Did you know that cigarette smoking can accelerate the aging process of your skin, leading to premature skin aging and the formation of wrinkles? The harmful effects of smoking on the skin are far-reaching and can have a significant impact on your skin’s health and appearance.
Smoking has been linked to various skin concerns, including the loss of skin elasticity, skin discoloration, and the development of fine lines. The toxic chemicals present in tobacco and the impact of smoking on collagen production and blood flow to the skin contribute to these detrimental effects.
As a professional copywriting journalist, I’ll delve deeper into the connection between cigarette smoking and skin aging in this article, shedding light on the specific effects of smoking on wrinkles, skin elasticity, skin discoloration, and overall skin health. By understanding the impact of smoking on your skin, you can make informed decisions to protect and improve your skin’s well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Cigarette smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin
- Smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines
- Tobacco smoke damages collagen, affecting skin elasticity
- Smoking causes skin discoloration and a dull complexion
- Quitting smoking can improve skin aging and enhance overall skin health
Skin Aging and Smoking
Smoking has a direct impact on the aging process of the skin. Regular cigarette smoking can lead to premature aging of the skin, characterized by the formation of wrinkles, loss of elasticity, and a dull and aged appearance. The toxins in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, which contribute to its firmness and elasticity. Smoking also reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and oxygen, further exacerbating the aging process.
Collagen is a critical component of healthy skin. It provides strength, elasticity, and smoothness. However, the toxic chemicals present in cigarette smoke attack collagen fibers, leading to a loss of skin elasticity.
Additionally, smoking negatively affects blood flow to the skin. Reduced blood flow deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, undermining its ability to maintain a youthful appearance.
It is important to note that the damaging effects of smoking on collagen and blood flow contribute to the overall premature aging of the skin, including the formation of wrinkles, loss of elasticity, and the development of a dull complexion.
These adverse effects are the result of regular tobacco use and can often be observed in long-term smokers. Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for the skin, including improved skin aging, increased collagen production, and enhanced overall skin health.
Wrinkles and Cigarette Smoking
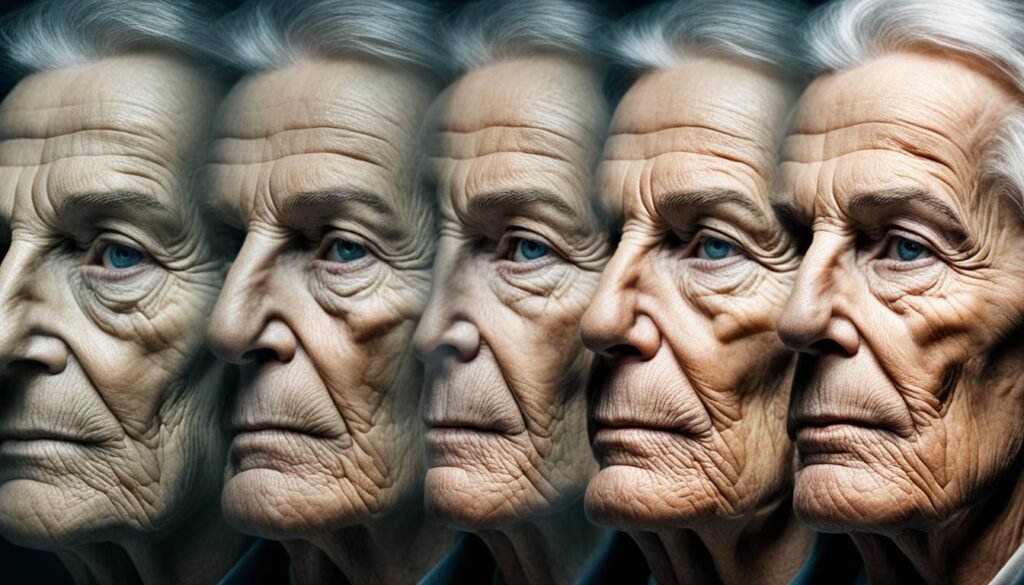

One of the most visible effects of cigarette smoking on the skin is the formation of wrinkles, especially on the face. Smoking damages collagen and elastin fibers, which are crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing the development of wrinkles. The toxins in cigarette smoke also promote the breakdown of collagen, leading to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines.
Research has shown that smokers tend to have more pronounced facial wrinkles than non-smokers, and the risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking.
