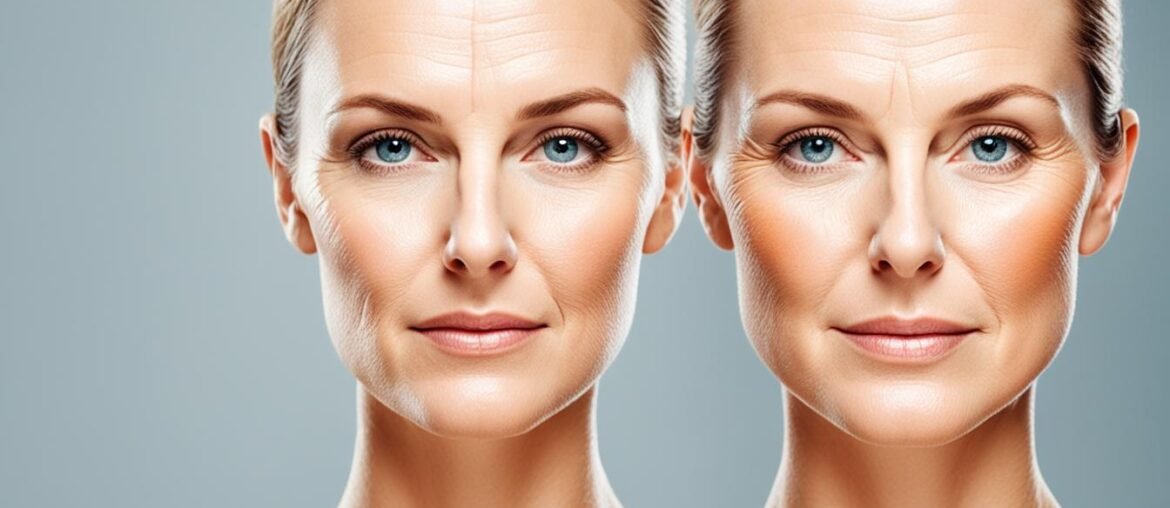
Did you know that alcohol consumption can expedite the skin aging process? It’s not just about causing temporary dehydration or lack of sleep – the effects of alcohol on the skin go much deeper. Studies have revealed that alcohol can lead to premature aging, causing skin wrinkles, reducing skin elasticity, and contributing to collagen degradation.
So, if you’ve been enjoying your alcoholic beverages without considering the impact on your skin, it’s time to take a closer look. Understanding the relationship between alcohol and skin aging is essential for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin. Let’s dive into the details and discover how alcohol affects your skin.
Key Takeaways:
- Alcohol accelerates the aging process by causing skin wrinkles, reducing skin elasticity, and contributing to collagen degradation.
- The effects of alcohol on the skin are more pronounced in heavy drinkers.
- Understanding the relationship between alcohol and skin aging is crucial for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin.
- Limiting alcohol consumption is essential for minimizing the detrimental effects on skin health.
- Stay tuned to discover the specific impacts of alcohol on facial aging, telomere length, dehydration, vital organs, cognitive function, immune system, and more!
The Link Between Alcohol and Facial Aging
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wcj8jWt1HNI
Research has found a clear association between alcohol consumption and facial aging. A large multinational study involving women from different countries showed that smoking and alcohol consumption have different effects on various facial characteristics related to aging. Smoking was found to be associated with increased severity of forehead lines, crow’s feet, glabellar lines, under-eye puffiness, and other signs of aging. Heavy alcohol use, defined as consuming at least eight drinks per week, was linked to increased upper facial lines, under-eye puffiness, oral commissures, midface volume loss, and visible blood vessels. These findings highlight the specific impact of alcohol on facial aging and provide insight into the mechanism by which alcohol contributes to premature skin aging.
Facial lines and wrinkles are common signs of facial skin aging. While genetics and other environmental factors play a role, lifestyle choices such as tobacco use and alcohol consumption can significantly impact the aging process. The specific effects may vary, but both tobacco and alcohol have been linked to the development of facial lines and other visible signs of aging.
Smoking and heavy alcohol use have different effects on facial characteristics related to aging. Smoking is associated with increased severity of forehead lines, crow’s feet, glabellar lines, under-eye puffiness, and other signs of aging. Heavy alcohol use is linked to increased upper facial lines, under-eye puffiness, oral commissures, midface volume loss, and visible blood vessels.
These findings provide valuable information for individuals who are concerned about facial skin aging. By understanding the impact of tobacco use and alcohol consumption, individuals can make informed decisions to promote healthier, more youthful-looking skin. It is important to note that addressing these lifestyle factors alone may not reverse all signs of aging, but they can help minimize additional damage and maintain a more youthful appearance.
