of various skin conditions and diseases.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging:
- Impaired collagen and elastin synthesis
- Decreased blood flow and nutrient supply
- Promotion of cell death in skin cells
- Increased oxidative stress and free radical damage
- Formation of wrinkles and sagging skin
- Uneven skin tone and texture
- Delayed wound healing
- Heightened risk of skin diseases and infections
It is important to note that the effects of smoking on skin aging can vary among individuals and may depend on factors such as smoking duration, intensity, and genetic predisposition. However, the detrimental impact of smoking on the skin is well-established, and quitting smoking can significantly improve skin health and slow down the aging process.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Appearance

Smoking can have a significant impact on the appearance of the skin, leading to various visible effects. One of the most noticeable effects is the formation of wrinkles, especially in the middle to lower third of the face. Smoking is considered an independent risk factor for wrinkle development, and the habit can accelerate the aging process of the skin.
Another effect of smoking on skin appearance is the promotion of age spots and dark spots. This is due to increased melanocyte formation, which can lead to hyperpigmentation in certain areas of the skin. Age spots, also known as liver spots, are small, flat, and dark areas that usually appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms.
Additionally, the skin of smokers may appear dull, pale, and have a wasted appearance. The toxic chemicals present in cigarette smoke can disrupt the production of collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining firm and vibrant skin. The narrowing of blood vessels caused by smoking can also reduce blood flow to the skin, resulting in uneven skin pigmentation and a sagging appearance.
Overall, smoking can have detrimental effects on the skin’s appearance, leading to the formation of wrinkles, age spots, and a dull complexion. Quitting smoking is crucial not only for improving overall health but also for enhancing the vitality and youthfulness of the skin.
Smoking and Skin Health
Smoking can have a significant impact on skin health. The toxic substances present in tobacco smoke can impair the skin’s natural ability to repair itself, resulting in slower wound healing and an increased risk of infections. Moreover, smoking weakens the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to fight off pathogens and maintain healthy skin.
Quitting smoking, on the other hand, offers numerous benefits for the skin. When individuals stop smoking, they experience improved wound healing, a reduced risk of infections, and overall healthier skin. By quitting, individuals can give their skin a chance to recover and regain its natural vitality.
The Effect of Smoking on Skin Healing
The toxic substances found in tobacco smoke, such as nicotine and carbon monoxide, restrict blood flow to the skin’s surface. This reduction in blood flow deprives the skin of essential nutrients and oxygen, making it more challenging for wounds to heal effectively. As a result, individuals who smoke may experience delayed wound healing and an increased likelihood of complications arising from cuts, burns, or surgical procedures.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve wound healing as the body’s blood flow returns to normal, providing essential nutrients and oxygen to the skin.
In addition to impaired wound healing, smoking compromises the skin’s structural integrity. The chemicals in tobacco smoke break down collagen and elastin fibers, which are responsible for maintaining the skin’s elasticity and firmness. Consequently, smoking can lead to the development of sagging skin and wrinkles, accelerating the signs of aging.
By quitting smoking, individuals can allow the skin to repair itself and restore its natural collagen and elastin production, resulting in a more youthful and rejuvenated appearance.
The Impact of Smoking on Skin Infections
Smoking weakens the immune system, making it less effective at protecting the body from infections. The harmful components of tobacco smoke impair the function of immune cells, compromising their ability to fight off bacteria and viruses that may affect the skin.
As a result, smokers are more susceptible to various skin infections, including bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. These infections can manifest as acne, cellulitis, folliculitis, and herpes outbreaks.
Quitting smoking improves immune function, reducing the risk of skin infections and promoting better overall skin health.
Furthermore, smoking suppresses the body’s natural defense mechanisms against harmful environmental factors, such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV radiation damages the skin and increases the risk of skin cancer. When combined with smoking, the risk of developing skin cancer becomes even greater.
By quitting smoking and adopting sun protection measures, individuals can reduce their risk of skin cancer and promote better long-term skin health.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Skin Health
Quitting smoking offers a range of benefits for the skin. Within just a few weeks of quitting, individuals may notice improvements in their skin’s appearance and overall health.
- Improved wound healing: With better blood flow and increased oxygen supply, wounds heal faster, reducing the risk of complications.
- Reduction in skin inflammation: Smoking-induced inflammation decreases, resulting in reduced redness, irritation, and swelling.
- Enhanced skin tone: Quitting smoking can lead to a more even skin tone and a healthier complexion.
- Younger-looking skin: By allowing the body to repair itself, quitting smoking can minimize the appearance of wrinkles and reverse some of the signs of aging.
- Healthy glow: Improved circulation and oxygenation contribute to a radiant and healthy complexion.
Quitting smoking is a fundamental step towards improving skin health and maintaining a youthful appearance. It is never too late to quit smoking and experience the positive effects on both the skin and overall well-being.
Smoking and Skin Diseases

Smoking is not only harmful to your overall health but can also have detrimental effects on your skin. Research has shown that smoking is associated with an increased risk and severity of various skin diseases.