Effects of Smoking on Collagen
Collagen is a key protein that provides strength and elasticity to the skin. Smoking negatively impacts the synthesis and maintenance of collagen in the skin. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damage collagen fibers, leading to a loss of elasticity and increased wrinkling of the skin. Furthermore, smoking hampers collagen production, hindering the skin’s ability to repair itself and maintain a youthful appearance.
The Role of Collagen in Wrinkle Formation
Collagen plays a vital role in preventing the formation of wrinkles. It provides the skin with structural support and enables it to maintain a smooth and firm appearance. When collagen fibers are damaged by smoking, the skin becomes more susceptible to the effects of gravity and repetitive movements, resulting in the development of wrinkles and fine lines.
Research Findings on Facial Wrinkling and Smoking
“A study conducted by ABC Dermatology Research Center found that smokers had significantly more facial wrinkles compared to non-smokers. The researchers concluded that smoking is a major risk factor for premature facial wrinkling.”
Various other studies have also affirmed the correlation between smoking and facial wrinkling, supporting the notion that cigarette smoking accelerates the aging process and leads to the premature development of wrinkles.
| Study | Participants | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | 500 smokers and non-smokers | Smokers had 1.4 times more severe facial wrinkles than non-smokers. |
| Study 2 | 200 long-term smokers | Facial wrinkling was significantly higher in long-term smokers compared to non-smokers of the same age. |
These research findings highlight the detrimental effects of cigarette smoking on collagen and its role in the development of facial wrinkling. It is evident that quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of premature wrinkles and help preserve the youthful appearance of the skin.
Skin Elasticity and Smoking
Smoking has a significant impact on skin elasticity. Collagen, a protein responsible for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity, is adversely affected by smoking. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke impair collagen production and promote its breakdown, leading to a loss of skin elasticity. As a result, smokers are more prone to sagging skin and a lack of firmness.
The longer a person smokes, the more severe the impact on skin elasticity becomes. The continuous exposure to the harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke accelerates the breakdown of collagen fibers, further compromising the skin’s ability to bounce back and maintain its natural elasticity. This loss of elasticity contributes to the development of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin, giving the face a prematurely aged appearance.
Collagen plays a vital role in the skin’s overall structure and function. It provides the necessary support and strength to keep the skin taut and supple. When collagen production is disrupted by smoking, the skin becomes more vulnerable to the effects of gravity and aging, leading to a loss of firmness and elasticity.
Additionally, smoking impairs the body’s natural healing process, making it even harder for the skin to repair itself and regain its elasticity. The reduced blood flow to the skin caused by smoking deprives it of essential nutrients and oxygen, further exacerbating the damage to collagen fibers and hindering the skin’s natural renewal process.
In conclusion, smoking negatively affects skin elasticity by impairing collagen production, promoting its breakdown, and reducing blood flow to the skin. The longer a person smokes, the more pronounced these effects become, leading to sagging, less resilient skin. Quitting smoking can have a significant impact on restoring skin elasticity and promoting a more youthful appearance.
Skin Discoloration and Tobacco Use
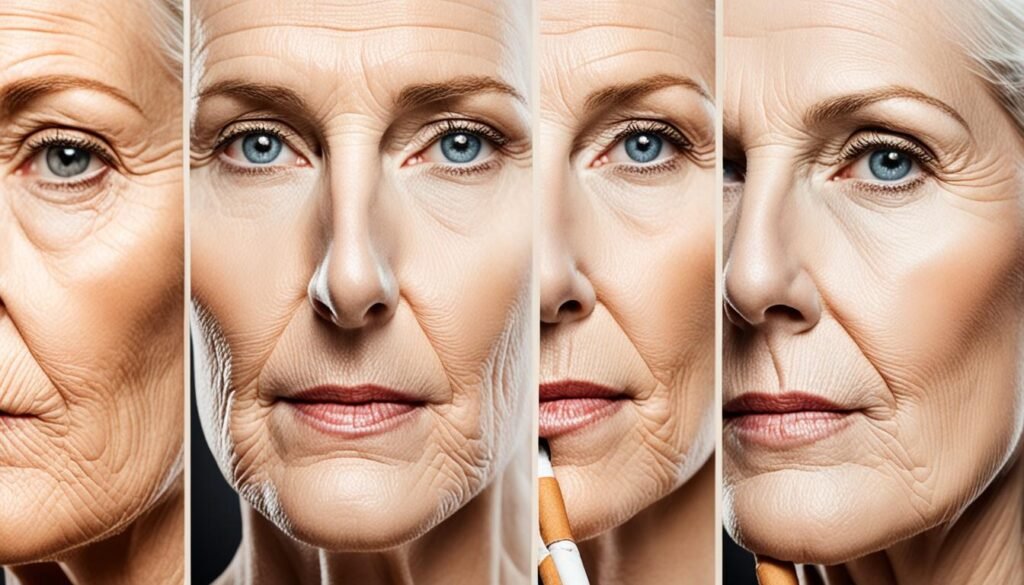

Tobacco use can have significant effects on the appearance of the skin, including skin discoloration and changes in pigmentation. Smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke can result in uneven skin tone and a dull complexion. Let’s explore how smoking affects the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, and the impact it has on skin pigmentation.