The Role of Volume-Related Aging
Volume-related aging is another important aspect to consider when it comes to facial aging. As we age, we naturally experience a loss of volume in certain areas of the face. This loss of volume can contribute to a sunken, hollow appearance. Alcohol consumption can exacerbate volume-related aging, leading to a more aged and tired look.
| Tobacco Use | Impact on Facial Aging |
|---|---|
| Increased severity of forehead lines | Smoking |
| Crow’s feet | Smoking |
| Glabellar lines | Smoking |
| Under-eye puffiness | Smoking |
| Visible blood vessels | Heavy alcohol use |
| Increased upper facial lines | Heavy alcohol use |
| Oral commissures | Heavy alcohol use |
| Midface volume loss | Heavy alcohol use |
| Visible blood vessels |
Alcohol’s Effect on Telomere Length

Recent genetic-based analysis has revealed fascinating insights into how alcohol consumption accelerates the aging process. Researchers have observed a direct impact of alcohol on telomere length, a crucial factor in cellular aging. Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that safeguard our chromosomes from damage. They act as protective caps, preventing DNA from unravelling or fusing with neighboring chromosomes.
Shortening of telomeres is regarded as a significant indicator of biological aging. As telomeres shrink, cell division becomes limited, giving rise to age-related diseases and a higher susceptibility to various health issues. One study in particular delved into the relationship between alcohol and telomere length, shedding light on the detrimental effects of excessive alcohol intake.
The study findings revealed:
- Higher alcohol consumption was associated with shorter telomere length.
- Shorter telomeres indicate accelerated cellular aging.
- Accelerated cellular aging contributes to a higher risk of age-related diseases.
This genetic-based analysis provides further evidence of the adverse impacts of alcohol on the aging process. By directly affecting telomere length, alcohol accelerates aging at a cellular level, making individuals more vulnerable to age-related ailments and conditions.
| Telomere Length | Alcohol Intake |
|---|---|
| Shortened | Higher |
| Longer | Lower |
This table illustrates the correlation between telomere length and alcohol intake. It clearly demonstrates that higher alcohol consumption is associated with shortened telomeres, indicative of accelerated cellular aging. Conversely, individuals with lower alcohol intake have longer telomeres, suggesting a slower rate of cellular aging.
Dehydration and Skin Aging
Alcohol consumption can contribute to dehydration, which can accelerate skin aging. As individuals age, the body naturally loses water and becomes more prone to dehydration. Alcohol exacerbates this issue by further dehydrating the body. Dehydration can lead to skin dryness, making the skin more susceptible to wrinkles and other signs of aging. To maintain optimal skin health and delay the aging process, it is important to limit alcohol consumption and ensure adequate hydration.
When you consume alcohol, it acts as a diuretic, causing increased urine production and fluid loss from the body. This dehydrating effect can be seen through symptoms such as dry mouth, increased thirst, and dark-colored urine. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to chronic dehydration, which can have long-term detrimental effects on the skin.
Dehydration affects both intrinsic and extrinsic aging. Intrinsic aging is the natural aging process that occurs internally and is influenced by factors such as genetics. Extrinsic aging, on the other hand, is the result of external factors such as sun exposure and lifestyle choices like smoking and alcohol consumption. Dehydration accelerates both types of aging, leading to the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and a lack of skin elasticity.
Dehydration can lead to skin dryness, making the skin more susceptible to wrinkles and other signs of aging. To maintain optimal skin health and delay the aging process, it is important to limit alcohol consumption and ensure adequate hydration.
One way to combat the dehydrating effects of alcohol is to drink plenty of water before, during, and after consuming alcoholic beverages. Staying hydrated not only helps the body maintain its fluid balance but also promotes healthy skin.
Another effective way to keep the skin hydrated is to use moisturizers that contain hydrating ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and glycerin. These ingredients attract and retain moisture in the skin, helping to combat dryness and maintain a youthful appearance.
Key takeaways:
- Alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration, which accelerates skin aging.
- Dehydration affects both intrinsic and extrinsic aging, leading to fine lines, wrinkles, and decreased skin elasticity.
- Limiting alcohol consumption and ensuring adequate hydration are essential for maintaining optimal skin health.
- Drinking plenty of water and using hydrating moisturizers can help combat the dehydrating effects of alcohol.
Impact on Vital Organs and Cognitive Function

Heavy alcohol consumption can have significant consequences for our vital organs, particularly the liver and kidneys. Long-term alcohol abuse can result in liver damage, including the development of cirrhosis. The liver plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body and metabolizing alcohol. Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption puts a strain on the liver, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. This can have serious implications for overall health and well-being.
The kidneys, responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, are also adversely affected by alcohol. Alcohol abuse can impair kidney function and increase the risk of developing conditions such as alcoholic kidney disease. This condition reduces the kidneys’ ability to properly filter waste, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body. It’s essential to prioritize kidney health by consuming alcohol in moderation and staying properly hydrated.
