Did you know that smoking cigarettes can accelerate the aging process of your skin, causing wrinkles and skin damage? It’s not just your lungs that are at risk; the harmful effects of tobacco smoke extend to your skin as well.
Smoking releases thousands of toxic chemicals into your body, and when these substances come into contact with your skin, they can wreak havoc on its health and appearance. From premature aging to increased risk of skin diseases, tobacco smoke takes a toll on your skin like you never imagined.
But don’t worry, there are ways to combat the skin aging effects of tobacco smoke and restore the health and vitality of your skin. In this article, I will explore the various ways smoking affects your skin, the related skin conditions, and the benefits of quitting smoking for skin health.
Key Takeaways:
- Smoking cigarettes accelerates skin aging and can lead to wrinkles and skin damage.
- Tobacco smoke contains harmful substances that can damage collagen and elastin fibers, leading to sagging skin and loss of skin tone.
- Smoking is associated with an increased risk of skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
- The restricted blood flow caused by smoking can result in dull skin and uneven skin tone.
- Quitting smoking can significantly improve skin health and reduce the signs of aging.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Aging
Smoking has a profound impact on the aging process of the skin, affecting its firmness, elasticity, and overall health. The harmful substances present in tobacco smoke directly disrupt the synthesis of collagen and elastin, two essential components for maintaining youthful skin. Collagen provides structural support to the skin, keeping it firm and smooth, while elastin enables the skin to stretch and bounce back.
When exposed to tobacco smoke, the collagen and elastin fibers become damaged, leading to sagging skin, loss of elasticity, and the formation of wrinkles. The repetitive facial movements associated with smoking, such as pursing the lips and squinting, further enhance the development of wrinkles, especially around the mouth and eyes.
Furthermore, smoking has a detrimental effect on the immune system in the skin, impairing its ability to fight off infections and delaying the wound healing process. This weakened immune response leaves the skin vulnerable to pathogens, increasing the risk of skin infections and other skin conditions.
Smoking compromises the synthesis of collagen and elastin, resulting in sagging skin, wrinkles, and reduced skin elasticity.
Additionally, smoking leads to a decrease in blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential oxygen and nutrients. This restricted blood flow contributes to a dull, lackluster complexion and uneven skin tone. Over time, smoking can also contribute to the development of age spots and dark spots due to increased melanocyte activity in the skin.
The Damaging Effects of Smoking on the Skin:
- Disruption of collagen and elastin synthesis
- Sagging skin and loss of elasticity
- Formation of wrinkles, particularly around the mouth and eyes
- Weakened immune system in the skin, increasing susceptibility to infections
- Delayed wound healing
- Restricted blood flow, resulting in a dull complexion and uneven skin tone
- Risk of age spots and dark spots
It is evident that smoking has a profound impact on the aging process of the skin. The damage to collagen and elastin fibers, the compromised immune response, and the restricted blood flow all contribute to premature aging, wrinkles, and various skin conditions. Quitting smoking is crucial for minimizing these effects and restoring the health and vitality of the skin.
Skin Conditions Related to Smoking

Smoking is known to be associated with a range of skin conditions. Let’s take a closer look at some of the effects of smoking on skin health.
Smoking and Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. Studies have shown that smoking can worsen the symptoms of psoriasis and reduce the effectiveness of treatments. Quitting smoking is an important step in managing psoriasis and improving overall skin health.
Smoking and Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Smoking has been found to be associated with a higher prevalence of eczema and can exacerbate the symptoms. If you have eczema, quitting smoking may help alleviate your symptoms and improve the condition of your skin.
Smoking and Acne
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. While the exact relationship between smoking and acne is still being studied, research suggests that smoking may contribute to the development and severity of acne. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on acne-prone skin.
Tobacco-Induced Vasculitis
Vasculitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the blood vessels, leading to symptoms such as palmoplantar pustulosis and telangiectasia. Smoking can cause tobacco-induced vasculitis, which is characterized by inflammation and damage to the blood vessels. Quitting smoking is essential for managing vasculitis and promoting the healing of blood vessels.