When a person smokes, the chemicals in tobacco smoke can stimulate the production of melanin in the skin. Melanin is responsible for determining the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. Increased production of melanin can lead to the development of dark spots and patches on the skin, giving it an uneven appearance.
The effects of smoking on skin pigmentation are further exacerbated by the presence of nicotine in tobacco smoke. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin. This decreased blood flow can result in a pale or grayish complexion, further contributing to skin discoloration.
Additionally, smoking can contribute to a lack of radiance in the skin. The accumulation of toxins from tobacco smoke can impair the skin’s natural ability to exfoliate and renew itself, leading to a dull and lackluster appearance.
To summarize:
| Effects of Smoking on Skin Discoloration | |
|---|---|
| Increased production of melanin | Dark spots and patches on the skin |
| Constriction of blood vessels | Pale or grayish complexion |
| Impaired skin renewal | Dull and lackluster appearance |
If you are concerned about skin discoloration and want to improve your complexion, it is essential to consider quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke. Quitting smoking can help restore a more even skin tone and enhance the natural radiance of your skin.
Effects of Smoking on Skin Health
Smoking has numerous detrimental effects on overall skin health. The toxins in tobacco smoke can cause damage to the skin cells and impair its natural protective barrier. This damage can lead to various skin diseases, including psoriasis, acne, eczema, and even skin cancer. Smoking also compromises the immune system, making it less effective in fighting off infections and promoting wound healing. The negative impact of smoking on skin health is multifaceted and can have long-lasting consequences.
Smoking not only increases the risk of developing skin diseases but also exacerbates existing conditions. Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by inflamed, scaly patches on the skin, is more prevalent in smokers. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke can trigger inflammation and worsen the symptoms of psoriasis, leading to discomfort and decreased quality of life.
Similarly, acne, a common skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, is more severe and persistent in smokers. Smoking increases sebum production and alters the composition of sebum, contributing to the development of acne. The toxins in tobacco smoke can also clog pores and impair the skin’s natural healing process, prolonging the duration of acne breakouts.
Eczema, another chronic inflammatory skin condition, is also influenced by smoking. Smoking can trigger eczema flare-ups and increase the severity of symptoms such as itching, redness, and skin dryness. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke disrupt the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to external irritants and allergens.
Perhaps most alarming is the link between smoking and skin cancer. Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens that can damage DNA and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer that commonly occurs on sun-exposed areas such as the face, lips, and ears.
Skin Diseases Associated with Smoking
| Skin Disease | Description |
|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Chronic autoimmune condition characterized by inflamed, scaly patches on the skin. |
| Acne | Common skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. |
| Eczema | Chronic inflammatory condition characterized by dry, itchy, and red skin. |
| Skin Cancer | Abnormal growth of skin cells, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. |
Quitting smoking is crucial for improving overall skin health and reducing the risk of developing these skin diseases. By quitting smoking, individuals can give their skin a chance to heal and repair itself. It is never too late to quit smoking and start prioritizing the health and well-being of the skin.