Psoriasis
Smoking has been found to worsen symptoms of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches. Regular smoking can trigger flare-ups and reduce the effectiveness of treatments for psoriasis.
Eczema
Smoking has also been linked to an increased risk of eczema, including atopic dermatitis and hand eczema. These conditions cause inflammation, itching, and dryness of the skin. Smoking can exacerbate these symptoms and make them more difficult to manage.
Acne
Although the exact relationship between smoking and acne is not fully understood, studies suggest that smoking may be associated with acne development, particularly in adult women. Smoking can contribute to the clogging of pores and inflammation, leading to acne breakouts.
Rare Skin Conditions
Smoking has also been associated with the development of rare skin conditions such as palmoplantar pustulosis. This condition causes pustules to form on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Smoking can increase the severity and duration of symptoms in individuals with this condition.
To improve the symptoms and severity of these skin diseases, quitting smoking is highly recommended. By quitting smoking, you can reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation, and allow your skin to heal more effectively. Quitting smoking is an important step towards achieving healthier skin.
| Skin Disease | Effect of Smoking |
|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Worsens symptoms and reduces treatment effectiveness |
| Eczema | Increases risk and exacerbates symptoms |
| Acne | Possible association, contributes to breakouts |
| Rare Skin Conditions | Increases severity and duration of symptoms |
Smoking and Skin Cancer
Smoking is a well-established risk factor for the development of skin cancer. When it comes to squamous cell carcinoma, both current and heavy smokers have a higher risk compared to nonsmokers.1 Additionally, smokers with melanoma, a potentially deadly form of skin cancer, have been found to have a lower survival rate than nonsmokers.2
The toxic substances present in tobacco smoke can directly damage the DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of genetic mutations that can lead to cancer.1 Furthermore, smoking weakens the immune system, impairing its ability to detect and destroy cancer cells, thus allowing them to multiply and form tumors.1
Given these risks, it is crucial for individuals to quit smoking in order to reduce their chances of developing skin cancer. By quitting, the body can begin to repair the damage caused by smoking and regain its ability to fight against cancer cells. Moreover, quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of skin cancer but also improves overall health and well-being.
“The association between smoking and skin cancer is undeniable. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke not only damage the DNA in our skin cells but also weaken our body’s natural defense mechanisms against cancer. Quitting smoking is a crucial step in protecting ourselves from skin cancer and improving our chances of survival.” – Dr. Emily Roberts, Dermatologist.
By quitting smoking, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing skin cancer and improve their overall health. It is never too late to quit smoking and every effort made towards cessation can have a positive impact on skin cancer prevention.
References:
- Mohr SB, Garland CF, Gorham ED, et al. “Could cigarette smoking & #8220;light up& #8221; your melanoma risk?” Melanoma Res. 2018; 28(3):267-268.
- Erovic BM, Crobach S, Pammer J. “Perioperative complications associated with smoking in patients undergoing head and neck free flap reconstruction.” Microsurgery. 2014; 34(5):339-343.
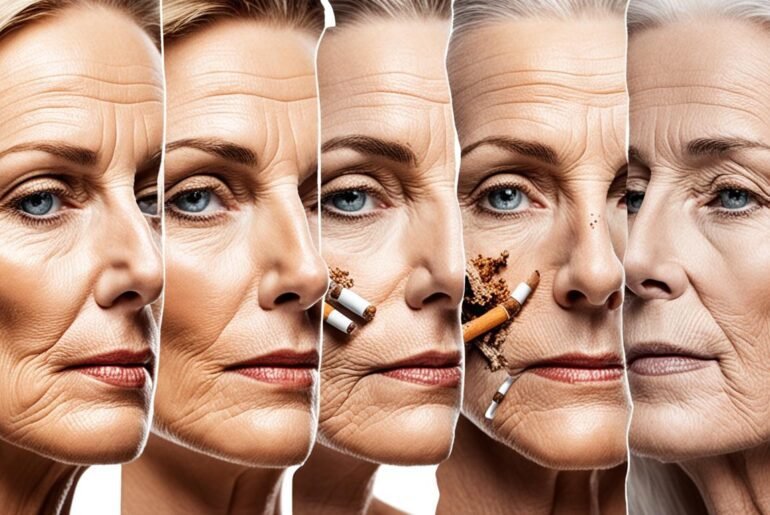
Smoking and Skin Aging Timeline

The effects of smoking on skin aging can begin to be detected as early as a person’s 20s or 30s. Smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots. The damage caused by smoking can be long-lasting, but some improvements can be seen after quitting.
Within a month of quitting smoking, age spots and redness may start to decrease. This is because quitting smoking allows the skin to recover from the harmful effects of tobacco smoke, leading to a reduction in pigmentation issues.
Changes in skin color can start to reverse within 4-12 weeks after quitting smoking. The circulation in the skin improves, resulting in a healthier complexion. Quitting smoking also helps improve hydration levels, elasticity, and collagen density in the skin, leading to a more youthful appearance.