In summary, smoking can have detrimental effects on the skin, contributing to the development and aggravation of various skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, acne, and tobacco-induced vasculitis. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for your overall health but also plays a significant role in improving the condition of your skin.
Skin Tone and Pigmentation Changes from Smoking
Smoking can have significant effects on skin tone and pigmentation, resulting in a dull and uneven complexion. The harmful substances in tobacco smoke restrict blood flow to the skin, depriving it of oxygen and essential nutrients. As a result, smokers may experience pale or bluish-gray skin, lacking the vibrant glow associated with healthy skin.
Moreover, smoking can contribute to the development of age spots and dark spots on the skin. Increased melanocyte formation, triggered by the harmful substances in tobacco smoke, can lead to the appearance of these pigmented areas, further adding to the unevenness of the skin tone.
Addressing these skin tone and pigmentation changes requires a multi-faceted approach. Quitting smoking is the first and most crucial step towards improving the overall health and vitality of the skin. By eliminating exposure to harmful substances, the skin has the opportunity to repair and rejuvenate itself.
In addition to smoking cessation, it’s essential to establish a comprehensive skincare routine that focuses on brightening and evening out the skin tone. This may include the use of products containing ingredients like vitamin C, retinol, and niacinamide, which are known for their skin-brightening and pigmentation-reducing properties. Regular exfoliation can also help remove dead skin cells and reveal a more radiant complexion.
| Potential Skin Effects from Smoking | Skin Tone and Pigmentation Changes |
|---|---|
| Pale or bluish-gray skin | Uneven complexion |
| Age spots and dark spots | Irregular pigmentation |
By quitting smoking and incorporating effective skincare practices, individuals can restore their skin’s natural radiance and diminish pigmentation issues. It’s never too late to take steps towards a healthier, more balanced complexion.
Wrinkles and Tobacco-Induced Aging
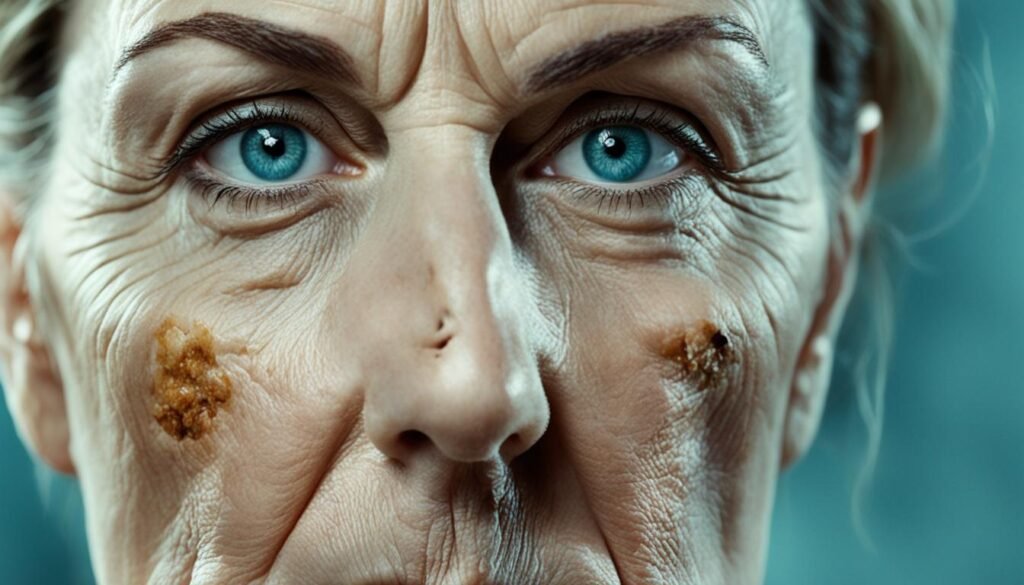
Smoking is a significant risk factor for the formation of wrinkles, especially in certain areas of the face like the forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper lip. The repetitive motion of smoking, such as pursing the lips and squinting, can enhance wrinkle formation in these areas. The impact of smoking on blood vessels and collagen fibers also contributes to the development of wrinkles.