Furthermore, long-term alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on brain cells, leading to alcohol-related brain damage (ARBD) and certain types of dementia. ARBD can manifest as cognitive impairments, lack of judgment, and trouble staying focused. It is a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life and independence. Protecting brain health requires mindful alcohol consumption and adopting a balanced lifestyle.
| Vital Organs | Effects of Alcohol |
|---|---|
| Liver | Liver damage, including cirrhosis |
| Kidneys | Impaired kidney function, increased risk of kidney disease |
| Brain | Damage to brain cells, alcohol-related brain damage, increased risk of dementia |
It is important to be aware of the impact excessive alcohol consumption can have on these vital organs and cognitive function. By practicing moderation and making informed choices, we can preserve the health of our liver, kidneys, and brain.
Effects on Immune System and Disease Susceptibility
Alcohol consumption can have significant effects on the immune system, increasing the susceptibility to life-threatening illnesses such as tuberculosis and pneumonia. The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body from infections and diseases, but excessive alcohol intake can weaken its defense mechanisms.
When the immune system is compromised, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections. Tuberculosis, a bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, can be particularly dangerous in individuals with a weakened immune system. Alcohol interferes with the immune system’s ability to fight off the tuberculosis bacteria, increasing the risk of developing severe forms of the disease.
Pneumonia, another serious respiratory infection, is also more likely to occur in individuals with compromised immune systems. Alcohol consumption can impair the function of immune cells responsible for fighting off pathogens, making it easier for pneumonia-causing bacteria or viruses to invade the lungs.
According to a study published in the journal Alcohol Research & Health, chronic alcohol abuse can lead to decreased immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections and impairing the body’s ability to heal.
In addition to tuberculosis and pneumonia, alcohol abuse is strongly associated with the development of alcoholic liver disease. This condition occurs when excessive alcohol consumption damages the liver, leading to inflammation, scarring, and impaired liver function. The immune system plays a significant role in the development of alcoholic liver disease.
Research suggests that the immune system’s response to alcohol-induced liver damage can contribute to the progression of alcoholic liver disease. The immune system may mistakenly attack healthy liver cells, triggering inflammation that further damages liver tissue. This immune-mediated response can contribute to the development of cirrhosis and other complications associated with alcoholic liver disease.
Reducing alcohol consumption is critical for maintaining a strong immune system and reducing the risk of developing diseases associated with alcohol abuse.
Moderation and Potential Benefits

While excessive alcohol consumption has detrimental effects, moderate alcohol intake, particularly in the form of red wine, has been associated with potential health benefits. Red wine contains antioxidants called polyphenols that can help improve cholesterol levels and protect blood vessels.
Several studies have shown that moderate red wine consumption, approximately one glass per day, can have positive effects on heart health. Red wine antioxidants have been found to raise the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly known as “good” cholesterol, while reducing the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. This beneficial effect on cholesterol levels can contribute to a healthier heart and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, the polyphenols in red wine have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can help protect blood vessels from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of developing heart disease. They can also improve blood flow and prevent the formation of blood clots, further promoting heart health.
Benefits of Red Wine Antioxidants:
- Improvement of cholesterol levels
- Protection of blood vessels from oxidative stress
- Promotion of healthy blood flow
- Reduction in the risk of cardiovascular diseases
It is important to note that the potential benefits of red wine are only associated with moderate consumption. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to a higher risk of various health problems, including liver disease, obesity, and addiction. Therefore, moderation is key when it comes to alcohol consumption.
As with any dietary or lifestyle change, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant modifications to your alcohol consumption habits.
While red wine can have potential health benefits, it is essential to consider individual circumstances and preferences. For individuals who do not consume alcohol or have a history of alcohol-related issues, it is not recommended to start solely for the potential health benefits. There are alternative ways to improve heart health, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress levels.
Overall, moderate consumption of red wine, with its red wine antioxidants, can be enjoyed as part of a healthy lifestyle. However, it is important to prioritize overall well-being and make informed choices based on individual health circumstances.
Increased Sensitivity and Aggravation of Medical Conditions

Alcohol consumption can have serious implications for individuals with certain medical conditions commonly associated with aging. Heavy drinkers are at a higher risk of developing various health issues, including:
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Ulcers
- Cancer
- Memory loss
- Mood disorders
When combined with regular alcohol consumption, these conditions can become more severe and challenging to manage. Minimizing alcohol intake is crucial for maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of developing or worsening these medical conditions.
| Medical Condition | Impact of Alcohol Consumption |
|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Alcohol interferes with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, thereby weakening bones and increasing the risk of fractures. |
| Diabetes | Alcohol can disrupt blood sugar levels and impair insulin sensitivity, making it more challenging to manage diabetes. |
| High blood pressure | Excessive alcohol consumption raises blood pressure and can increase the risk of hypertension. |
| Stroke | Alcohol consumption can lead to an increased risk of stroke by promoting high blood pressure and clot formation. |
| Ulcers | Alcohol irritates the lining of the stomach and intestines, exacerbating ulcers and delaying healing. |
| Cancer | Alcohol consumption contributes to the development of certain types of cancer, including breast, liver, and esophageal cancer. |
| Memory loss | Long-term alcohol abuse can impair memory and cognitive function, leading to memory loss and difficulties with learning and decision-making. |
| Mood disorders | Alcohol can disrupt brain chemistry and exacerbate mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. |
Understanding the potential consequences of alcohol consumption on these medical conditions is vital for individuals looking to mitigate risks and preserve their well-being.