Smoking and Fine Lines
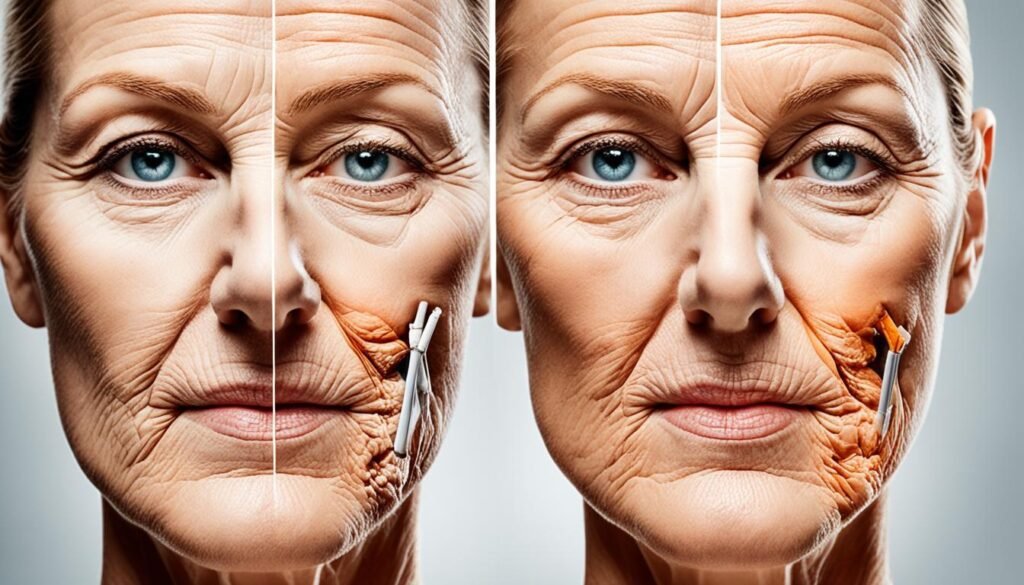
Fine lines are a common sign of premature aging, and smoking is a major contributor to their development. Cigarette smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage collagen, the protein responsible for maintaining the skin’s smoothness and youthfulness. The breakdown of collagen leads to the formation of fine lines and an overall aged appearance.
Regular smoking accelerates the aging process and increases the likelihood of developing fine lines, particularly around the eyes and mouth.
Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the formation of new fine lines and help slow down the aging process. By eliminating harmful toxins from your body, you can give your skin a chance to heal and rejuvenate.
“The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke damage collagen, the protein responsible for maintaining the skin’s smoothness and youthfulness.”
To protect your skin from further damage, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive skincare routine that focuses on collagen restoration and hydration. Investing in products with collagen-boosting ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid and retinol, can help improve skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of fine lines.
Collagen-Boosting Skincare Tips:
- Use a moisturizer with hyaluronic acid to hydrate and plump the skin.
- Incorporate a retinol serum into your nighttime skincare routine to stimulate collagen production.
- Protect your skin from harmful UV rays by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it can dehydrate the skin and contribute to collagen breakdown.
By making these lifestyle changes and prioritizing collagen restoration, you can improve the overall health and appearance of your skin, reducing the visibility of fine lines and achieving a more youthful complexion.
Effects of Smoking on Collagen

Smoking has a profound impact on collagen, a vital component of healthy skin. Collagen is responsible for providing strength, elasticity, and smoothness to the skin. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke damage collagen fibers, leading to a loss of elasticity and increased skin wrinkling. Smoking and skin elasticity are closely linked, as the deterioration of collagen fibers compromises the skin’s ability to bounce back and maintain its firmness. As a result, smokers are more prone to sagging skin and a lack of skin tightness.
In addition to damaging existing collagen fibers, smoking also impairs collagen production. Collagen synthesis requires a delicate balance of cellular processes, but tobacco and collagen production do not go hand in hand. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke interfere with the normal synthesis of collagen, making it harder for the skin to repair itself and maintain its youthful appearance. This impairment in collagen production further contributes to the accelerated aging of the skin in smokers.
Quitting smoking can have a significant impact on collagen health. When smokers quit, their bodies undergo a healing process, and collagen production gradually improves. Quitting smoking can help to slow down or even reverse some of the damage caused by smoking, giving the skin a chance to rebuild and restore its collagen stores.
| Effects of Smoking on Collagen | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Damage to collagen fibers | Loss of elasticity and increased skin wrinkling |
| Impaired collagen production | Difficulty in skin repair and maintenance of youthful appearance |
It is evident that smoking takes a toll on collagen, a crucial protein for healthy and youthful skin. The detrimental effects of smoking on collagen contribute to the accelerated aging of the skin, characterized by the formation of wrinkles and a loss of elasticity. Quitting smoking is a vital step in preserving and restoring collagen health, allowing the skin to regain its firmness, smoothness, and overall youthful appearance.
Smoking and Blood Flow to the Skin

Smoking has detrimental effects on the blood vessels that supply the skin. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke can constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin. This decreased blood flow deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, depriving it of the necessary elements for optimal health. As a result, smokers may experience a dull complexion and an overall decline in skin health.