When you smoke, you engage in repetitive facial movements like pursing your lips and squinting your eyes. These actions, combined with the harmful effects of tobacco on collagen and elastin fibers, can lead to the formation of wrinkles. Collagen and elastin are essential proteins for maintaining the elasticity and firmness of the skin. Smoking damages these fibers, resulting in sagging skin and the appearance of wrinkles.
The nasolabial folds, also known as smile lines, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of smoking. These folds occur from the side of the nose to the corners of the mouth and can deepen over time due to smoking. The repetitive motions and the impact of smoking on collagen production contribute to the formation of deep nasolabial folds and wrinkles in this area.
“Smoking cigarettes accelerates the aging process, causing wrinkles, lines, and sagging skin. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin, making the skin lose its firmness and elasticity.”
The upper lip is another area prone to wrinkles from smoking. The act of inhaling cigarettes involves repetitive muscle movements that can lead to the development of vertical lip lines. These lines can become more pronounced over time, resulting in lip wrinkles.
To visualize the effect of smoking on wrinkles, refer to the image below:
As seen in the image, smoking can contribute to the formation of deep forehead lines, nasolabial folds, and wrinkles around the lips. These visible signs of aging are not only undesirable but also indicative of the damage smoking can cause to the skin.
To prevent and reduce wrinkles caused by smoking, it is essential to quit smoking and adopt a comprehensive skincare routine. By quitting smoking, you can halt further damage to collagen and elastin fibers, allowing the skin to start the healing process and regain some of its elasticity. Additionally, incorporating anti-aging skincare products and practices, such as moisturizing, using retinoids, and protecting the skin from sun damage, can help minimize the appearance of wrinkles and restore a more youthful complexion.
Effect of Smoking on Wound Healing
Smoking has a significant negative impact on the wound healing process. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds effectively, leading to delayed healing and an increased risk of postsurgical complications.
One of the ways smoking affects wound healing is by impairing the inflammatory response. Inflammation is a crucial stage of the healing process that helps remove debris, fight off bacteria, and promote the growth of new tissue. However, smoking can disrupt this inflammatory response, making it less efficient and hindering the healing process.
Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the skin and tissues, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the wound site. By decreasing blood flow, smoking deprives the wound of the necessary resources for optimal healing, further delaying the process.
Moreover, smoking compromises the immune function, leaving the body more susceptible to infections. The immune system plays a vital role in fighting off bacteria and other pathogens that can hinder wound healing. When compromised by smoking, the immune system becomes less effective at combating these potential threats, resulting in a higher risk of infections and potential complications.
Quitting smoking before undergoing surgery can significantly reduce these risks. By quitting, individuals allow their bodies to restore the natural healing process, improve blood flow, and enhance immune function. It is essential to inform healthcare providers about smoking habits to ensure appropriate measures are taken to optimize wound healing outcomes.
“Smoking impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds effectively, leading to delayed wound healing and an increased risk of postsurgical complications.”
It is clear that smoking has a notable negative impact on wound healing. By understanding these effects, individuals can make informed decisions about quitting smoking and take proactive steps to enhance their overall health and well-being.
References:
- Johnson, T. S., O’Brien, D. P., Austin, M., & Platt, P. (2016). Effect of smoking on wound healing after foot and ankle surgery. Foot & ankle international, 37(4), 373-377.
- Stojadinovic, O., Lee, B., Vouthounis, C., Vukelic, S., Pastar, I., Blumenberg, M., & Tomic-Canic, M. (2008). Novel genes underlying diabetic foot ulceration: insights from tissue based studies. Cell and tissue research, 332(3), 451-465.