Interaction with Medications
Alcohol can have detrimental effects when combined with certain medications, especially among older individuals. It can interfere with the normal metabolism of drugs in the body, leading to potential side effects and reduced effectiveness of the medication. Alcohol and medication interactions can be dangerous and should be taken seriously.
| Medication Class | Possible Interaction with Alcohol |
|---|---|
| Pain Medications (e.g., opioids) | Mixing alcohol with pain medications can depress the central nervous system, leading to increased drowsiness, dizziness, and respiratory problems. It can be life-threatening and should be avoided. |
| Sleeping Pills (e.g., benzodiazepines) | Combining alcohol with sleeping pills can intensify the sedative effects, resulting in excessive drowsiness, impaired coordination, and difficulty awakening. It can increase the risk of accidents and respiratory problems. |
| Anxiety Drugs (e.g., benzodiazepines) | Alcohol and anxiety medications have similar sedative effects. Mixing them can cause extreme drowsiness, confusion, and impaired judgment. It can lead to severe respiratory problems and increase the risk of accidents. |
It is crucial to consult healthcare professionals and carefully read medication labels to understand potential interactions with alcohol. Your healthcare provider can provide personalized advice on whether it is safe to consume alcohol while taking specific medications. Never hesitate to reach out for guidance and clarification regarding alcohol and medication interactions.
An important step in promoting your well-being and ensuring the safe and effective use of medications is to limit alcohol consumption, particularly if you are on prescription drugs. By doing so, you can avoid potential risks and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Through various studies and research, it is clear that alcohol consumption can significantly contribute to the skin aging process, resulting in premature signs of aging such as wrinkles and reduced skin elasticity. Moreover, heavy alcohol use can have detrimental effects on vital organs, cognitive function, and overall health. However, it is important to note that moderate alcohol intake, particularly in the form of red wine, may offer potential health benefits when consumed in moderation.
Understanding the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption and the importance of moderation is crucial for maintaining optimal skin health and overall well-being. By being mindful of alcohol’s impact on the skin and other bodily systems, individuals can make informed choices to reduce their alcohol consumption and prioritize their health.
While enjoying an occasional glass of red wine in moderation may provide some potential health benefits, it is vital to remember that moderation is key. Consuming alcohol in excess can outweigh any potential benefits and lead to numerous health problems. To maintain youthful and healthy-looking skin, it is recommended to limit alcohol intake and adopt a lifestyle that prioritizes hydration, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a skincare routine that targets specific skin concerns.
FAQ
How does alcohol consumption accelerate the skin aging process?
Alcohol consumption can cause skin wrinkles, reduce skin elasticity, and contribute to collagen degradation, leading to premature aging.
What is the link between alcohol and facial aging?
Studies have shown that heavy alcohol use is associated with increased upper facial lines, under-eye puffiness, oral commissures, midface volume loss, and visible blood vessels.
How does alcohol affect telomere length?
Research has found that higher alcohol intake is associated with shorter telomere length, indicating accelerated aging at the cellular level.
Does alcohol consumption contribute to dehydration and skin aging?
Yes, alcohol can worsen dehydration, leading to skin dryness and increased vulnerability to wrinkles and other signs of aging.
What impact does alcohol have on vital organs and cognitive function?
Heavy alcohol consumption can result in liver damage, impaired kidney function, alcohol-related brain damage, and increased risk of dementia.
How does alcohol affect the immune system and disease susceptibility?
Alcohol can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses such as tuberculosis and pneumonia.
Is there any potential health benefit to moderate alcohol consumption?
Moderate red wine consumption, in particular, has been associated with positive effects on heart health due to its antioxidant content.
Does alcohol aggravate certain medical conditions?
Yes, heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk and severity of conditions such as osteoporosis, diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, ulcers, cancer, memory loss, and mood disorders.
Can alcohol interact negatively with medications?
Yes, alcohol can affect the metabolism of various medications, leading to potential side effects and reduced efficacy.
What is the conclusion regarding alcohol and skin aging?
Alcohol consumption can accelerate the skin aging process, but moderate intake, particularly in the form of red wine, may have potential health benefits when consumed in moderation.