Overall, quitting smoking can have a significant positive impact on the aging process of the skin. It is never too late to quit smoking and start taking better care of your skin. The sooner you quit, the sooner you can start to see improvements in your skin’s health and appearance.
Key Points:
- Smoking accelerates skin aging in your 20s or 30s.
- Age spots and redness can decrease within a month of quitting smoking.
- Improvements in skin color can be seen within 4-12 weeks after quitting.
- Quitting smoking improves hydration, elasticity, and collagen density.
The Effects of Quitting Smoking on Skin Aging
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for skin aging. When you quit smoking, your body has the opportunity to restore collagen production, which leads to brighter and smoother skin. Additionally, improved circulation and reduced carbon exposure contribute to overall healthier skin.
“Quitting smoking can lead to visible improvements in skin health and appearance.”
Research has shown that quitting smoking can have a remarkable impact on the aging process. In a study, participants who quit smoking experienced an average reduction of 13 years in their biological age, highlighting the rejuvenating effects of quitting.
One of the key benefits of quitting smoking is the improved ability of the body to repair and renew skin cells. This leads to noticeable improvements in skin health and appearance over time.

Smoking can have several other effects on the skin and overall health. In addition to its impact on skin aging, smoking is associated with various skin-related issues, oral health problems, and changes in body shape.
Smoking Effects on Oral Health
Smoking can negatively affect oral health, leading to various issues such as stained teeth and periodontitis. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke can discolor teeth, resulting in a yellow or brown appearance. Furthermore, smoking weakens the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to gum disease and tooth loss caused by periodontitis.
Smoking Impact on Body Shape
Smoking has been linked to changes in body shape, including a higher waist-to-hip ratio. Smokers often have a larger waist circumference compared to their hip circumference, which is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. This change in body shape may be attributed to various factors, including the effects of smoking on metabolism and the distribution of body fat.
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Wound Healing | Smoking impairs the skin’s ability to heal wounds, leading to slower healing times and an increased risk of infections. |
| Stained Teeth | The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause teeth discoloration, resulting in stained and yellowed teeth. |
| Periodontitis | Smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of gum disease, which can eventually lead to tooth loss. |
| Changes in Body Shape | Smokers tend to have a higher waist-to-hip ratio, which is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. |
It is important to note that the negative effects of smoking on oral health and body shape can be mitigated by quitting smoking. Quitting smoking not only improves skin health but also reduces the risk of various diseases and promotes overall well-being.
By understanding the detrimental effects of smoking on the skin, oral health, and body shape, individuals can make informed decisions to prioritize their well-being and embrace a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
Smoking has significant and long-lasting effects on skin aging and overall skin health. The habit of smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles, sagging skin, age spots, and an increased risk of skin diseases and cancer. The detrimental impact of smoking on the skin is undeniable.
However, there is good news for those who want to improve their skin health. Quitting smoking can help reverse some of the damage caused by smoking and improve skin health. By quitting smoking, individuals can give their skin a chance to recover and repair itself.
It is important to recognize that the benefits of quitting smoking extend beyond skin health. Quitting smoking contributes to overall well-being and reduces the risk of various diseases and health complications. Prioritizing quitting smoking not only protects the skin but also improves the overall quality of life.
FAQ
How long does smoking affect skin aging?
Smoking can have long-lasting effects on the aging process of the skin.
What are the effects of smoking on skin aging?
Smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots. It can impair collagen production, damage blood vessels, and reduce blood flow to the skin.
How does smoking affect skin appearance?
Smoking can promote the formation of wrinkles, age spots, and a dull, pale appearance. It can also result in uneven skin pigmentation and a sagging skin.
What is the impact of smoking on skin health?
Smoking can impair the skin’s ability to repair itself, leading to slower wound healing and an increased risk of infections. It weakens the immune system and contributes to the development of various skin diseases.
Smoking can worsen symptoms of psoriasis, increase the risk of eczema, and contribute to the development of acne and rare skin conditions.
What is the association between smoking and skin cancer?
Smoking is a risk factor for the development of skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma. Current and heavy smokers have a higher risk, and smokers with melanoma have a lower survival rate compared to nonsmokers.
What is the timeline of skin aging due to smoking?
The effects of smoking on skin aging can start to be detected as early as a person’s 20s or 30s. However, some improvements can be seen after quitting, such as a decrease in age spots and changes in skin color.
What are the effects of quitting smoking on skin aging?
Quitting smoking can lead to visible improvements in skin health, including improved hydration, elasticity, and collagen density. The body’s ability to repair and renew skin cells improves after quitting.
Smoking is associated with poor wound healing, oral health problems, and changes in body shape. It can stain teeth, contribute to periodontitis, and increase the waist-to-hip ratio.
What is the conclusion on smoking effects on skin aging?
Smoking has significant and long-lasting effects on skin aging and overall skin health. However, quitting smoking can help improve skin health and reverse some of the damage caused by smoking.