- Myers, R. A. (2004). Smoking: effects on wound healing. Clinics in plastic surgery, 31(1), 11-16.
Skin Cancer and Smoking

Smoking is a known risk factor for skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Current and heavy smokers have a higher likelihood of developing these types of skin cancer compared to nonsmokers. Additionally, smokers with melanoma tend to have a lower survival rate.
The harmful substances present in tobacco smoke can contribute to the development and progression of skin cancer. These substances can damage the DNA within skin cells, leading to genetic mutations that can trigger the formation of cancerous cells. Moreover, smoking can impair the immune response of the skin, making it more difficult for the body to detect and eliminate cancer cells.
“Smoking increases the risk of developing skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.”
To further understand the correlation between smoking and skin cancer, refer to the following table:
| Type of Skin Cancer | Risk in Smokers |
|---|---|
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Higher likelihood |
| Melanoma | Increased risk, lower survival rate |
It is important for smokers to be aware of the elevated risk of skin cancer associated with tobacco use. Taking steps to quit smoking or avoid exposure to tobacco smoke can greatly reduce the chances of developing these types of cancer and improve overall skin health.
Effects of Smoking on Hair and Nail Health

Smoking doesn’t just harm your lungs and skin – it can also have negative effects on the health of your hair and nails. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can impact the growth and strength of both hair and nails, leading to various issues.
Smoking and Hair Loss
One of the most prominent effects of smoking on hair health is hair loss. Research has shown that smoking is associated with an increased risk of hair loss, particularly in men. Smoking can accelerate the rate of hair thinning and even lead to premature balding. The harmful toxins in cigarette smoke can damage hair follicles and interfere with the normal hair growth cycle.
Smoking and Stained Nails
Smoking can also cause staining of the nails, leaving them discolored and brittle. The tar and nicotine present in cigarettes can seep into the nails, resulting in unsightly yellow or brown stains. These stains can be difficult to remove and may require professional intervention to restore the nails to their natural color.
To improve hair and nail health, it is essential to quit smoking. By quitting, you can help reverse some of the damage caused by smoking and give your hair and nails a chance to recover. Combining smoking cessation with a healthy diet and lifestyle can further support the growth and strength of your hair and nails.
In the next section, we will explore the effects of smoking on oral health and the importance of quitting smoking for maintaining a healthy mouth.
Smoking and Oral Health
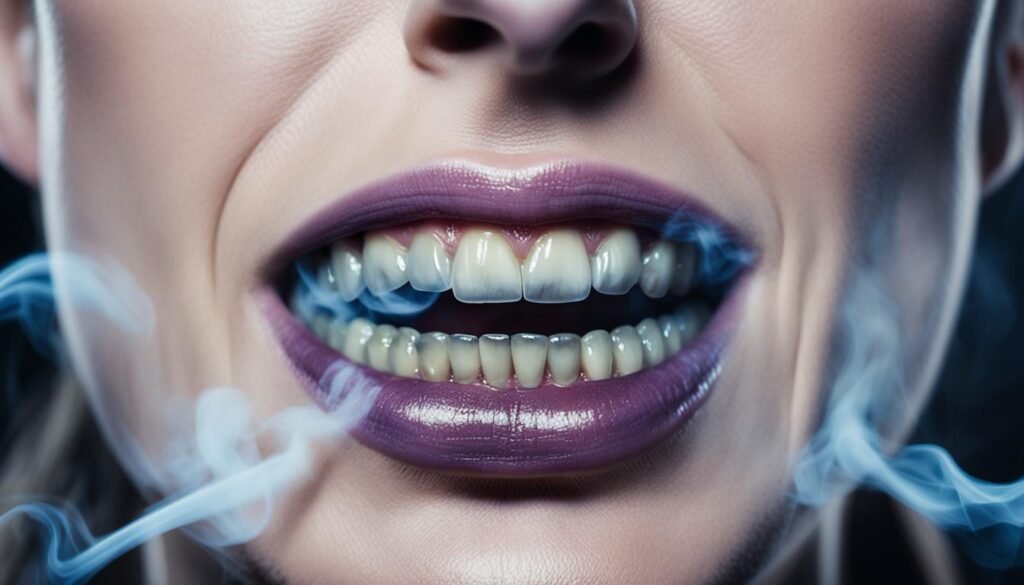

Smoking has detrimental effects on oral health. The habit of smoking increases the risk of developing gum disease, a condition that can lead to serious oral health problems if left untreated. It can also cause persistent bad breath, commonly referred to as halitosis. Smokers are more likely to experience tooth loss compared to nonsmokers. In fact, studies show that smokers are twice as likely to lose their teeth than those who do not smoke.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. It starts with the build-up of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth. Smoking weakens the body’s immune system, making it more difficult to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums. This makes smokers more susceptible to gum disease and its progression. If left untreated, gum disease can result in tooth loss and even affect overall health, as it has been linked to various systemic conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Furthermore, smoking can cause persistent bad breath. The chemicals found in tobacco products, such as nicotine and tar, can linger in the mouth and throat, causing an unpleasant odor. This can lead to social discomfort and self-consciousness.