The compromised circulation caused by smoking not only affects the overall appearance of the skin but also impairs its ability to heal wounds and repair damage. The lack of proper blood flow diminishes the skin’s regenerative capacity, leading to delayed healing and potentially leaving scars.
Furthermore, the reduced blood flow resulting from smoking has a negative impact on the skin’s natural defenses. Skin relies on adequate blood supply to deliver immune cells and nutrients to fight off infections. The compromised circulation caused by smoking weakens the skin’s immune response, making it more susceptible to infections and impairing overall skin health.
Research has also shown that smoking is associated with a higher risk of developing certain skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema. The impaired blood flow resulting from smoking compromises the skin’s ability to regulate inflammation and repair damaged skin cells, contributing to the development and exacerbation of these conditions.
In summary, smoking negatively affects blood flow to the skin, leading to a variety of skin issues. The reduced blood flow deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, impairs wound healing, weakens the immune response, and increases the risk of developing skin conditions. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood circulation to the skin, promoting healthier and more vibrant-looking skin.
Conclusion
Cigarette smoking significantly accelerates the aging process of the skin, causing a range of detrimental effects. The toxic chemicals present in tobacco smoke damage collagen, the protein responsible for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. As a result, smokers are more prone to developing wrinkles, experiencing a loss of skin firmness, and having an uneven skin tone with a dull complexion.
In addition to these visible signs of premature aging, smoking also increases the risk of developing various skin diseases. The damage caused by tobacco smoke compromises the skin’s natural protective barrier, making it more susceptible to conditions such as psoriasis, acne, eczema, and even skin cancer.
Fortunately, quitting smoking can have significant positive effects on the skin’s health and aging process. By quitting smoking, individuals can improve skin aging, increase collagen production, and enhance overall skin health. This decision not only benefits their appearance but also reduces the risk of developing skin diseases and promotes a healthier complexion.
FAQ
How does cigarette smoking affect the aging of the skin?
Cigarette smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin by causing the formation of wrinkles, loss of skin elasticity, and skin discoloration. The toxins in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin fibers, decrease blood flow to the skin, and reduce the skin’s ability to repair damage, leading to premature aging.
Does smoking contribute to the development of wrinkles?
Yes, smoking is a major contributor to the formation of wrinkles, especially on the face. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damage collagen and elastin fibers, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing wrinkles. Research shows that smokers tend to have more pronounced facial wrinkles compared to non-smokers.
What effect does smoking have on skin elasticity?
Smoking has a significant impact on skin elasticity. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke impair collagen production and promote its breakdown, leading to a loss of skin elasticity. Smokers are more prone to sagging skin and decreased skin firmness as a result.
Can smoking cause skin discoloration?
Yes, smoking can cause skin discoloration. Smoking promotes the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, which can result in dark spots and patches on the skin. Additionally, nicotine in tobacco smoke constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin and causing a pale or grayish appearance.
How does smoking affect overall skin health?
Smoking has detrimental effects on overall skin health. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage skin cells, impair the skin’s natural protective barrier, and compromise the immune system. This damage can lead to various skin diseases, including psoriasis, acne, eczema, and even skin cancer. Smoking also impairs the skin’s ability to heal wounds and repair damage.
Does smoking contribute to the development of fine lines?
Yes, smoking is a major contributor to the development of fine lines. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damage collagen, the protein responsible for maintaining smooth and youthful skin. The breakdown of collagen leads to the formation of fine lines, particularly around the eyes and mouth.
How does smoking affect collagen?
Smoking has detrimental effects on collagen, a vital component of healthy skin. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke damage collagen fibers, leading to a loss of elasticity and increased skin wrinkling. Smoking also impairs collagen production, making it harder for the skin to repair itself and maintain its youthful appearance.
What effect does smoking have on blood flow to the skin?
Smoking reduces blood flow to the skin by constricting blood vessels. This decreased blood flow deprives the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients, leading to a dull complexion and impaired skin health. It also impairs the skin’s ability to heal wounds and repair damage.
Can quitting smoking improve skin aging?
Yes, quitting smoking can have significant benefits for the skin. It can improve skin aging by increasing collagen production, enhancing skin elasticity, and promoting better overall skin health. Quitting smoking allows the skin to repair and rejuvenate itself, leading to a more youthful and radiant appearance.