Tooth loss is another significant concern for smokers. The harmful substances in tobacco smoke and the reduced blood flow to the gums can affect the bone structure supporting the teeth. Over time, this can lead to tooth loss and a compromised smile. Smokers are also more likely to experience difficulties with dental implant procedures, as smoking impairs the healing process.
Quitting smoking is crucial for improving oral health and reducing the risks associated with smoking. By quitting, individuals can lower their risk of developing gum disease, bad breath, and tooth loss. It is also important to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. Addressing smoking as part of overall lifestyle changes can lead to a healthier mouth and smile.
Effects of Smoking on Oral Health
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Gum Disease | Increased risk of developing periodontal disease |
| Bad Breath | Persistent halitosis due to chemicals in tobacco smoke |
| Tooth Loss | Higher likelihood of experiencing tooth loss |
| Compromised Healing | Impaired healing process after dental procedures |
Quitting smoking is essential for improving oral health and reducing the risks associated with smoking. It is never too late to make a positive change and prioritize your oral health. Your dentist can provide guidance and support to help you quit smoking and maintain good oral hygiene habits. By quitting smoking, you can protect your smile and overall well-being.
Smoking and Overall Health Implications

Smoking has far-reaching consequences for overall health, with various detrimental effects on the body. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke can lead to numerous health conditions and increase the risk of developing serious diseases. Let’s explore some of the major health implications associated with smoking:
Osteoporosis
Smoking is linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. The harmful substances in tobacco smoke interfere with the absorption of calcium, reducing bone density and making them more prone to fractures.
Heart Disease
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage blood vessels, increase blood pressure, and contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries. This can lead to conditions like coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and stroke.
Fertility and Menopause
Smoking can have detrimental effects on fertility in both men and women. In women, smoking can lead to fertility problems, hormonal imbalances, and early menopause. In men, smoking can lower sperm count and reduce sperm quality, affecting fertility outcomes.
Cancer Risk
Smoking is a leading cause of various types of cancer, including lung, throat, mouth, esophageal, pancreatic, bladder, kidney, and cervical cancers. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage DNA and increase the risk of abnormal cell growth and tumor formation.
Lung Health
Smoking is extremely harmful to lung health. It is the primary cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive lung condition that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Smoking also increases the risk of respiratory infections, exacerbates asthma symptoms, and damages lung tissue.
Here is a table summarizing the health implications of smoking:
| Health Implication | Description |
|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Increased risk of weak and brittle bones |
| Heart Disease | Higher likelihood of coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and stroke |
| Fertility and Menopause | Impaired fertility and increased risk of early menopause |
| Cancer Risk | Elevated chances of developing various types of cancer |
| Lung Health | Higher susceptibility to lung diseases like COPD and increased risk of respiratory infections |
Quitting smoking is the most effective way to mitigate these health risks and improve overall well-being. By taking the step to quit smoking, individuals can significantly reduce the negative impact on their health and enjoy a better quality of life in the long run.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Skin Health
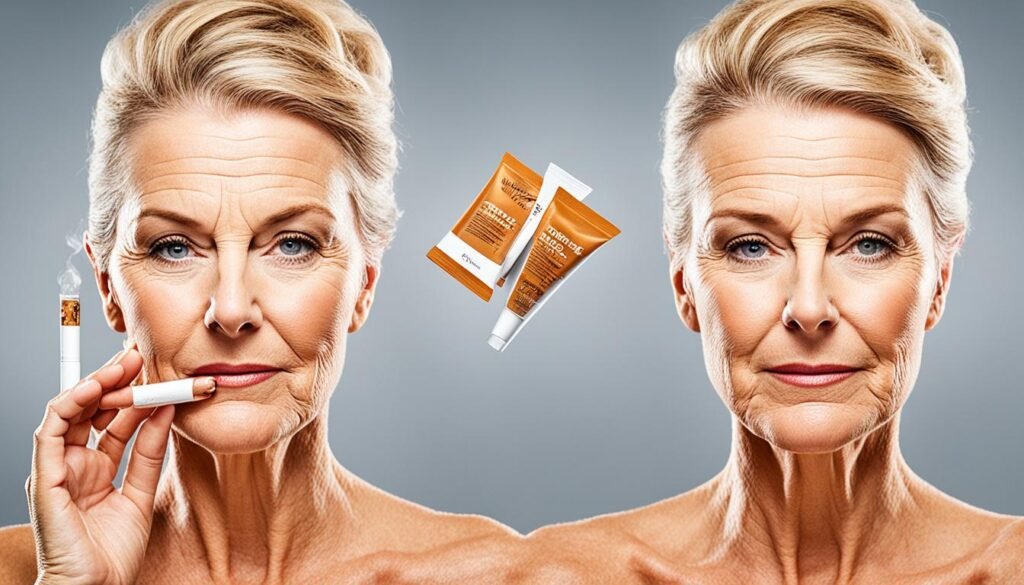

Quitting smoking can have remarkable benefits for skin health, reversing the damage caused by smoking and leading to significant improvements in the skin’s appearance and condition.
Within just a month of quitting smoking, individuals may start to notice promising changes in their skin. Age spots and skin redness may begin to decrease, giving the skin a more even tone. This improvement is a direct result of the body’s natural healing processes and the elimination of the harmful substances found in cigarettes.
After a few months of quitting, more noticeable transformations in the skin become apparent. Changes in skin color, which were previously affected by smoking, start to reverse. The skin becomes brighter and smoother, restoring a youthful glow. This improvement can be attributed to better blood circulation and increased oxygen supply to the skin, resulting in a healthier complexion.
Furthermore, quitting smoking plays a vital role in restoring collagen production in the skin. Collagen, a protein responsible for skin elasticity and hydration, is frequently damaged by the toxins in cigarette smoke. By quitting smoking, collagen production can rebound, leading to improvements in skin hydration and elasticity. This effect helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin, providing a more youthful and vibrant complexion.
In the long term, quitting smoking for the sake of skin health offers even more significant benefits. By eliminating the harmful effects of smoking, individuals can experience a reduction in the visible signs of aging. This includes a decrease in the appearance of wrinkles, age spots, and other skin imperfections associated with tobacco use. Quitting smoking also lowers the risk of developing various skin conditions and diseases that are more prevalent among smokers.
The benefits of quitting smoking for skin health extend beyond just the surface. It is a holistic approach that supports overall well-being, allowing individuals to embrace a healthier lifestyle. By quitting smoking, individuals give their skin a chance to recover and rejuvenate, resulting in a more youthful, radiant, and healthier complexion.
| Time After Quitting | Beneficial Changes in the Skin |
|---|---|
| 1 Month | Decrease in age spots and skin redness |
| 3-6 Months | Reversal of skin color changes, brighter and smoother skin |
| 6-12 Months | Improved skin hydration and elasticity, reduction in fine lines and wrinkles |
| Long Term | Reduction in the signs of aging, healthier complexion, lower risk of skin conditions |
Conclusion
Quitting smoking is of utmost importance for maintaining skin health and combating the negative effects of tobacco smoke. Smoking not only accelerates the aging process, leading to premature wrinkles and sagging skin, but it also increases the risk of various skin conditions, impairs wound healing, and raises the likelihood of skin cancer. By quitting smoking, individuals can significantly reduce these risks and improve their overall skin condition.
One of the long-term benefits of smoking cessation is the improvement in collagen production, which helps restore skin elasticity and hydration. As a result, the skin becomes brighter, smoother, and more youthful-looking. Age spots and skin redness may also decrease within a month of quitting smoking, further enhancing the complexion.
Furthermore, quitting smoking reduces the risk of developing and worsening skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne. It also plays a crucial role in preventing the formation of wrinkles, especially in areas prone to repetitive motion, such as the forehead and lip region. By quitting smoking, individuals can reverse skin damage caused by tobacco smoke and enjoy a healthier, more radiant complexion in the long run.
In conclusion, the importance of quitting smoking for skin health cannot be overstated. By quitting, individuals can not only reduce the risk of skin aging, wrinkles, and diseases, but they can also improve collagen production, reverse skin damage, and achieve a healthier complexion. Making the decision to quit smoking not only benefits overall health but also results in long-term benefits for the skin.
FAQ
What are the effects of smoking on skin aging?
Smoking can cause premature aging, wrinkles, and skin diseases. It also impairs wound healing and compromises the immune system of the skin.
Smoking can worsen symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, and acne. It can also cause vasculitis, resulting in conditions like palmoplantar pustulosis and telangiectasia.
How does smoking affect skin tone and pigmentation?
Smoking can lead to dull and uneven skin tone, as well as the development of age spots and dark spots due to increased melanocyte formation in the skin.
Is smoking responsible for wrinkles?
Yes, smoking is a significant risk factor for the formation of wrinkles, especially in areas like the forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper lip due to repetitive motions and the impact on blood vessels and collagen fibers.
Does smoking affect wound healing?
Yes, smoking impairs the body’s inflammatory response, decreases blood flow, and compromises the immune function, resulting in delayed wound healing and an increased risk of complications.
What is the relationship between smoking and skin cancer?
Smoking increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma and reduces the survival rate in smokers with melanoma. The harmful substances in tobacco smoke damage DNA and impair the immune response, contributing to the development and progression of skin cancer.
Does smoking impact hair and nail health?
Yes, smoking is associated with an increased risk of hair loss and can cause staining and brittleness of the nails.
How does smoking affect oral health?
Smoking increases the risk of gum disease, bad breath, and tooth loss. Smokers are twice as likely to lose their teeth compared to nonsmokers.
What are the overall health implications of smoking?
Smoking is linked to osteoporosis, heart disease, fertility problems, early menopause, and various types of cancer. It also damages the lungs and increases the risk of respiratory problems and lung diseases.
What are the benefits of quitting smoking for skin health?
Quitting smoking can lead to improvements in skin tone, hydration, and elasticity. It can reverse skin damage and reduce the risk of various skin conditions and diseases.
How important is quitting smoking for skin health?
Quitting smoking is crucial for combating tobacco-related skin aging and improving overall skin health. It has long-term benefits, including a reduction in the signs of aging and a healthier complexion.




